0 引言
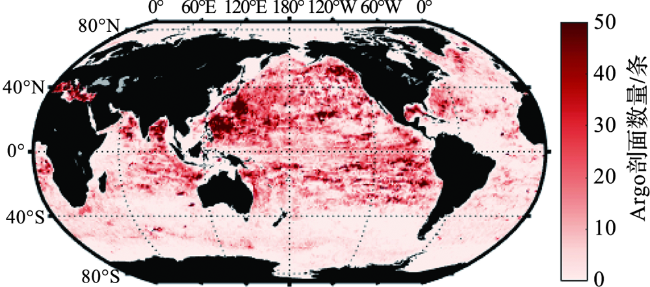
1 数据和方法
1.1 数据资料
1.2 方法
1.2.1 内波混合的计算
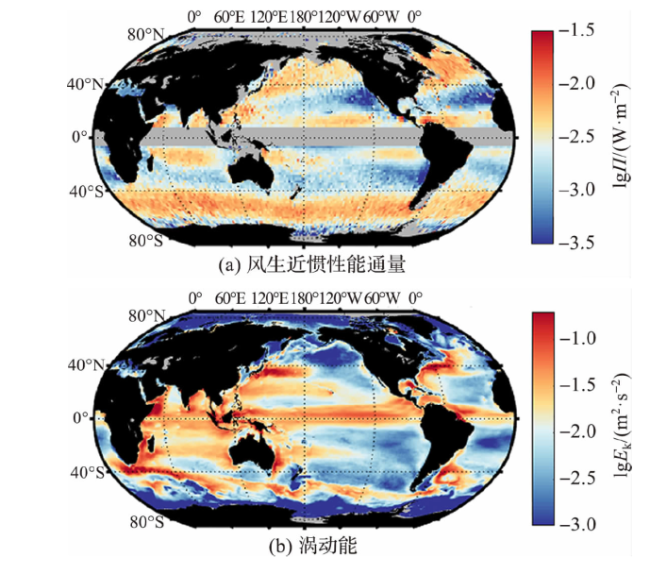
1.2.2 风生近惯性能通量的计算
1.2.3 涡动能的计算
2 结果与分析
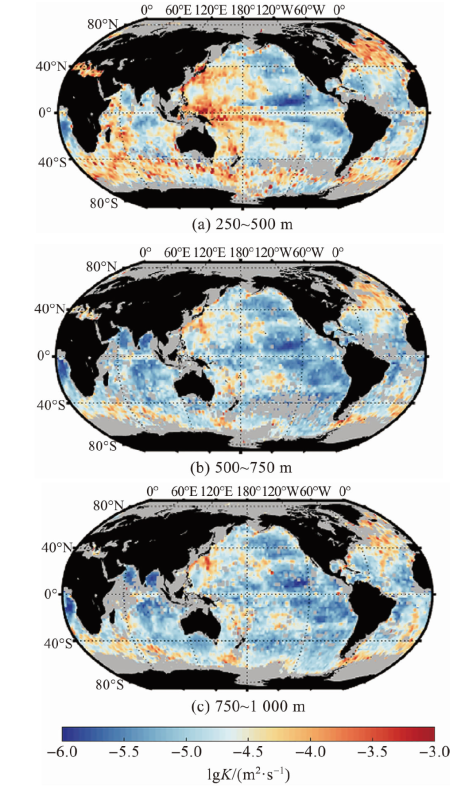
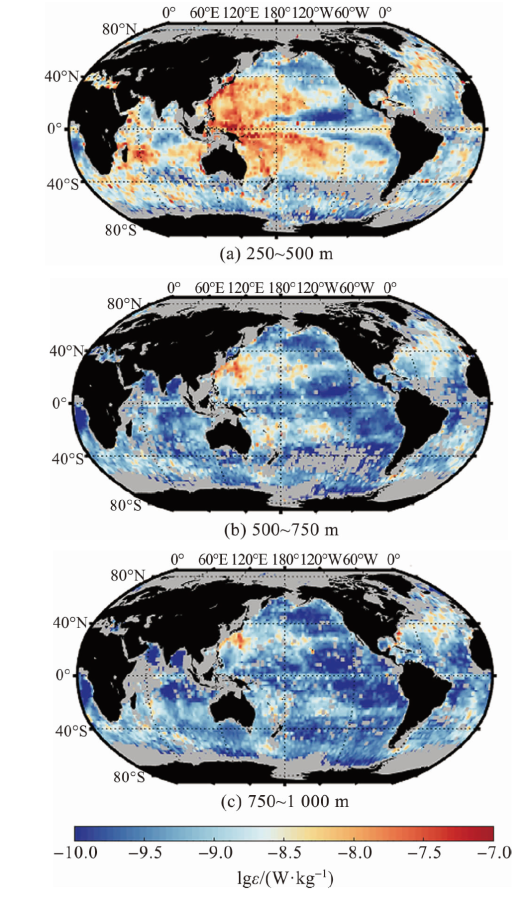
2.1 内波混合的空间分布
图2 全球不同深度的平均内波混合扩散率(计算结果的空间分辨率为1°×1°。图中灰色区域代表没有数据的海域。) Fig.2 The global averaged internal wave-induced mixing diffusivity at different depths (Spatial resolution of the calculation results is 1°×1°. The gray areas in the figure represent seas for which there is no data.) |
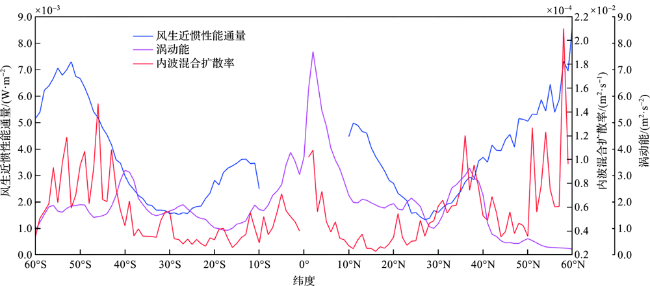
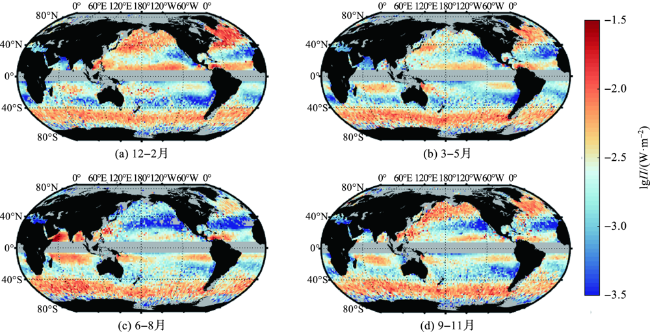
2.2 风生近惯性能通量和涡旋对内波混合空间分布的影响
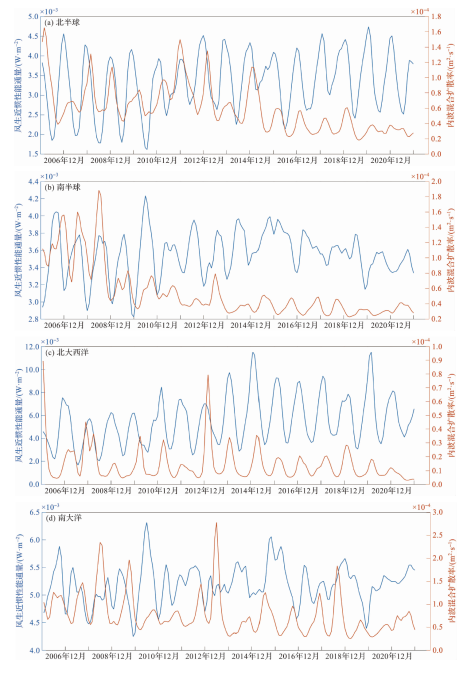
2.3 风生近惯性能通量对内波混合季节变化的影响
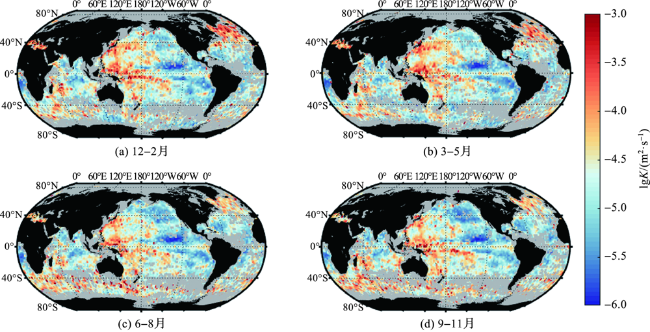
图6 全球250~500 m层平均内波混合扩散率的季节变化Fig.6 Seasonal variation of global average internal wave-induced mixing diffusivity at 250-500 m |
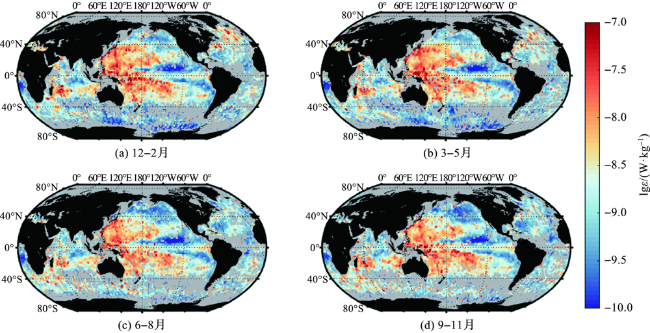
图7 全球250~500 m层平均内波混合耗散率的季节变化Fig.7 Seasonal variation of global average internal wave-induced mixing dissipation rate at 250-500 m |
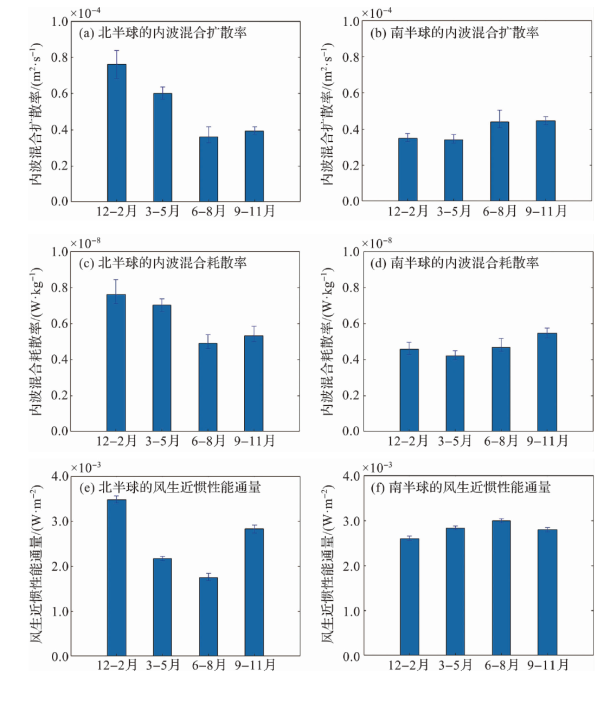
图9 南、北半球250~500 m层平均内波混合扩散率、耗散率以及表层风生近惯性能通量的季节变化(图中细线表示95%的置信区间。) Fig.9 Seasonal variation of average internal wave-induced mixing diffusivity, dissipation rate at 250-500 m, and wind-induced near-inertial energy flux at surface in the northern hemisphere and southern hemisphere (The thin line is a 95%confidence interval.) |