0 引言
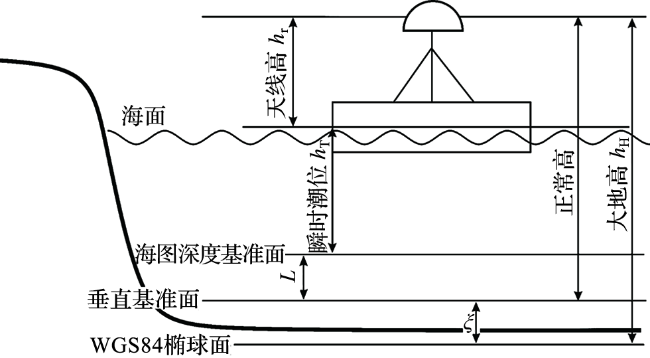
1 PPP原理和验潮应用
1.1 PPP原理
1.2 PPP验潮
2 数据与方法
2.1 数据来源
2.2 数据处理
2.2.1 数据解算
表1 PPP处理策略汇总表Tab.1 Summary table of PPP processing strategy |
| 参数 | 策略 |
|---|---|
| 处理模式 | 动态处理 |
| 卫星观测系统 | GPS,GLONASS,BDS |
| 观测值类型 | 伪距和载波相位 |
| 频率 | GPS/GLONASS(L1,L2),BDS(B1,B2) |
| 卫星轨道和钟差 | wum最终产品 |
| 卫星产品格式 | RINEX |
| 产品插值 | 是 |
| 对流层模型 | 参数估计 |
| 电离层模型 | 无电离层组合 |
| 卫星截止高度角 | 10° |
| 观测周期 | 30 s; 60 s;90 s;120 s |
| 天线相位改正 | PCO+PCV改正 |
| 相位缠绕改正 | 模型改正 |
| 模糊度固定方法 | 固定解 |
2.2.2 剔除粗差
2.2.3 滤波
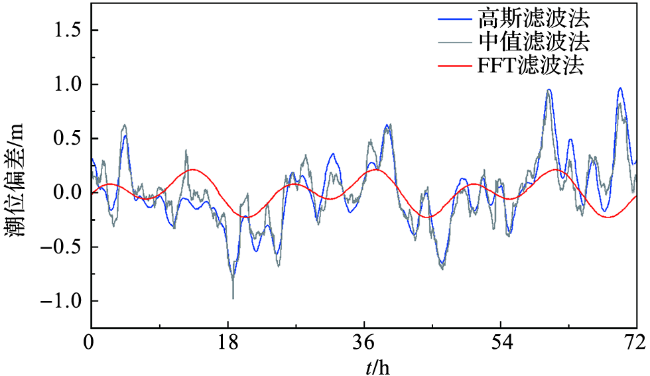
图2 基于不同滤波方法的潮位偏差分布Fig.2 Tidal level deviance distribution based on different filtering methods |
表2 基于不同滤波方法的潮位偏差统计Tab.2 Statistical results of tidal level deviance based on different filtering methods |
| 滤波方法 | 最大偏差/m | 最小偏差/m | 标准差/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFT滤波法 | 0.212 | -0.228 | 0.125 |
| 高斯滤波法 | 0.967 | -0.778 | 0.323 |
| 中值滤波法 | 0.944 | -0.980 | 0.301 |
3 结果与分析
3.1 FFT滤波效果
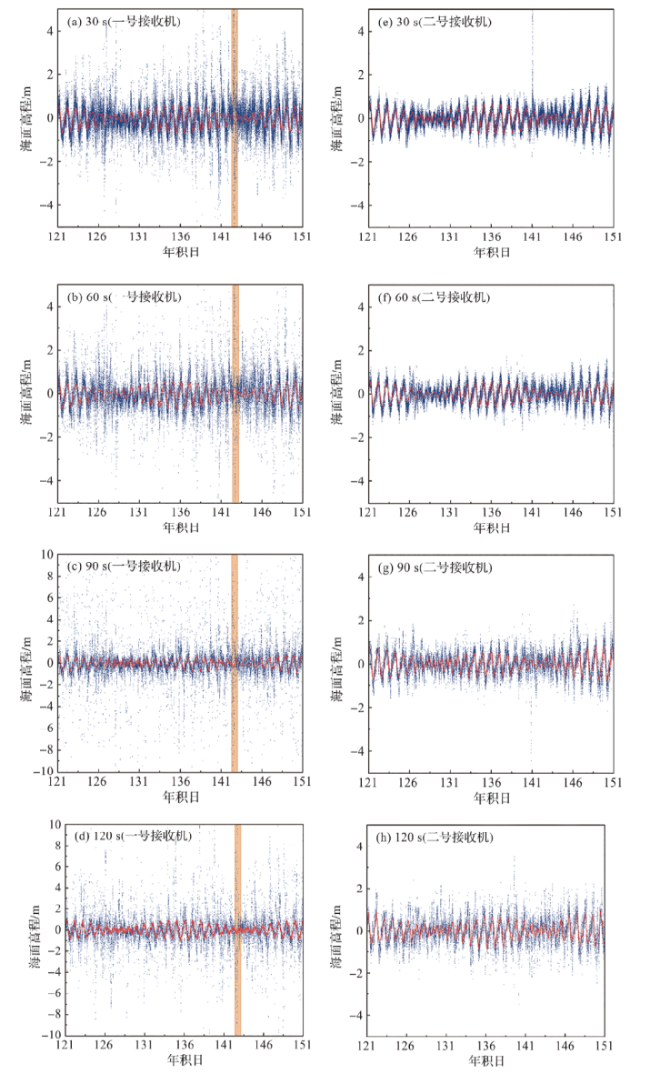
图3 滤波前、后海面高程数据对比(橙色表示年积日为143时的海面高程,蓝点是原始海面高程,红线是滤波后的海面高程。) Fig.3 Comparison of sea level elevation data before and after filtering (Orange indicates the sea level elevation at DOY 143, the blue dots are the raw sea level elevation measured by GNSS, and the red line is the filtered sea level elevation data.) |
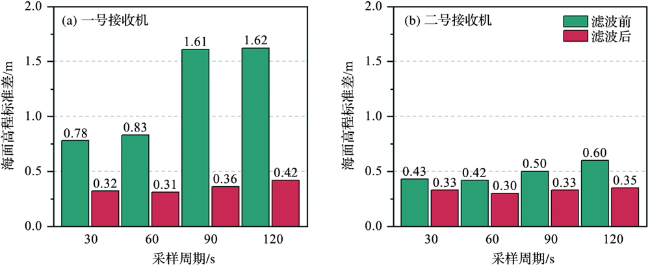
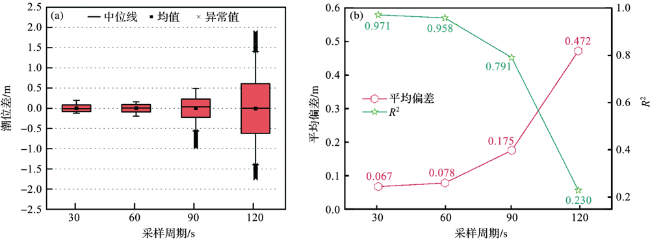
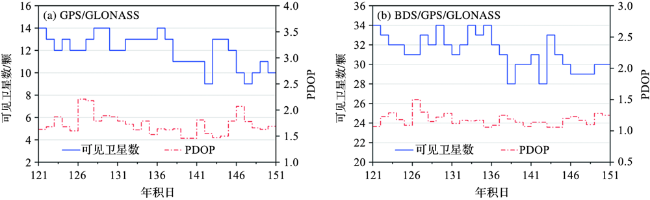
3.2 采样周期对三系统PPP验潮精度的影响
表3 不同采样周期潮位测量精度对比Tab.3 Comparison of measuring accuracy of tidal level at different sampling periods |
| 采样周期 | 平均偏差/m | 标准差/m | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 s | 0.067 | 0.081 | 0.971 |
| 60 s | 0.078 | 0.090 | 0.958 |
| 90 s | 0.175 | 0.227 | 0.791 |
| 120 s | 0.472 | 0.613 | 0.230 |
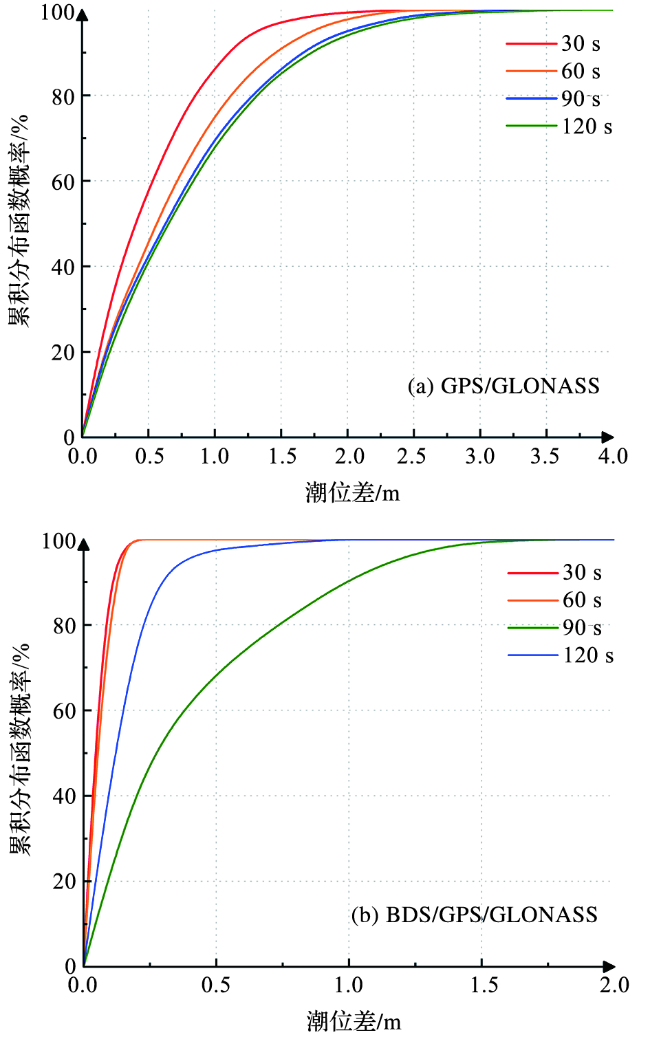
3.3 BDS系统对PPP验潮精度的影响
表4 三系统PPP与双系统PPP验潮结果差异统计Tab.4 Statistical differences of tide test results of the three-systems PPP and the dual-systems PPP 单位/m |
| 采样 周期 | 标准差 | 最大偏差 | 最小偏差 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 三系统 | 双系统 | 三系统 | 双系统 | 三系统 | 双系统 | |||
| 30 s | 0.081 | 0.733 | 0.197 | 2.007 | -0.122 | -2.389 | ||
| 60 s | 0.090 | 0.936 | 0.158 | 2.588 | -0.194 | -2.708 | ||
| 90 s | 0.227 | 1.065 | 0.488 | 3.522 | -0.965 | -2.614 | ||
| 120 s | 0.613 | 1.108 | 1.885 | 3.395 | -1.735 | -3.738 | ||