Journal of Marine Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 110-120.DOI: 10.3969-j.issn.1001-909X.2023.01.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Conservation gap analysis of coastal blue carbon ecosystems: Taking Guangdong and Guangxi as examples
DONG Di1,2,3( ), HUANG Huamei1,4,*(
), HUANG Huamei1,4,*( ), GAO Qing1,5, CHEN Mianrun1,3, YANG Xi3,6
), GAO Qing1,5, CHEN Mianrun1,3, YANG Xi3,6
- 1. South China Sea Institute of Planning and Environmental Research, SOA, Guangzhou 510300, China
2. Key Laboratory of Marine Ecological Monitoring and Restoration Technologies, MNR, Shanghai 201206, China
3. Key laboratory of Marine Environmental Survey Technology and Application, Guangzhou 510300, China
4. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou),Guangzhou 511458, China
5. School of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434025, China
6. South China Sea Environmental Monitoring Center, SOA, Guangzhou 510300, China
-
Received:2022-08-30Revised:2022-11-17Online:2023-03-15Published:2023-04-28
CLC Number:
Cite this article
DONG Di, HUANG Huamei, GAO Qing, CHEN Mianrun, YANG Xi. Conservation gap analysis of coastal blue carbon ecosystems: Taking Guangdong and Guangxi as examples[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2023, 41(1): 110-120.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://hyxyj.sio.org.cn/EN/10.3969-j.issn.1001-909X.2023.01.009
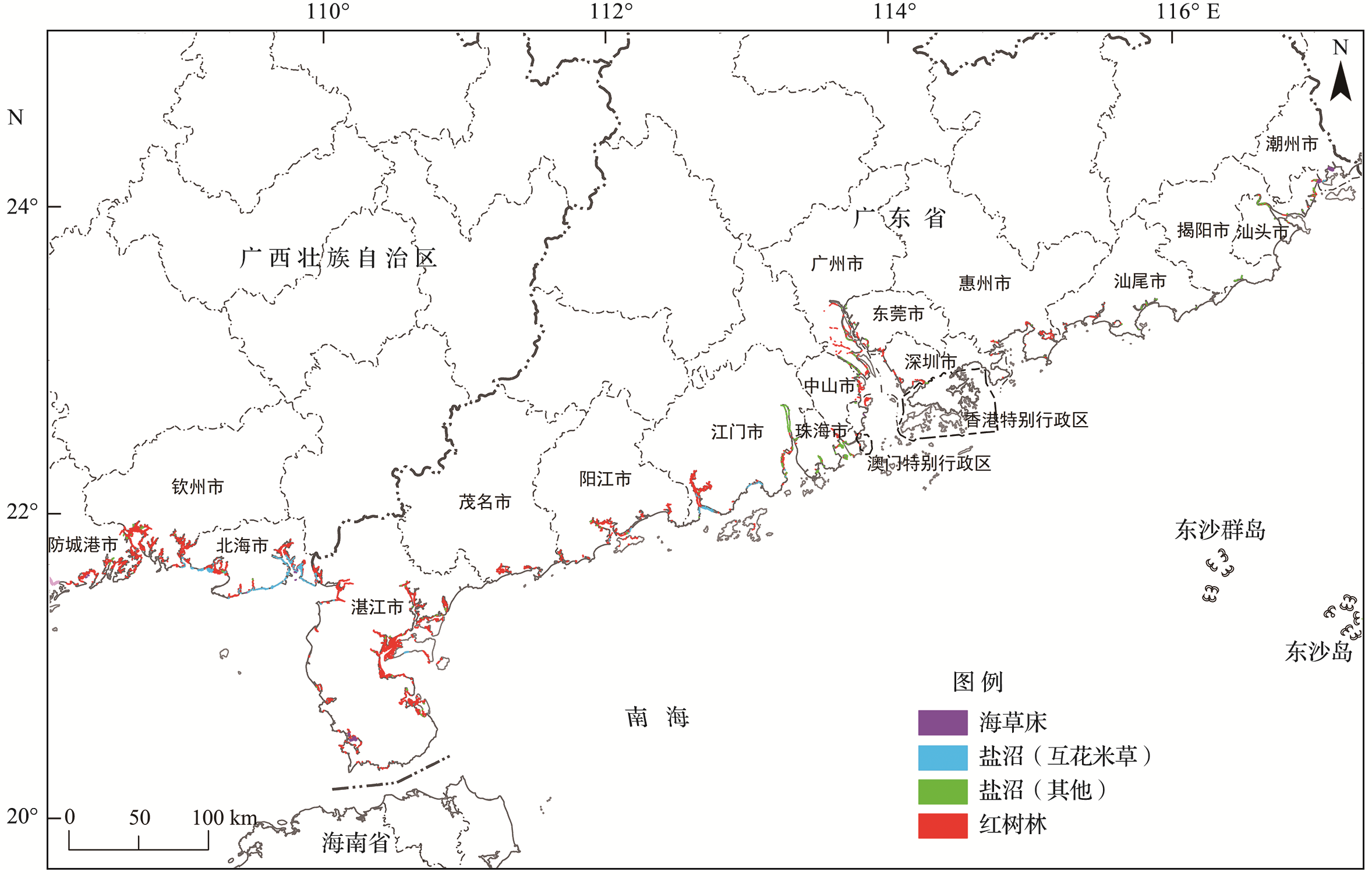
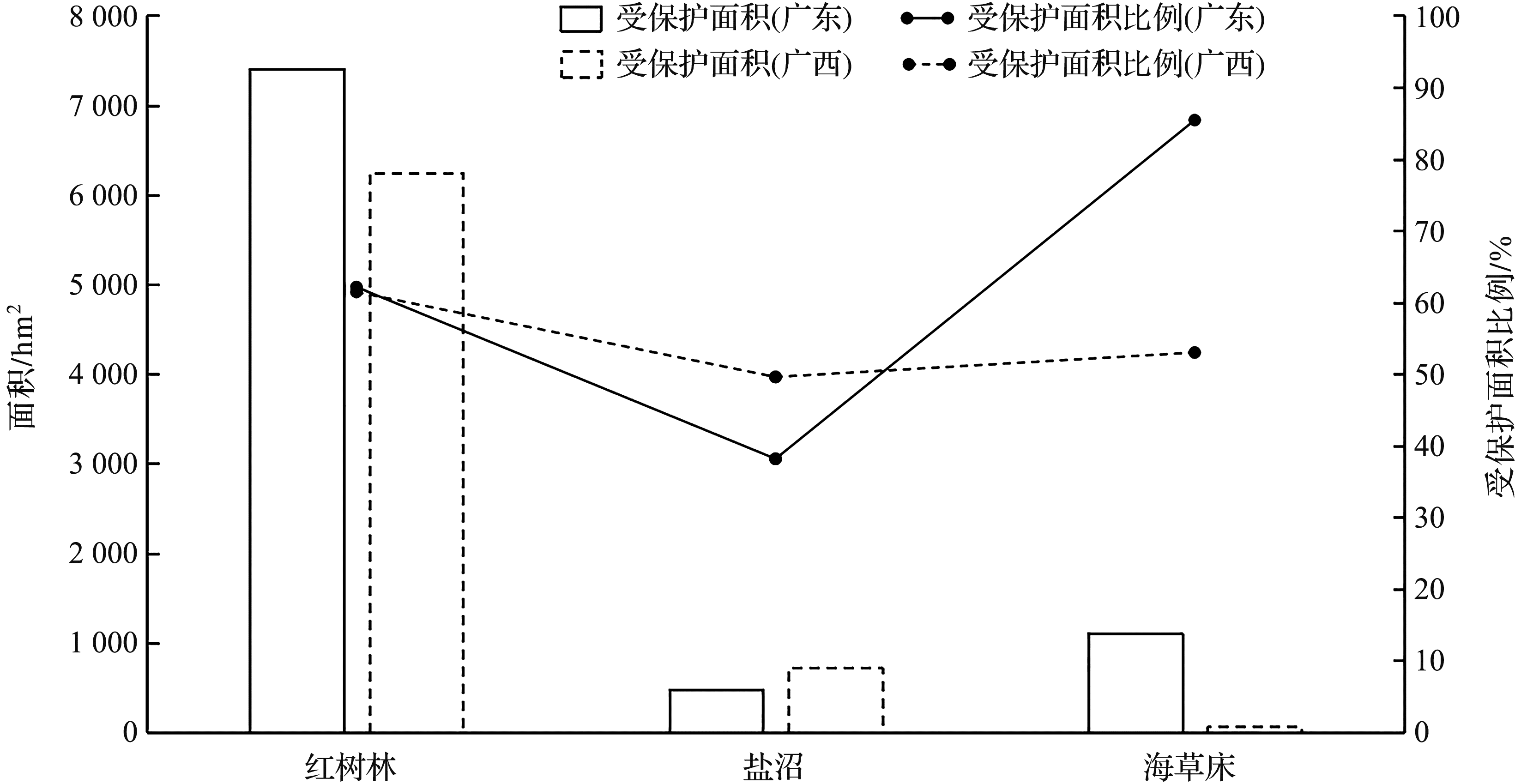
| 生态系统 类型 | 区域 | 海洋生态红线内面积/ hm2 | 海洋生态红线外 面积/ hm2 | 总面积/ hm2 | 海洋生态红线内面积占省/区的 对应生态系统总面积的比例/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 禁止类 | 限制类 | |||||
| 红树林 | 广东 | 1 110.79 | 6 300.08 | 4 518.00 | 11 928.87 | 62.13 |
| 广西 | 1 764.41 | 4 484.92 | 3 922.37 | 10 171.70 | 61.44 | |
| 盐沼① | 广东 | 0(0) | 480.11(59.87) | 777.89(268.08) | 1 258.00(327.95) | 38.16 |
| 广西 | 380.13(380.13) | 339.02(329.28) | 731.21(602.60) | 1 450.36(1 312.01) | 49.58 | |
| 海草床 | 广东 | 0 | 1 105.69 | 188.83 | 1 294.52 | 85.41 |
| 广西 | 32.96 | 35.52 | 60.77 | 129.24 | 52.99 | |
Tab.1 Areas of the CBCEs inside and outside of the marine ecological redlines in Guangdong and Guangxi
| 生态系统 类型 | 区域 | 海洋生态红线内面积/ hm2 | 海洋生态红线外 面积/ hm2 | 总面积/ hm2 | 海洋生态红线内面积占省/区的 对应生态系统总面积的比例/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 禁止类 | 限制类 | |||||
| 红树林 | 广东 | 1 110.79 | 6 300.08 | 4 518.00 | 11 928.87 | 62.13 |
| 广西 | 1 764.41 | 4 484.92 | 3 922.37 | 10 171.70 | 61.44 | |
| 盐沼① | 广东 | 0(0) | 480.11(59.87) | 777.89(268.08) | 1 258.00(327.95) | 38.16 |
| 广西 | 380.13(380.13) | 339.02(329.28) | 731.21(602.60) | 1 450.36(1 312.01) | 49.58 | |
| 海草床 | 广东 | 0 | 1 105.69 | 188.83 | 1 294.52 | 85.41 |
| 广西 | 32.96 | 35.52 | 60.77 | 129.24 | 52.99 | |
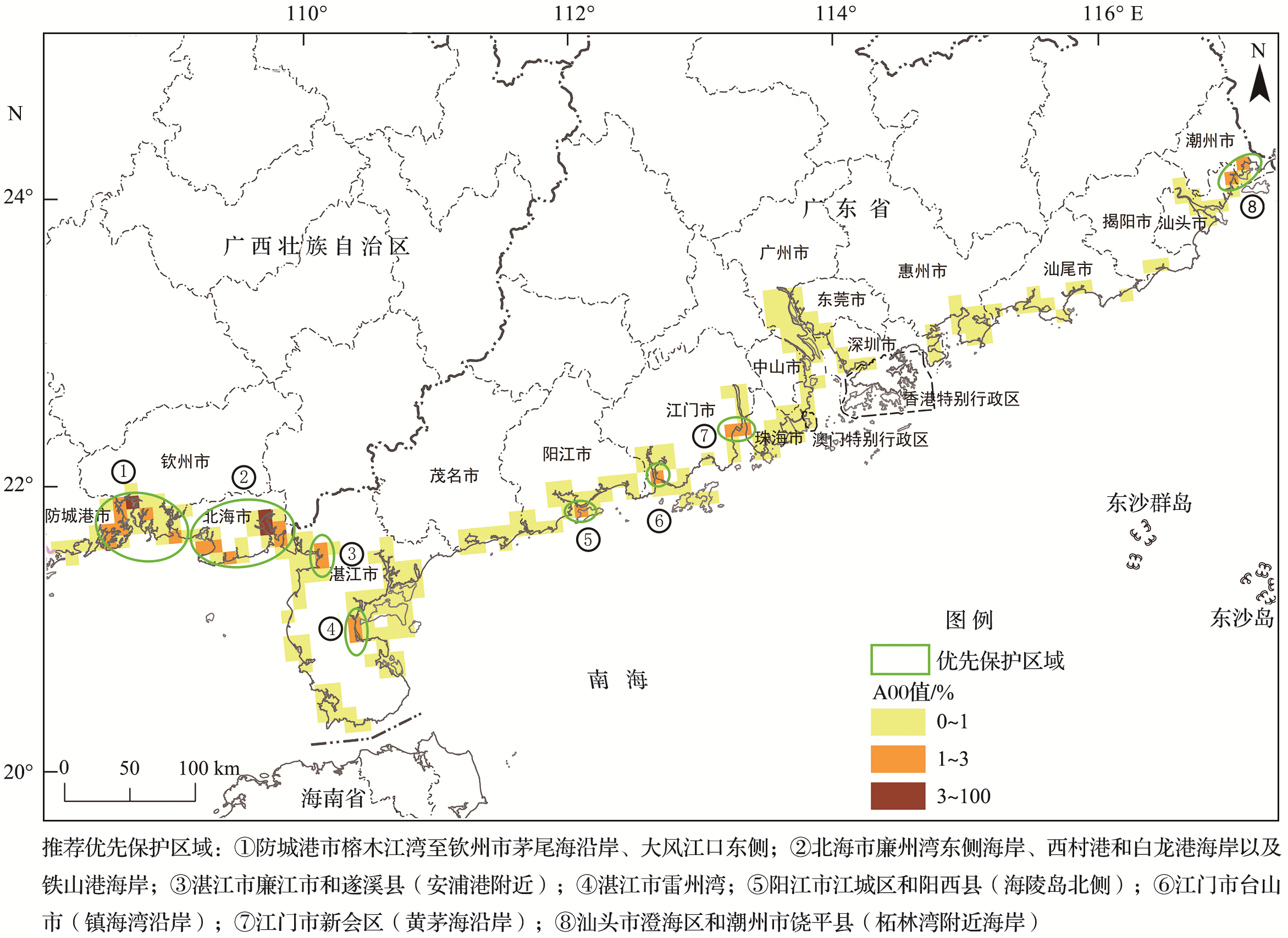
Fig.3 The occupancy area of the unprotected CBCE in the coastal zone (AOO value refers to the area of CBCEs (except Spartina alterniflora) that are not inside the MERs within each 10 km×10 km grid, the darker color refers to the higher AOO value.)
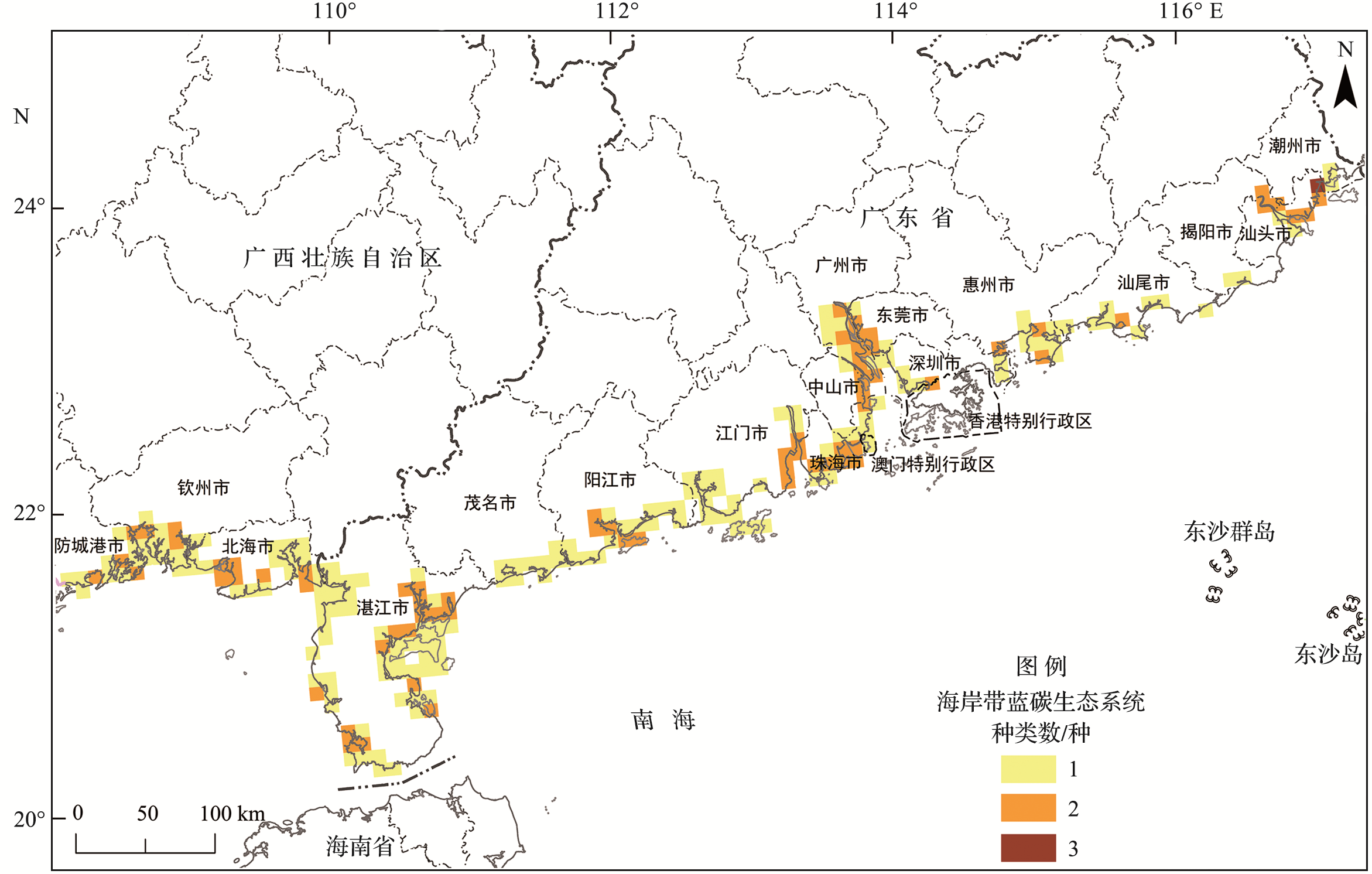
Fig.4 The spatial distribution of species number of the unprotected CBCEs (3 different colors represent the species number of the CBCEs (except Spartina alterniflora) that are outside of the MERs in each 10 km×10 km grid.)
| [1] | NELLEMANN C, CORCORAN E, DUARTE C M, et al. Blue carbon: The role of healthy oceans in binding carbon: A rapid response assessment[M]. Norway: Birkeland Trykkeri AS, 2009. |
| [2] |
向爱, 揣小伟, 李家胜. 中国沿海省份蓝碳现状与能力评估[J]. 资源科学, 2022, 44(6):1138-1154.
DOI |
|
XIANG A, CHUAI X W, LI J S. Assessment of the status and capacity of blue carbon in China’s coastal provinces[J]. Resources Science, 2022, 44(6): 1138-1154.
DOI |
|
| [3] | 唐剑武, 叶属峰, 陈雪初, 等. 海岸带蓝碳的科学概念、研究方法以及在生态恢复中的应用[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2018, 48(6):661-670. |
|
TANG J W, YE S F, CHEN X C, et al. Coastal blue carbon: Concept, study method, and the application to ecological restoration[J]. Scientia Sinica: Terrae, 2018, 48(6): 661-670.
DOI URL |
|
| [4] | 王法明, 唐剑武, 叶思源, 等. 中国滨海湿地的蓝色碳汇功能及碳中和对策[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2021, 36(3):241-251. |
| WANG F M, TANG J W, YE S Y, et al. Blue carbon sink function of Chinese coastal wetlands and carbon neutrality strategy[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021, 36(3): 241-251. | |
| [5] | 李捷, 刘译蔓, 孙辉, 等. 中国海岸带蓝碳现状分析[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(10):207-216. |
|
LI J, LIU Y M, SUN H, et al. Analysis of blue carbon in China’s coastal zone[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(10): 207-216.
DOI URL |
|
| [6] | 周晨昊, 毛覃愉, 徐晓, 等. 中国海岸带蓝碳生态系统碳汇潜力的初步分析[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2016, 46(4):475-486. |
|
ZHOU C H, MAO Q Y, XU X, et al. Preliminary analysis of C sequestration potential of blue carbon ecosystems on Chinese coastal zone[J]. Scientia Sinica: Vitae, 2016, 46(4): 475-486.
DOI URL |
|
| [7] | HE Z W, FENG X, CHEN Q P, et al. Evolution of coastal forests based on a full set of mangrove genomes[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2022, 6: 738-749. |
| [8] |
DEEGAN L A, JOHNSON D S, WARREN R S, et al. Coastal eutrophication as a driver of salt marsh loss[J]. Nature, 2012, 490(7420): 388-392.
DOI |
| [9] |
DUARTE C M, MIDDELBURG J J, CARACO N. Major role of marine vegetation on the oceanic carbon cycle[J]. Biogeosciences, 2005, 2(1): 1-8.
DOI URL |
| [10] | 段克, 刘峥延, 李刚, 等. 滨海蓝碳生态系统保护与碳交易机制研究[J]. 中国国土资源经济, 2021, 34(12):37-47. |
| DUAN K, LIU Z Y, LI G, et al. Research on the coastal blue carbon ecosystem conservation and carbon trading mechanism[J]. Natural Resource Economics of China, 2021, 34(12): 37-47. | |
| [11] |
MCLEOD E, CHMURA G L, BOUILLON S, et al. A blueprint for blue carbon: Toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2011, 9(10): 552-560.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 陈战是, 于涵, 孙铁, 等. 生态文明视野下自然保护地规划的研究与思考[J]. 中国园林, 2020, 36(11):14-18. |
| CHEN Z S, YU H, SUN T, et al. Discussion on the planning of protected areas from the perspective of ecological civilization[J]. Chinese Landscape Architecture, 2020, 36(11): 14-18. | |
| [13] | 卢元平, 徐卫华, 张志明, 等. 中国红树林生态系统保护空缺分析[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(2):684-691. |
| LU Y P, XU W H, ZHANG Z M, et al. Gap analysis of mangrove ecosystem conservation in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(2): 684-691. | |
| [14] | 王燕, 吴晓东. 湛江市红树林资源状况及其保护成效[J]. 林业科技管理, 2004(2):33-34,36. |
| WANG Y, WU X D. Status of mangrove resources in Zhanjiang city and its protection effect[J]. Forest Science & Technology Management, 2004(2): 33-34, 36. | |
| [15] |
侯鹏, 王桥, 杨旻, 等. 生态保护红线成效评估框架与指标方法[J]. 地理研究, 2018, 37(10):1927-1937.
DOI |
| HOU P, WANG Q, YANG M, et al. China’s ecological protection redlines: Evaluation framework and method of protection effect[J]. Geographical Research, 2018, 37(10): 1927-1937. | |
| [16] | 曾容, 刘捷, 许艳, 等. 海洋生态保护红线存在问题及评估调整建议[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(4):576-581,590. |
| ZENG R, LIU J, XU Y, et al. Discussions and adjustment suggestions on the marine ecological protection red line[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(4): 576-581, 590. | |
| [17] | 黄伟, 陈全震. 中国海洋生态红线区划理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019. |
| HUANG W, CHEN Q Z. Theory and method of marine ecological red line zoning in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. | |
| [18] | 黄华梅, 谢健, 陈绵润, 等. 基于资源环境承载力理论的海洋生态红线制度体系构建[J]. 生态经济, 2017, 33(9):174-179. |
| HUANG H M, XIE J, CHEN M R, et al. Research on marine ecological red-line management system based on resource and environment carrying capacity theory[J]. Ecological Economy, 2017, 33(9): 174-179. | |
| [19] | 刘晓颖. 海洋生态红线区遥感监测方案设计与实践[D]. 天津: 天津师范大学, 2016. |
| LIU X Y. The marine ecological red zone remote sensing program design and pratice[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin Normal University, 2016. | |
| [20] | 岳文. 广东省海洋生态红线区渔业生产活动现状[J]. 海洋与渔业, 2018(8):20-21. |
| YUE W. Current situation of fishery production activities in marine ecological red line area of Guangdong Province[J]. Ocean and Fishery, 2018(8): 20-21. | |
| [21] |
郑凤英, 邱广龙, 范航清, 等. 中国海草的多样性、分布及保护[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(5):517-526.
DOI |
|
ZHENG F Y, QIU G L, FAN H Q, et al. Diversity, distribution and conservation of Chinese seagrass species[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(5): 517-526.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 贾明明, 王宗明, 毛德华, 等. 面向可持续发展目标的中国红树林近50年变化分析[J]. 科学通报, 2021, 66(30):3886-3901. |
| JIA M M, WANG Z M, MAO D H, et al. Spatial-temporal changes of China’s mangrove forests over the past 50 years: An analysis towards the Sustainable Development Goals(SDGs)[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(30): 3886-3901. | |
| [23] | 中国海洋工程咨询协会. 海岸带生态系统现状调查与评估技术导则第2部分:海岸带生态系统遥感识别与现状核查:T/CAOE 20.2—2020[S]. 2020. |
| China Association of Oceanic Engineering. Technical guideline for investigation and assessment of coastal ecosystem—Part 2: Remote sensing identification and results verification of the coastal ecosystem: T/CAOE 20.2—2020[S]. 2020. | |
| [24] | 中国海洋工程咨询协会. 海岸带生态系统现状调查与评估技术导则第6部分:海草床:T/CAOE 20.6—2020[S]. 2020. |
| China Association of Oceanic Engineering. Technical guideline for investigation and assessment of coastal ecosystem—Part 6: Seagrass Bed: T/CAOE 20.6—2020[S]. 2020. | |
| [25] |
LINDGREN J P, COUSINS S A O. Island biogeography theory outweighs habitat amount hypothesis in predicting plant species richness in small grassland remnants[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2017, 32(9): 1895-1906.
DOI URL |
| [26] | KEITH D A, RODRÍGUEZ J P, RODRÍGUEZ-CLARK K M, et al. Scientific foundations for an IUCN red list of ecosystems[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(5): e62111. |
| [27] |
MAO D H, WANG Z M, DU B J, et al. National wetland mapping in China: A new product resulting from object-based and hierarchical classification of Landsat 8 OLI images[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2020, 164: 11-25.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 赵欣怡. 基于时序光学和雷达影像的中国海岸带盐沼植被分类研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2020. |
| ZHAO X Y. Classification of salt marsh vegetation in coastal zone of China based on temporal optics and radar images[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2020. | |
| [29] | CHEN G W, JIN R J, YE Z J, et al. Spatiotemporal mapping of salt marshes in the intertidal zone of China during 1985—2019[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2022, 2022: 9793626. |
| [30] | 王小东. 自治区人大常委会执法检查组关于检查《广西壮族自治区红树林资源保护条例》实施情况的报告[R/OL].(2022-07-26)[2022-08-29].https://www.gxrd.gov.cn/html/art174755.html. |
| WANG X D. Report of the law enforcement inspection team of the Autonomous Region People’s Congress Standing Committee on checking the implementation of the Regulations of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region on the Protection of Mangrove Forest Resources[R/OL]. (2022-07-26) [2022-08-29]. https://www.gxrd.gov.cn/html/art174755.html. | |
| [31] |
ZHAO C P, QIN C Z. A detailed mangrove map of China for 2019 derived from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth images[J]. Geoscience Data Journal, 2022, 9(1): 74-88.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 广西壮族自治区海洋和渔业厅. 广西壮族自治区2017年海洋环境状况公报[R/OL].(2018-06-30)[2022-08-29].http://hyj.gxzf.gov.cn/zwgk_66846/hygb_66897/hyhjzlgb/P020201203463404 821051.pdf. |
| Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Ocean and Fisheries Department. Bulletin on the state of the marine environment in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region in 2017[R/OL]. (2018-06-30) [2022-08-29].http://hyj.gxzf.gov.cn/zwgk_66846/hygb_66897/hyhjzlgb/P020201203463404 821051.pdf. | |
| [33] | JIANG Z J, CUI L J, LIU S L, et al. Historical changes in seagrass beds in a rapidly urbanizing area of Guangdong Province: Implications for conservation and management[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2020, 22: e01035. |
| [34] | 国家海洋局. 2002年中国海洋环境质量公报[R/OL].(2010-04-01)[2022-08-29]. http://g.mnr.gov.cn/201701/t20170123_1428316.html. |
| State Oceanic Administration. Bulletin of marine environ-mental quality of China in 2002[R/OL]. (2010-04-01) [2022-08-29]. http://g.mnr.gov.cn/201701/t20170123_1428316.html. | |
| [35] | 黄小平, 黄良民, 李颖虹, 等. 华南沿海主要海草床及其生境威胁[J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(S3):114-119. |
| HUANG X P, HUANG L M, LI Y H, et al. Main seagrass beds along the coast of South China and their habitat threats[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(S3): 114-119. | |
| [36] | 黄小平, 黄良民. 中国南海海草研究[M]. 广州: 广东经济出版社, 2007. |
| HUANG X P, HUANG L M. Study on seaweed in South China Sea of China[M]. Guangdong: Guangdong Economy Publishing House, 2007. | |
| [37] | 邓超冰. 北部湾儒艮及海洋生物多样性[M]. 南宁: 广西科学技术出版社, 2002. |
| DENG C B. Dugong and marine biodiversity in Beibu Gulf[M]. Nanning: Guangxi Science and Technology Press, 2002. | |
| [38] |
WU R D, ZHANG S, YU D W, et al. Effectiveness of China’s nature reserves in representing ecological diversity[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2011, 9(7): 383-389.
DOI URL |
| [39] | 黎静, 鞠瑞亭, 吴纪华, 等. 海岸带生物入侵的生态后果及管理对策建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2016, 31(10):1204-1210. |
| LI J, JU R T, WU J H, et al. Ecological consequences and management of biological invasions in Chinese coastal zone[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016, 31(10): 1204-1210. | |
| [40] | 覃盈盈, 梁士楚. 外来种互花米草在广西海岸的入侵现状及防治对策[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 2008, 4(2):47-50. |
| QIN Y Y, LIANG S C. Current status and eradication strategy of invasive alien plants Spartina alterniflora in Guangxi[J]. Wetland Science & Management, 2008, 4(2): 47-50. | |
| [41] | 邓必玉, 吴玲巧, 秦旭东, 等. 广西红树林主要外来植物现状及防控对策研究[J]. 林业调查规划, 2020, 45(4):54-60. |
| DENG B Y, WU L Q, QIN X D, et al. Current situation and control measures of exotic plants in mangrove forest of Guangxi[J]. Forest Inventory and Planning, 2020, 45(4): 54-60. | |
| [42] | 孙学超, 黄展鹏, 张琼锐, 等. 珠海淇澳岛人工次生无瓣海桑纯林的植被碳储量变化[J]. 华南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 54(4):89-100. |
| SUN X C, HUANG Z P, ZHANG Q R, et al. The biological carbon storage change of artificial secondary Sonneratia apetala on Qi’ao Island, Zhuhai[J]. Journal of South China Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2022, 54(4): 89-100. |
| [1] | . Dynamics of mangrove change: Insights from 30-year observations of Maowei Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(3): 132-141. |
| [2] | ZOU Yarong, LIU Jianqiang, LIANG Chao, ZHU Haitian. Monitoring of mangrove growth using HY-1C Satellite CZI data based on remote sensing [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2020, 38(1): 68-76. |
| [3] | ZHENG Yu-jun, SHI Lian-qiang, XU Dai-lu, JIANG Zu-yin, GUO Jun-li. Analysis on the rules of spatial and temporal distribution of salt marsh in Yancheng coastal area over the past 30 years and its influencing factors [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2018, 36(3): 57-66. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||