海洋学研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 69-78.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2025.01.007
1993—2021年舟山及邻近东海海平面变化特征分析
金杰( ), 陈宇杰, 姚永衡, 张思远, 胡镇涛, 丁梦蓉, 贾彬*(
), 陈宇杰, 姚永衡, 张思远, 胡镇涛, 丁梦蓉, 贾彬*( )
)
- 浙江海洋大学 海洋科学与技术学院,浙江 舟山 316022
-
收稿日期:2024-05-09修回日期:2024-10-14出版日期:2025-03-15发布日期:2025-05-30 -
通讯作者:*贾彬(1994—),女,讲师,主要从事近海水动力及海平面变化方面的研究,E-mail: 2022172@zjou.edu.cn。 -
作者简介:金杰(2003—),男,浙江省绍兴市人,主要从事海平面上升方面的研究,E-mail:19818006791@163.com。 -
基金资助:浙江省大学生科技创新活动计划暨新苗人才计划(2023R411001);浙江省自然科学基金(LQ24D060002)
Analysis of the variation characteristics of the sea level in Zhoushan and the adjacent East China Sea from 1993 to 2021
JIN Jie( ), CHEN Yujie, YAO Yongheng, ZHANG Siyuan, HU Zhentao, DING Mengrong, JIA Bin*(
), CHEN Yujie, YAO Yongheng, ZHANG Siyuan, HU Zhentao, DING Mengrong, JIA Bin*( )
)
- College of Marine Science and Technology, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan 316022, China
-
Received:2024-05-09Revised:2024-10-14Online:2025-03-15Published:2025-05-30
摘要:
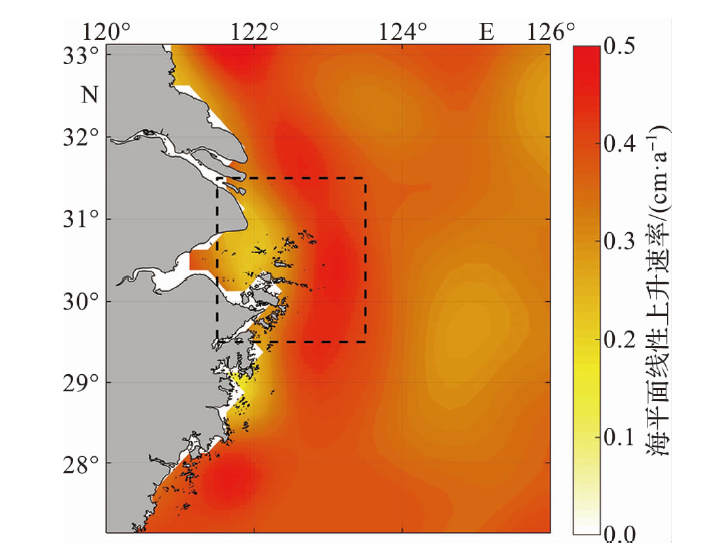
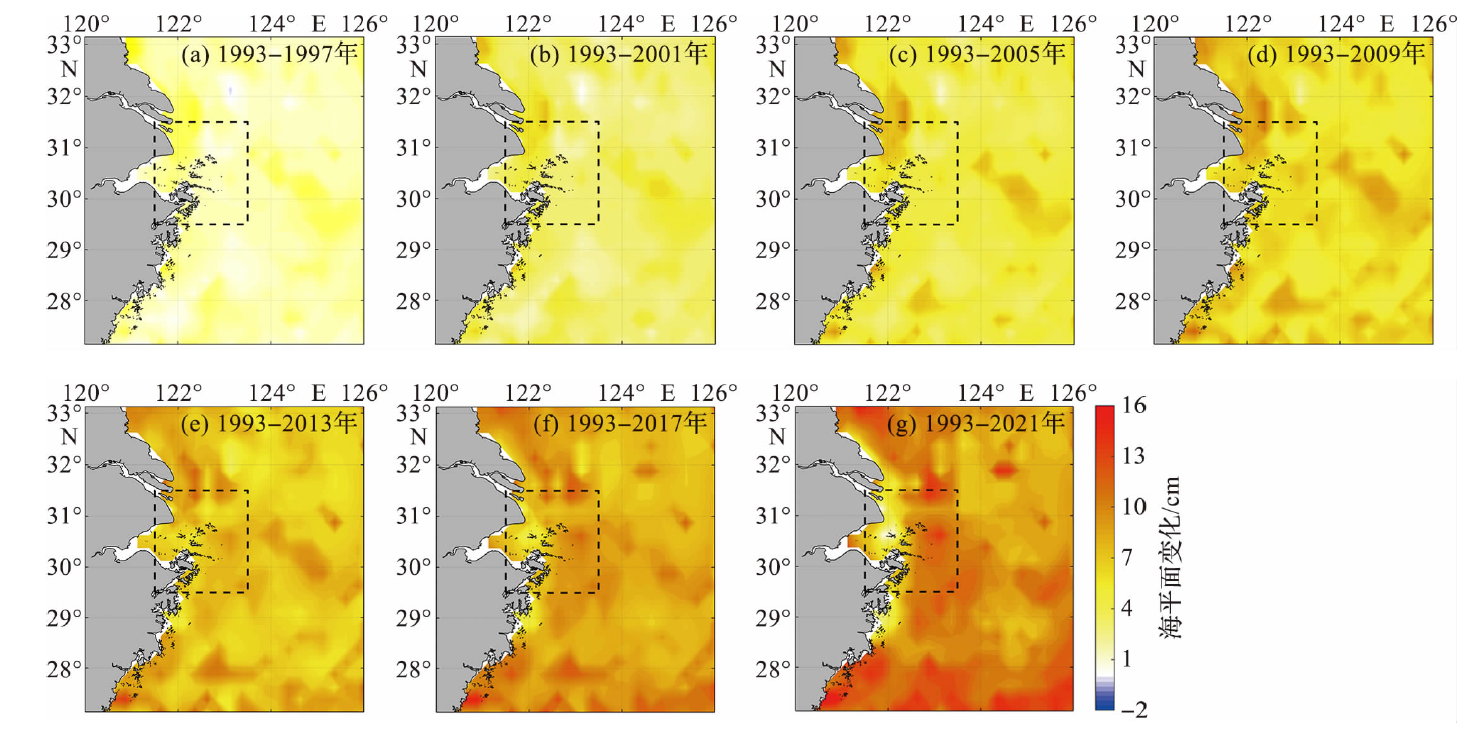
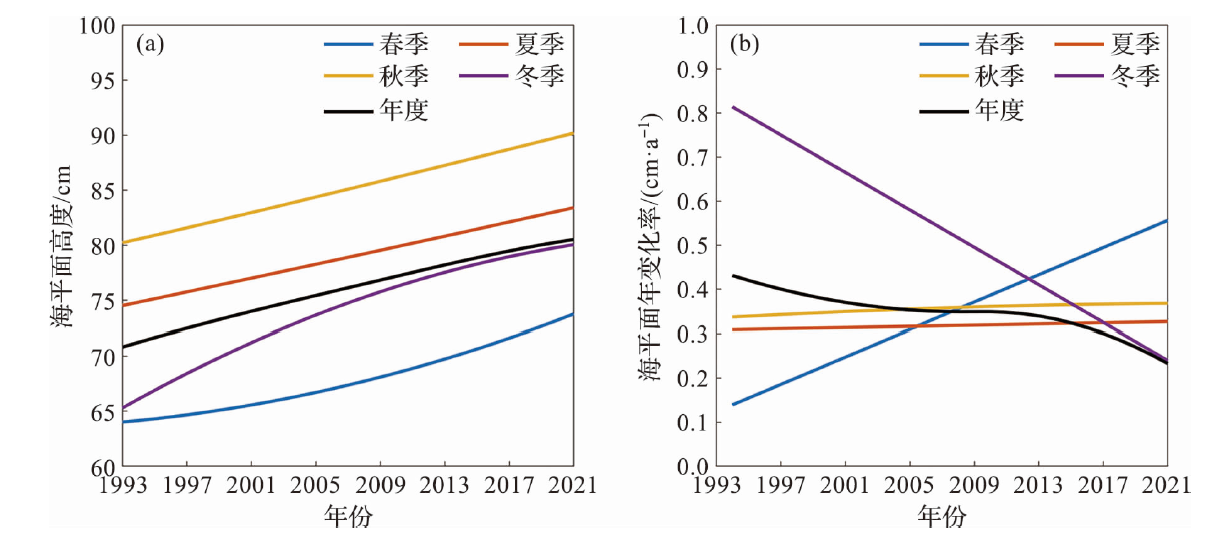
本文基于1993年1月至2021年12月的卫星高度计数据,利用最小二乘法和集合经验模态分解对舟山及邻近东海海平面的长期变化及其影响因子进行分析。研究发现,研究区海平面整体以上升趋势为主,在舟山群岛东侧海域,上升趋势更为明显;平均线性速率为0.36±0.10 cm/a,2018年起上升趋势有所减缓。研究区海平面变化具有明显的季节差异,其线性速率为秋季最大(0.37±0.12 cm/a),冬季次之,春、夏两季略小(约为0.34±0.10 cm/a)。近30年来的非线性变化趋势显示,夏、秋季的上升速率几乎不变,冬季的上升速率呈减缓态势,春季呈加速上升态势。研究区海平面变化存在年振幅增大的趋势,长期变化与温度引起的海水热膨胀效应以及风应力引起的增-减水效应密切相关。
中图分类号:
引用本文
金杰, 陈宇杰, 姚永衡, 张思远, 胡镇涛, 丁梦蓉, 贾彬. 1993—2021年舟山及邻近东海海平面变化特征分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2025, 43(1): 69-78.
JIN Jie, CHEN Yujie, YAO Yongheng, ZHANG Siyuan, HU Zhentao, DING Mengrong, JIA Bin. Analysis of the variation characteristics of the sea level in Zhoushan and the adjacent East China Sea from 1993 to 2021[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2025, 43(1): 69-78.
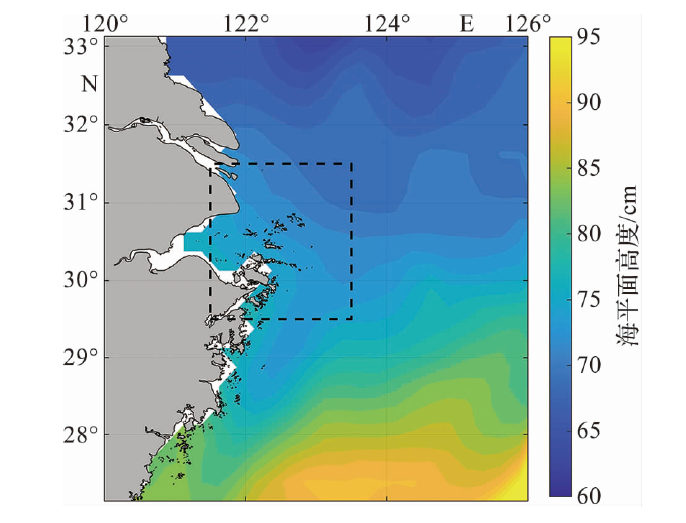
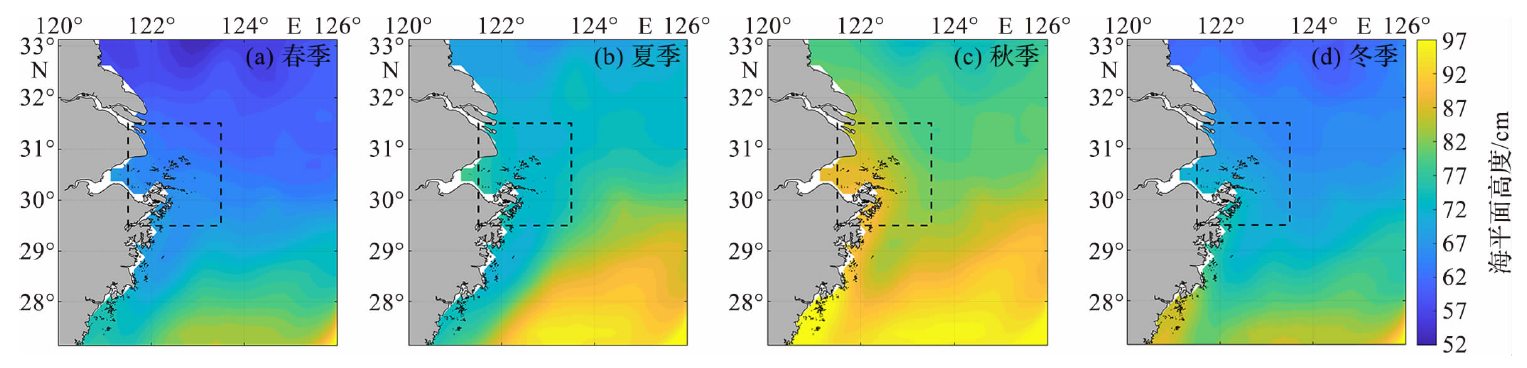
图2 1993—2021年舟山及邻近海域多年平均海平面的空间变化
Fig.2 The spatial variation of the multi-year average sea level in Zhoushan and its adjacent sea areas during 1993-2021
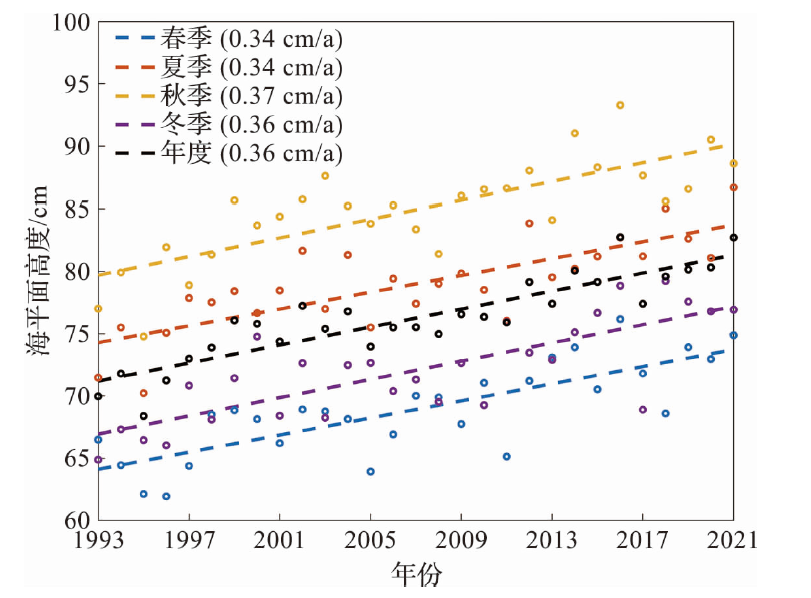
图6 1993—2021年研究区海平面的线性变化趋势 (圆点为海平面年度或季节平均值,直线为线性拟合结果。)
Fig.6 The linear change trend of the sea level in the study area during 1993-2021 (The dots represent the annual or seasonal mean sea level and the dashed lines represent the linear fitting results.)

图8 1993—2021年研究区海平面春季平均非线性变化的空间分布
Fig.8 The spatial distribution of nonlinear variation of mean sea level in spring in the study area during 1993-2021
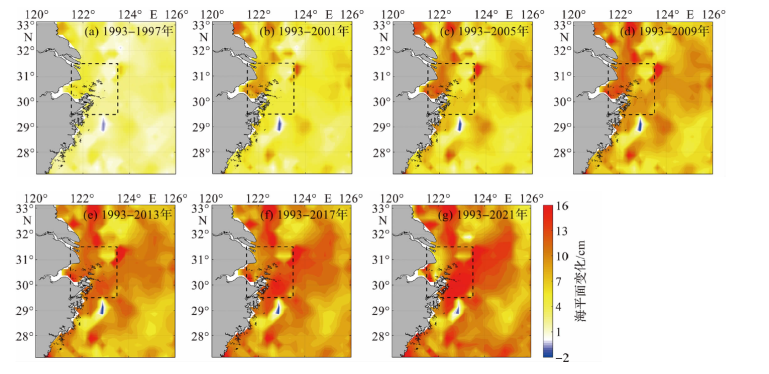
图9 1993—2021年研究区海平面秋季平均非线性变化的空间分布
Fig.9 The spatial distribution of nonlinear variation of mean sea level in autumn in the study area during 1993-2021
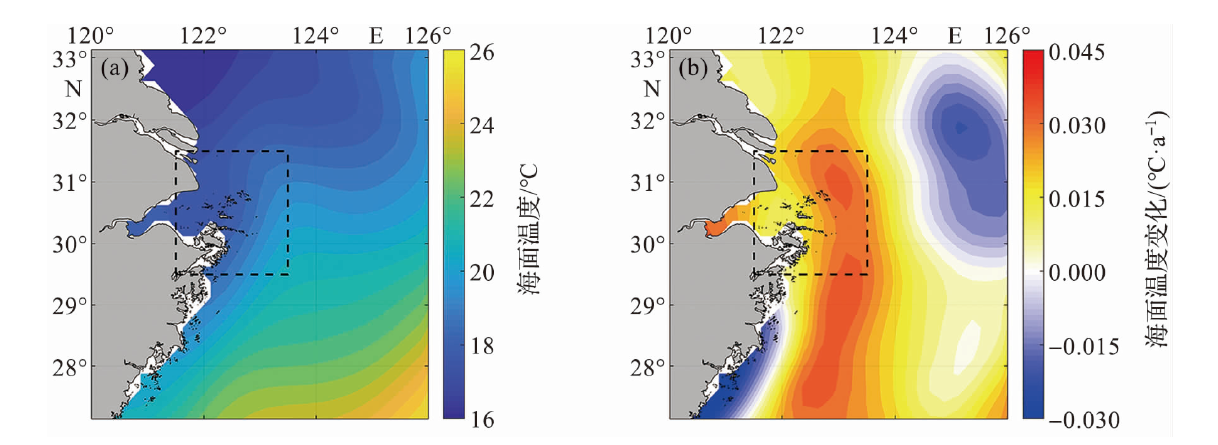
图11 1993—2021年气候态年平均海面温度(a)及其线性变化(b)的空间分布
Fig.11 The spatial distribution of climatological annual-mean sea surface temperature (a) and its linear variation (b) during 1993-2021
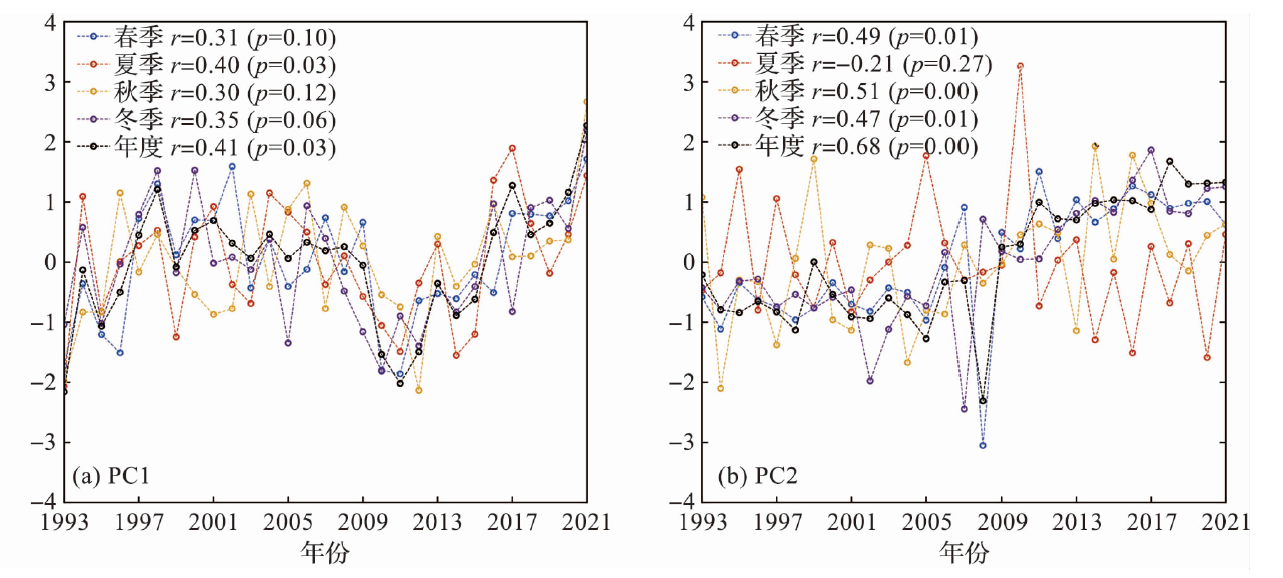
图12 1993—2021年海面温度的经验正交分解第一(a)和第二模态时间序列(b)
Fig.12 Time series of the first(a) and second principal component (b) for the empirical orthogonal decomposition of sea surface temperature during 1993-2021

图13 1993—2021年多年平均海面风场(a)及其线性变化(b)的空间分布
Fig.13 The spatial distribution of multi-year average sea surface wind (a) and its linear variation (b) during 1993-2021
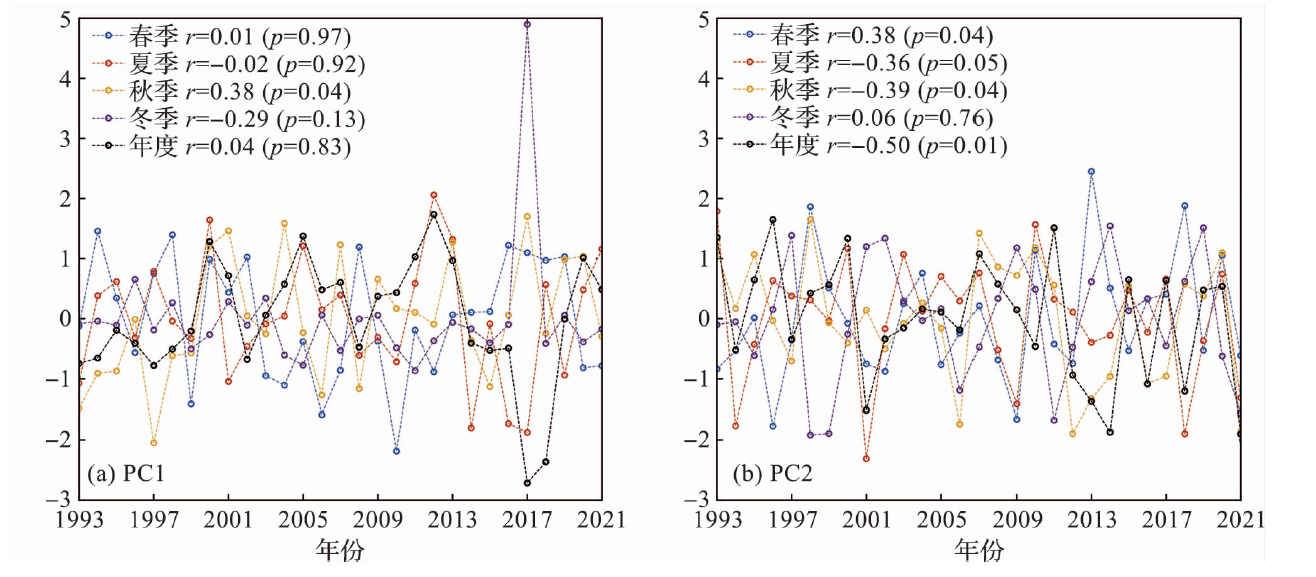
图14 1993—2021年海面风场的经验正交分解第一(a)和第二模态(b)时间序列
Fig.14 Time series of the first (a) and second principal component (b) for the empirical orthogonal decomposition of sea surface wind during 1993-2021
| [1] | 蔡榕硕, 谭红建. 海平面加速上升对低海拔岛屿、沿海地区及社会的影响和风险[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(2):163-171. |
| CAI R S, TAN H J. Impacts and risks of accelerating sea level rise on low lying islands, coasts and communities[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(2): 163-171. | |
| [2] | 王阳. 在稳定与公平之间:海平面上升对海洋边界的影响及其应对[J]. 中国海商法研究, 2022, 33(4):15-26. |
| WANG Y. Between stability and equality: The impact of sea level rise on maritime boundaries and its response[J]. Chinese Journal of Maritime Law, 2022, 33(4): 15-26. | |
| [3] | 李加林, 张殿发, 杨晓平, 等. 海平面上升的灾害效应及其研究现状[J]. 灾害学, 2005, 20(2):49-53. |
| LI J L, ZHANG D F, YANG X P, et al. Disaster effect of sea level rise in China and the research status in quo[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2005, 20(2): 49-53. | |
| [4] | 李杰, 杜凌, 张守文, 等. A1B气候情景下海平面变化对东中国海风暴潮的影响[J]. 海洋预报, 2014, 31(5):20-29. |
| LI J, DU L, ZHANG S W, et al. Impact of sea level variations on storm surge under SRES A1B scenario in the East China Sea[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2014, 31(5): 20-29. | |
| [5] |
孙鸿程, 蔡廷禄, 夏小明, 等. 舟山六横岛海域浅部地层结构与水下滑坡分布特征[J]. 海洋学研究, 2019, 37(1):59-66.
DOI |
| SUN H C, CAI T L, XIA X M, et al. Distribution characteristics of subaqueous landslides in the sea area of Liuheng Island, Zhoushan[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2019, 37(1): 59-66. | |
| [6] | 羊天柱, 应仁方, 张俊彪, 等. 浙江沿岸海平面研究和变化预测[J]. 东海海洋, 1999, 17(4):1-11. |
| YANG T Z, YING R F, ZHANG J B, et al. The research and prediction of the sea level along the coast of Zhejiang Province[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1999, 17(4):1-11. | |
| [7] | 乔新, 陈戈. 基于11年高度计数据的中国海海平面变化初步研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2008, 32(1): 60-64. |
| QIAO X, CHEN G. A preliminary analysis on the China Sea level using 11 years’ TOPEX/Poseidon altimeter data[J]. Marine Science, 2008, 32(1):60-64. | |
| [8] | 詹金刚, 王勇, 许厚泽, 等. 我国近海1992-2006年海平面变化的小波分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2008, 37(4):438-443. |
| ZHAN J G, WANG Y, XU H Z, et al. The wavelet analysis of sea level change in China Sea during 1992-2006[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2008, 37(4): 438-443. | |
| [9] | 自然资源部. 2023年中国海平面公报[R]. https://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202404/t20240429_2844012.html. |
| Ministry of Natural Resources. China Sea Level Bulletin 2023[R]. https://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202404/t20240429_2844012.html. | |
| [10] | 王慧, 全梦媛, 徐卫青, 等. 中国沿海和近海海平面上升预测[J]. 海洋学报, 2023, 45(8):1-10. |
| WANG H, QUAN M Y, XU W Q, et al. Sea level rise projection in China’s coastal and offshore areas[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2023, 45(8): 1-10. | |
| [11] | 王龙, 王晶, 杨俊钢. 东海海平面变化的综合分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(1):28-37. |
| WANG L, WANG J, YANG J G. The Comprehensive analysis of sea level change in the East China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(1): 28-37. | |
| [12] | 杨洋, 孙群, 杨敏, 等. 东中国海海平面高度的时空变化特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(3):481-489. |
| YANG Y, SUN Q, YANG M, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of sea level of the East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(3): 481-489. | |
| [13] |
TABURET G, SANCHEZ-ROMAN A, BALLAROTTA M, et al. DUACS DT2018: 25 years of reprocessed sea level altimetry products[J]. Ocean Science, 2019, 15(5): 1207-1224.
DOI |
| [14] | HUANG B Y, LIU C Y, BANZON V, et al. Improvements of the Daily Optimum Interpolation Sea Surface Temperature (DOISST) Version 2.1[J]. Journal of Climate, 2021, 34(8): 2923-2939. |
| [15] | WENTZ F J, SCOTT J, HOFFMAN R, et al. Remote Sensing Systems Cross-Calibrated Multi-Platform (CCMP) 6-hourly ocean vector wind analysis product on 0.25 deg grid, Version 2.0.[EB/OL]. https://remss.com/measurements/ccmp/. |
| [16] | HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. |
| [17] | WU Z, HUANG N E. Ensemble empirical mode decom-position: a noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. |
| [18] | JI F, WU Z H, HUANG J P, et al. Evolution of land surface air temperature trend[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2014, 4: 462-466. |
| [19] | 张静, 方明强. 1993—2012年中国海海平面上升趋势[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 45(1):121-126. |
| ZHANG J, FANG M Q. Sea level trends of China Seas from 1993 to 2012[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(1): 121-126. |
| [1] | 李志超, 郭俊如, 宋军, 白志鹏, 富砚昭, 蔡宇, 王喜风. 东海黑潮周边中尺度涡的分布、运动规律以及生成机制[J]. 海洋学研究, 2022, 40(4): 1-10. |
| [2] | 王磊, 李春峰, 李珂迪, 姚泽伟, 陶天生. 东海陆架盆地中生代残留地层特征及其构造启示[J]. 海洋学研究, 2022, 40(4): 11-24. |
| [3] | 周锋, 钱周奕, 刘安琪, 马晓, 倪晓波, 曾定勇, . 长江口及邻近海域底层水体低氧物理机制的研究进展[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(4): 17-38. |
| [4] | 王斌, 刘希真, 李林蔚, 李德望, 金海燕, 高生泉, 李宏亮, 陈建芳, . 2011年长江口-东海P-PN断面碳酸盐体系参数的季节分布特征及影响因素[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(4): 39-51. |
| [5] | 李德望, 林华, 陈思杨, 王斌, 王奎, 王尧, 马云龙, 金海燕, 陈建芳, . 2017年春季长江口-东海连续体pCO2的空间分布特征及其控制因素[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(4): 52-62. |
| [6] | 陶天生, 李春峰, 李珂迪, 姚泽伟. 东海深部地层时深转换关系的分段优化拟合[J]. 海洋学研究, 2020, 38(3): 65-75. |
| [7] | 曾宇兰, 陆斗定, 王鹏斌, 郭若玉, 管卫兵, 戴鑫烽. 东海原甲藻藻华和台湾暖流种源关系的进一步研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2020, 38(2): 38-48. |
| [8] | 张桃, 李君益, 谢玲玲, 郑少军, 郑慧源. 东海陆架区中尺度涡运动路径的统计特征分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2020, 38(1): 77-86. |
| [9] | 陈燕萍, 李琰. 舟山DZ-1钻孔沉积物粒度特征与沉积环境辨别[J]. 海洋学研究, 2018, 36(4): 53-59. |
| [10] | 武则州, 周锋. 基于卫星漂流浮标轨迹的东海边界交换估算方法研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2018, 36(1): 27-34. |
| [11] | 沈辉, 黄大吉. 渤、黄、东海冬季海表冷暖水舌的时空变化及机理分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2017, 35(1): 1-13. |
| [12] | 高艳秋, 苏洁, 李磊, 吕咸青. 海表面温度的变分同化预报模式:初始场的全局优化[J]. 海洋学研究, 2015, 33(1): 1-8. |
| [13] | 肖武鹏, 柳欣, 黄邦钦. 春季东海近岸表层浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋学研究, 2013, 31(3): 76-82. |
| [14] | 徐晓晖, 毛志华, 陶邦一. 基于光谱差异的东海赤潮提取算法[J]. 海洋学研究, 2013, 31(2): 26-34. |
| [15] | 周志远, 高金耀, 吴招才, 沈中延, 张涛, 孙运凡. 东海莫霍面起伏与地壳减薄特征初步分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2013, 31(1): 16-25. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||