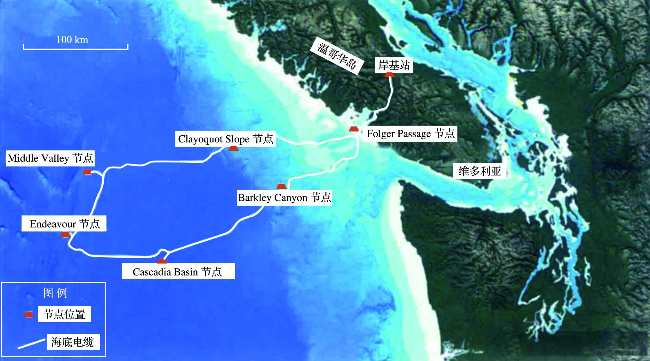
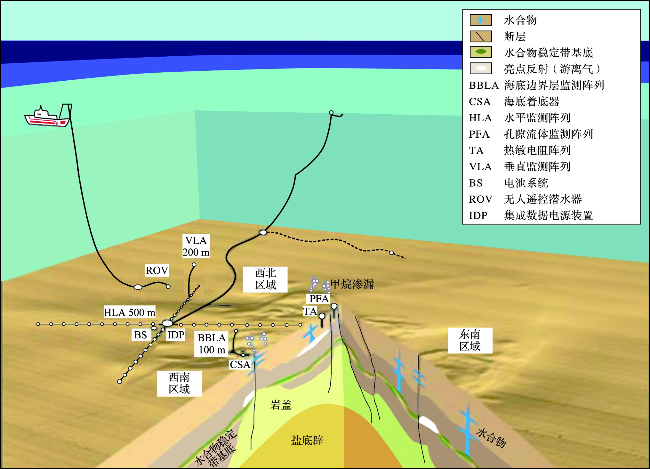
0 引言
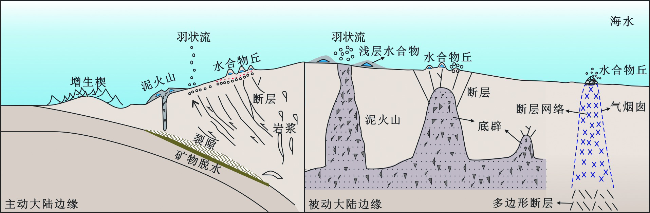
1 甲烷等烃类气体的运移及渗漏
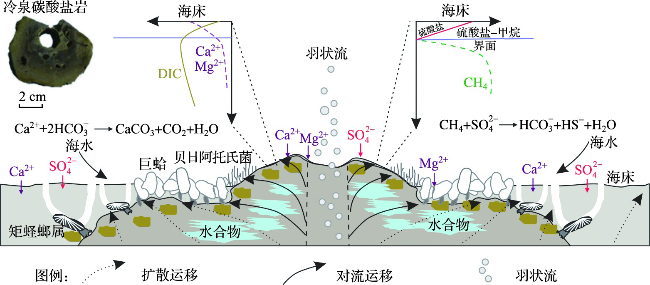
2 海底水合物及冷泉流体渗漏的走航式原位观测
2.1 运移通道的观测
2.2 羽状流的观测
图3 (a)船载多波束声呐实时探测羽状流示意图[37];(b)从多波束声学图像中识别出的羽状流[38];(c)船载侧扫声呐示意图;(d)从侧扫声纳图像上辨识出的鄂霍次克海海底冷泉喷口[40]Fig.3 (a)Acoustic exploration of the plume using the vessel-based multibeam sonar system[37]; (b)Multibeam acoustic image of a gas bubble plume in a water column[38]; (c)Vessel-based side-scan sonar system; (d)Cold seep venting captured by the side-scan sonar system in Okhotsk[40] |
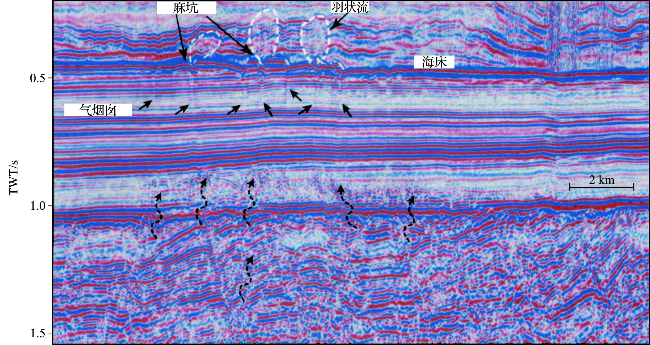
图4 经过处理的海水层和地层地震反射剖面[45](深部流体突破地层后沿气烟囱垂直运移,在海底发生渗漏,形成麻坑和羽状流。白色虚线为圈定的羽状流轮廓。) Fig.4 Combined seismic profile of the water column and sediment layers[45] (The deep sourced fluids migrate through the chimney and discharge on the seafloor, generating pockmarks at the seabed and plumes in the water column. The white dashed lines were demarcated based on the boundaries of the plumes.) |
2.3 冷泉流体渗漏区海底微地貌的观测
3 海底边界层冷泉流体渗漏的原位观测
3.1 海底甲烷浓度原位监测技术
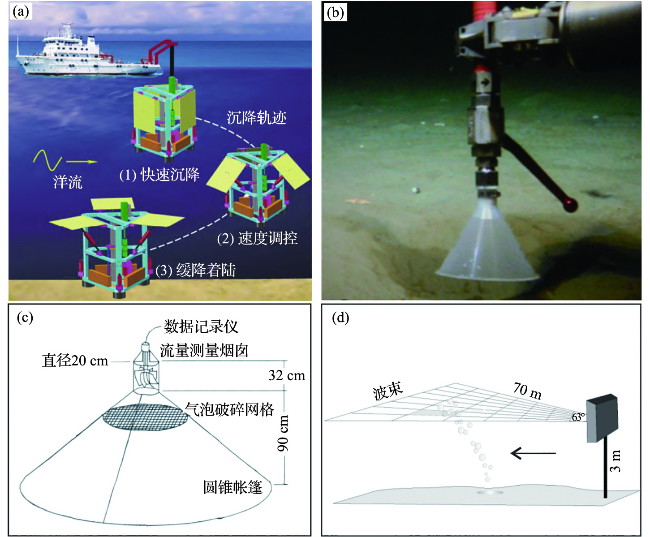
图5 (a)集成甲烷等传感器的海底着底器布放过程[56];(b)ROV机械手操纵带刻度的倒立漏斗装置测量单束羽状流的渗漏通量[57];(c)涡轮渗漏帐篷示意图[58];(d)坐底式水平声呐羽状流观测系统示意图[59-60]Fig.5 (a)Case diagram showing the deployment process of a bottom lander equipped with various sensors, such as CH4 sensor[56]; (b)Inverted funnel mounted on an ROV measuring the flux of a single plume[57]; (c)Turbine seep-tent schematic[58]; (d)Schematic sketch of the horizonal multibeam system monitoring on a plume[59-60] |
3.2 海底边界层甲烷通量原位测定技术
4 海面及低空渗漏甲烷的监测
5 海底视像观测
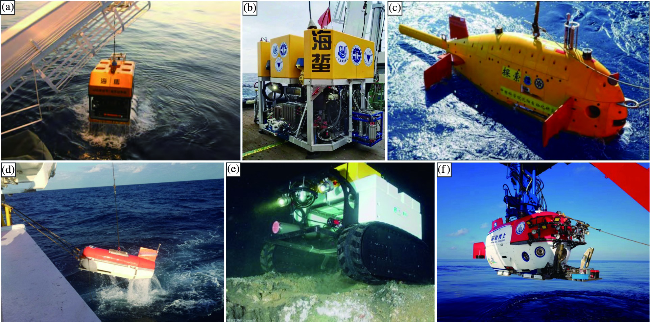
图7 几种国内外的海底水合物及冷泉视像观测系统(a.“海马号”ROV; b.“海蜇号”ROV; c.“探索4500”AUV; d.声学拖体系统; e.加拿大海底观测网Barkley Canyon节点海底爬行车“Wally”; f.“深海勇士号”HOV。) Fig.7 Selected visual systems for investigating on hydrate or cold seep areas (a.Haima ROV; b.Haizhe ROV; c.Tansuo 4500 AUV; d.Deep-tow geo-acoustic system; e.Crawl vehicle “Wally” deployed at the Barkley Canyon Node of the NEPTUNE-Canada; f.Shen Hai Yong Shi HOV) |
6 与水合物及冷泉流体渗漏相关的海底原位观测网络
6.1 欧洲ESONET-EMSO海底观测网
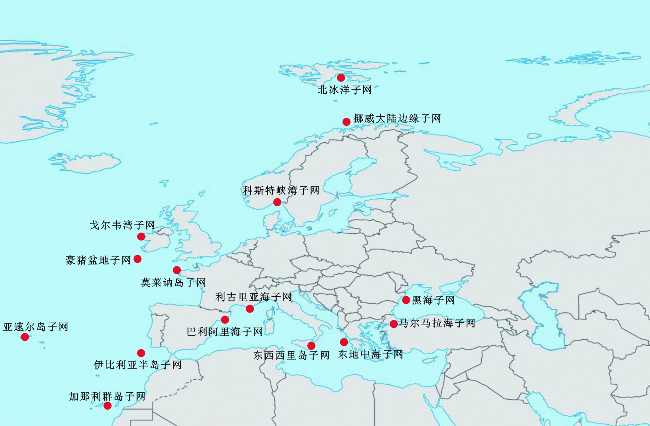
表1 欧洲ESONET-EMSO海底观测网中与海底水合物及冷泉流体渗漏相关的子网络Tab.1 Sub-networks of ESONET-EMSO that are associated with marine gas hydrate or methane leakage |
| 子网络 | 最大水深/m | 深/浅水 | 所属海域 | 建设国 | 原有基础 | 研究目标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑海子网 | 2 000 | 深水 | 黑海 | 黑海周边国家 | CRIMEA等 | 甲烷渗漏、水合物分解、海底泥火山活动及地质灾害 |
| 挪威大陆边缘子网 | 1 200 | 深水 | 北大西洋 | 挪威 | HMMV泥火山活动及水合物分解对海底稳定性的影响 | |
| 北冰洋子网 | >5 000 | 深水 | 北冰洋 | 德国 | HAUSGARTEN站 | 海底水合物分解及甲烷渗漏对气候的影响 |
| 东地中海子网 | 3 800 | 深水 | 地中海 | 希腊 | NESTOR | 甲烷渗漏与构造运动的关系、流体通道的水声学研究、地震、海啸等 |
| 马尔马拉海子网 | >1 000 | 深水 | 地中海与 黑海交界 | 土耳其 | MARMARA-DM | 观测北安那托利亚断层活动、甲烷渗漏、地震及海底滑坡 |
| 伊比利亚半岛子网 | 4 000 | 深水 | 大西洋 | 葡萄牙,西班牙 | NEAREST, LIDO | 地震、海啸;加的斯湾甲烷渗漏相关的泥火山、麻坑、丘体及碳酸盐岩烟囱体等 |
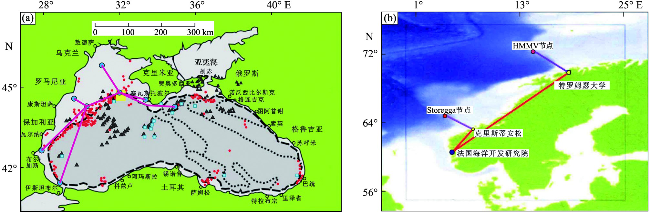
图9 (a)黑海海底观测网示意图[89];(b)挪威大陆边缘海底观测网节点[77](图9a中粗黑虚线代表陆架边缘;密方形虚线代表构造单元;红色圆点表示甲烷渗漏点;冰蓝色正方形表示水合物;黑色三角形代表泥火山;红线和蓝色圆点分别表示海底电缆和节点;黄色矩形表示甲烷渗漏密集的第聂伯罗古三角洲。) Fig.9 (a)Sketch showing the submarine seafloor observatory network in the Black Sea[89]; (b)Seafloor observatory network and nodes at Norwegian Continental margin[77] (In Figure 9a, bold dashed lines in black represent shelf edge; bold squared lines represent boundaries of tectonic units; dots in red represent methane seeps; ice blue squares represent gas hydrate; black triangles represent mud volcanoes; red lines represent cables; blue dots represent nodes; the yellow rectangle represents the Dnipro palaeo-delta area with intensive methane seepages.) |