Journal of Marine Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 102-112.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2023.04.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Macrobenthos community and living organic carbon pools on muddy tidal flat: Implications from Aiwan Bay of Wenling in summer
TIAN Sujie( ), TANG Yanbin, YU Peisong, LIU Chenggang, LIU Qinghe, ZHANG Rongliang, SHOU Lu, ZENG Jiangning, LIAO Yibo(
), TANG Yanbin, YU Peisong, LIU Chenggang, LIU Qinghe, ZHANG Rongliang, SHOU Lu, ZENG Jiangning, LIAO Yibo( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Marine Ecosystem Dynamics, Second Institute of Oceanography, MNR, Hangzhou 310012, China
-
Received:2022-08-25Revised:2023-03-21Online:2023-12-15Published:2024-01-30
CLC Number:
Cite this article
TIAN Sujie, TANG Yanbin, YU Peisong, LIU Chenggang, LIU Qinghe, ZHANG Rongliang, SHOU Lu, ZENG Jiangning, LIAO Yibo. Macrobenthos community and living organic carbon pools on muddy tidal flat: Implications from Aiwan Bay of Wenling in summer[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2023, 41(4): 102-112.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://hyxyj.sio.org.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2023.04.010
| 功能群 | 类群 | 物种 | AWB1断面 | AWB2断面 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高潮区 | 中潮区 | 低潮区 | 高潮区 | 中潮区 | 低潮区 | ||||||
| 肉食者 | 多毛类动物 | 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 | Nephtys oligobranchia | + | + | ||||||
| 索沙蚕属 | Lumbrineris sp. | + | + | ||||||||
| 长吻沙蚕 | Glycera chirori | + | + | + | |||||||
| 甲壳类动物 | 鲜明鼓虾 | Alpheusdistinguendus | + | + | |||||||
| 软体动物 | 斑玉螺 | Naticatigrina | + | ||||||||
| 半褶织纹螺 | Nassarius semiplicatus | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 秀丽织纹螺 | Reticunassa festiva | + | |||||||||
| 其他类动物 | 红狼牙虾虎鱼 | Odontamblyopus rubicundus | + | + | |||||||
| 纽虫 | Nemertinea sp. | + | |||||||||
| 浮游生物食者 | 软体动物 | 彩虹明樱蛤 | Iridona iridescens | + | |||||||
| 短拟沼螺 | Assiminea brevicula | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| 金星蝶铰蛤 | Trigonothracia jinxingae | + | |||||||||
| 婆罗囊螺 | Semiretusa borneensis | + | + | + | |||||||
| 青蛤 | Cyclina sinensis | + | |||||||||
| 小荚蛏 | Siliqua minima | + | |||||||||
| 缢蛏 | Sinonovacula constricta | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 植食者 | 甲壳类动物 | 淡水泥蟹 | Ilyoplax tansuiensis | + | + | ||||||
| 弧边招潮 | Tubuca arcuata | + | + | + | |||||||
| 隆线拳蟹 | Philyracarinata | + | + | + | |||||||
| 日本大眼蟹 | Mareotis japonicus | + | + | + | |||||||
| 绒螯近方蟹 | Hemigrapsus peniciillatus | + | |||||||||
| 长足长方蟹 | Metaplax longipes | + | + | + | |||||||
| 软体动物 | 珠带拟蟹守螺 | Cerithidea cingulata | + | ||||||||
| 碎屑食者 | 多毛类动物 | 不倒翁虫 | Sternaspis scutata | + | + | + | |||||
| 棘皮动物 | 倍棘蛇尾属 | Amphioplus sp. | + | ||||||||
| 软体动物 | 褐蚶 | Didimacar tenebrica | + | + | |||||||
| 杂食者 | 多毛类动物 | 琥珀刺沙蚕 | Neanthes succinea | + | |||||||
| 软体动物 | 泥螺 | Bullacta exarata | + | + | + | + | |||||
| 其他类动物 | 弹涂鱼 | Periophthalmus novaeguineaensis | + | + | |||||||
| 物种数量/种 | 29 | 6 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 20 | 6 | ||||
Tab.1 Distribution of functional groups, taxa and species of macrobenthos in Aiwan Bay
| 功能群 | 类群 | 物种 | AWB1断面 | AWB2断面 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高潮区 | 中潮区 | 低潮区 | 高潮区 | 中潮区 | 低潮区 | ||||||
| 肉食者 | 多毛类动物 | 寡鳃齿吻沙蚕 | Nephtys oligobranchia | + | + | ||||||
| 索沙蚕属 | Lumbrineris sp. | + | + | ||||||||
| 长吻沙蚕 | Glycera chirori | + | + | + | |||||||
| 甲壳类动物 | 鲜明鼓虾 | Alpheusdistinguendus | + | + | |||||||
| 软体动物 | 斑玉螺 | Naticatigrina | + | ||||||||
| 半褶织纹螺 | Nassarius semiplicatus | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 秀丽织纹螺 | Reticunassa festiva | + | |||||||||
| 其他类动物 | 红狼牙虾虎鱼 | Odontamblyopus rubicundus | + | + | |||||||
| 纽虫 | Nemertinea sp. | + | |||||||||
| 浮游生物食者 | 软体动物 | 彩虹明樱蛤 | Iridona iridescens | + | |||||||
| 短拟沼螺 | Assiminea brevicula | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| 金星蝶铰蛤 | Trigonothracia jinxingae | + | |||||||||
| 婆罗囊螺 | Semiretusa borneensis | + | + | + | |||||||
| 青蛤 | Cyclina sinensis | + | |||||||||
| 小荚蛏 | Siliqua minima | + | |||||||||
| 缢蛏 | Sinonovacula constricta | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 植食者 | 甲壳类动物 | 淡水泥蟹 | Ilyoplax tansuiensis | + | + | ||||||
| 弧边招潮 | Tubuca arcuata | + | + | + | |||||||
| 隆线拳蟹 | Philyracarinata | + | + | + | |||||||
| 日本大眼蟹 | Mareotis japonicus | + | + | + | |||||||
| 绒螯近方蟹 | Hemigrapsus peniciillatus | + | |||||||||
| 长足长方蟹 | Metaplax longipes | + | + | + | |||||||
| 软体动物 | 珠带拟蟹守螺 | Cerithidea cingulata | + | ||||||||
| 碎屑食者 | 多毛类动物 | 不倒翁虫 | Sternaspis scutata | + | + | + | |||||
| 棘皮动物 | 倍棘蛇尾属 | Amphioplus sp. | + | ||||||||
| 软体动物 | 褐蚶 | Didimacar tenebrica | + | + | |||||||
| 杂食者 | 多毛类动物 | 琥珀刺沙蚕 | Neanthes succinea | + | |||||||
| 软体动物 | 泥螺 | Bullacta exarata | + | + | + | + | |||||
| 其他类动物 | 弹涂鱼 | Periophthalmus novaeguineaensis | + | + | |||||||
| 物种数量/种 | 29 | 6 | 14 | 9 | 8 | 20 | 6 | ||||

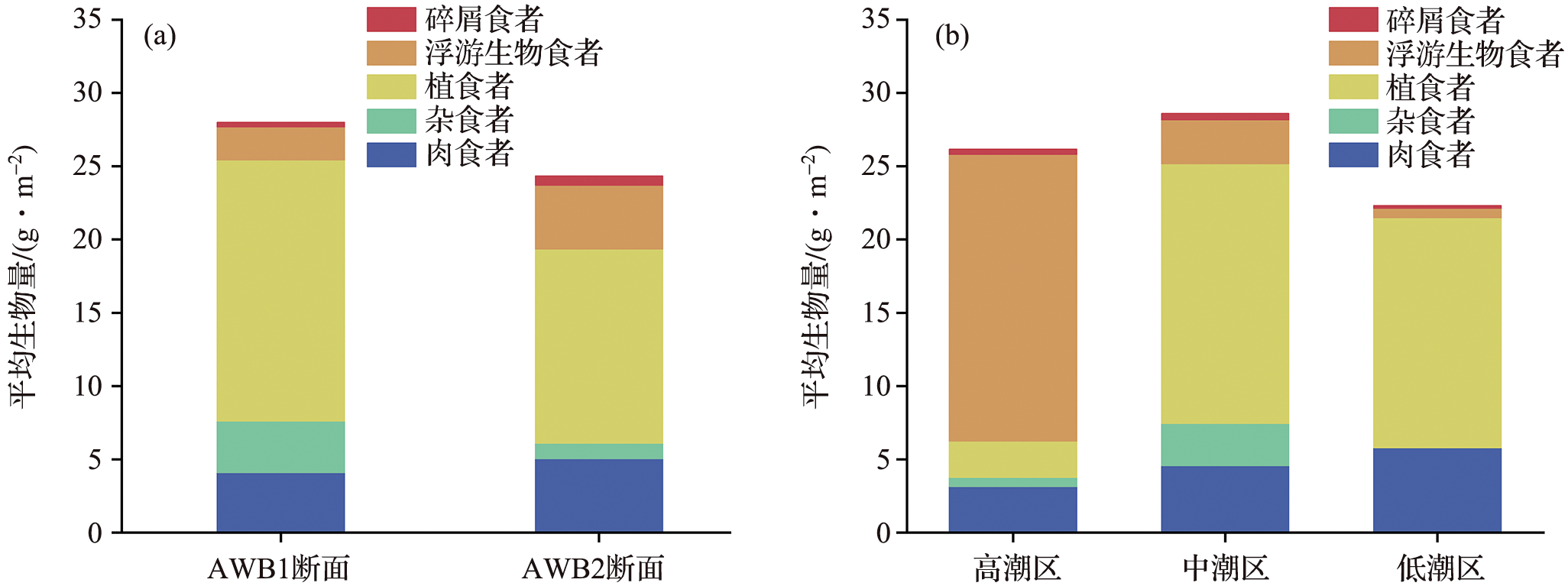
Fig.2 Average abundance and biomass of the macrobenthos at different sample stations in Aiwan Bay (a, b and c are significant difference markers, p<0.05.)
| 类群 | 大型底栖动物有机碳含量平均值/% | |
|---|---|---|
| AWB1断面 | AWB2断面 | |
| 甲壳类动物 | 12.30±3.86 | 22.17±4.29 |
| 软体动物 | 4.63±2.12 | 16.88±4.38 |
| 多毛类动物 | 17.49±14.14 | 28.46±4.87 |
| 其他类动物 | 42.19 | 39.71 |
| 棘皮动物 | 15.90 | |
Tab.2 Organic carbon content among different taxa of macrobenthos in Aiwan Bay
| 类群 | 大型底栖动物有机碳含量平均值/% | |
|---|---|---|
| AWB1断面 | AWB2断面 | |
| 甲壳类动物 | 12.30±3.86 | 22.17±4.29 |
| 软体动物 | 4.63±2.12 | 16.88±4.38 |
| 多毛类动物 | 17.49±14.14 | 28.46±4.87 |
| 其他类动物 | 42.19 | 39.71 |
| 棘皮动物 | 15.90 | |
| 海域 | 调查时间 | 多样性指数H' | 丰富度指数D | 均匀度指数J | 平均丰度/(ind·m-2) | 平均生物量/(g·m-2) | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 隘顽湾 | 2021年8月 | 3.18 | 3.29 | 0.72 | 105.2 | 46.9 | 本研究 |
| 南麂 列岛 | 2006年11月 | 1.39 | 1.19 | 0.71 | 51.0 | 6.5 | 文献[ |
| 2007年4月 | 3.06 | 4.23 | 0.90 | 319.0 | 302.4 | ||
| 2010年2月 | 1.62 | 1.99 | 0.65 | 250.7 | 55.4 | 文献[ | |
| 2010年8月 | 2.12 | 5.48 | 0.60 | 359.2 | 497.5 | ||
| 崇明东滩 | 2019年8月 | 96.4 | 68.4 | 文献[ | |||
| 南汇边滩 | 2019年8月 | 160.4 | 45.7 | 文献[ | |||
| 三门湾 | 2012年8月 | 0.62~1.87 | 2.64~4.32 | 407.3 | 171.9 | 文献[ | |
| 湄洲湾 | 2010年10月 | 2.32 (0.93~3.18) | 1.84 (1.21~2.63) | 0.79 (0.27~0.97) | 91.0 | 73.9 | 文献[ |
| 莱州湾 | 2016年7月 | 2.21 | 1.25 | 0.63 | 68.5 | 24.6 | 文献[ |
| 2016年10月 | 2.39 | 1.20 | 0.71 | 55.1 | 18.2 | ||
| 南黄海 | 2019年8月 | 2.33 | 1.51 | 0.85 | 115.0 | 245.0 | 文献[ |
| 2019年10月 | 2.01 | 1.22 | 0.81 | 126.0 | 174.5 |
Tab.3 Statistics of macrobenthos community structure, abundance and biomass at muddy tidal flat in China
| 海域 | 调查时间 | 多样性指数H' | 丰富度指数D | 均匀度指数J | 平均丰度/(ind·m-2) | 平均生物量/(g·m-2) | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 隘顽湾 | 2021年8月 | 3.18 | 3.29 | 0.72 | 105.2 | 46.9 | 本研究 |
| 南麂 列岛 | 2006年11月 | 1.39 | 1.19 | 0.71 | 51.0 | 6.5 | 文献[ |
| 2007年4月 | 3.06 | 4.23 | 0.90 | 319.0 | 302.4 | ||
| 2010年2月 | 1.62 | 1.99 | 0.65 | 250.7 | 55.4 | 文献[ | |
| 2010年8月 | 2.12 | 5.48 | 0.60 | 359.2 | 497.5 | ||
| 崇明东滩 | 2019年8月 | 96.4 | 68.4 | 文献[ | |||
| 南汇边滩 | 2019年8月 | 160.4 | 45.7 | 文献[ | |||
| 三门湾 | 2012年8月 | 0.62~1.87 | 2.64~4.32 | 407.3 | 171.9 | 文献[ | |
| 湄洲湾 | 2010年10月 | 2.32 (0.93~3.18) | 1.84 (1.21~2.63) | 0.79 (0.27~0.97) | 91.0 | 73.9 | 文献[ |
| 莱州湾 | 2016年7月 | 2.21 | 1.25 | 0.63 | 68.5 | 24.6 | 文献[ |
| 2016年10月 | 2.39 | 1.20 | 0.71 | 55.1 | 18.2 | ||
| 南黄海 | 2019年8月 | 2.33 | 1.51 | 0.85 | 115.0 | 245.0 | 文献[ |
| 2019年10月 | 2.01 | 1.22 | 0.81 | 126.0 | 174.5 |
| 生境类型 | 调查深度/cm | 植物有机碳含量/(Mg·hm-2) | 沉积物有机碳含量/(Mg·hm-2) | 数据来源 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上 | 地下 | ||||
| 红树林 | 100 | 138.0±21.6 | 52.0±8.9 | 307.0±33.2 | 文献[ |
| 海草 | 0.09±0.03 | 0.07±0.03 | 138.0±8.6 | ||
| 泥滩 | 143.0±15.5 | ||||
| 沙洲 | 124.0±3.1 | ||||
| 红树林 | 50 | 179±82 | 文献[ | ||
| 红树林边缘 | 68±11 | ||||
| 泥滩 | 62±10 | ||||
| 红树林 | 100 | 253.98 | 83.96 | 344.67±42.23 | 文献[ |
| 海草 | 0.36 | 0.41 | 175.14±23.81 | ||
| 盐沼植物 | 8.82 | 9.95 | 134.37±19.43 | ||
| 15年红树林 | 100 | 50.98±8.82 | 171.57 | 文献[ | |
| 45年红树林 | 116.56±13.72 | 274.53 | |||
| 80年红树林 | 289.90±18.33 | 380.72 | |||
| 泥滩 | 111.23 | ||||
| 本土红树林 | 100 | 154.6±27.1 | 69.9±11.6 | 文献[ | |
| 外来红树林 | 245.2 | 65.1 | |||
| 海三棱藨草 | 100 | 5.6 | 165.1 | 文献[ | |
| 芦苇 | 29.4 | 165.7 | |||
| 互花米草 | 38.3 | 171.1 | |||
| 泥滩 | 151.2 | ||||
Tab.4 Organic carbon content in common coastal habitats
| 生境类型 | 调查深度/cm | 植物有机碳含量/(Mg·hm-2) | 沉积物有机碳含量/(Mg·hm-2) | 数据来源 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地上 | 地下 | ||||
| 红树林 | 100 | 138.0±21.6 | 52.0±8.9 | 307.0±33.2 | 文献[ |
| 海草 | 0.09±0.03 | 0.07±0.03 | 138.0±8.6 | ||
| 泥滩 | 143.0±15.5 | ||||
| 沙洲 | 124.0±3.1 | ||||
| 红树林 | 50 | 179±82 | 文献[ | ||
| 红树林边缘 | 68±11 | ||||
| 泥滩 | 62±10 | ||||
| 红树林 | 100 | 253.98 | 83.96 | 344.67±42.23 | 文献[ |
| 海草 | 0.36 | 0.41 | 175.14±23.81 | ||
| 盐沼植物 | 8.82 | 9.95 | 134.37±19.43 | ||
| 15年红树林 | 100 | 50.98±8.82 | 171.57 | 文献[ | |
| 45年红树林 | 116.56±13.72 | 274.53 | |||
| 80年红树林 | 289.90±18.33 | 380.72 | |||
| 泥滩 | 111.23 | ||||
| 本土红树林 | 100 | 154.6±27.1 | 69.9±11.6 | 文献[ | |
| 外来红树林 | 245.2 | 65.1 | |||
| 海三棱藨草 | 100 | 5.6 | 165.1 | 文献[ | |
| 芦苇 | 29.4 | 165.7 | |||
| 互花米草 | 38.3 | 171.1 | |||
| 泥滩 | 151.2 | ||||
| [1] | NELLEMANN C, CORCORAN E, DUARTE C M, et al. Blue carbon: the role of healthy oceans in binding carbon[M]. Norway: Birkeland Trykkeri AS, 2009. |
| [2] |
GIOVANNONI S J, STINGL U. Molecular diversity and ecology of microbial plankton[J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7057): 343-348.
DOI |
| [3] |
SIMON N, CRAS A L, FOULON E, et al. Diversity and evolution of marine phytoplankton[J]. Comptes Rendus Biologies, 2009, 332(2/3): 159-170.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
BEAUMONT N J, JONES L, GARBUTT A, et al. The value of carbon sequestration and storage in coastal habitats[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 137: 32-40.
DOI URL |
| [5] | PERILLO G M E, WOLANSKI E, DONALD R C, et al. Coastal wetlands: An integrated ecosystem approach[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019. |
| [6] |
MACREADIE P I, ANTON A, RAVEN J A, et al. The future of blue carbon science[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 3998.
DOI PMID |
| [7] |
MCLEOD E, CHMURA G L, BOUILLON S, et al. A blueprint for blue carbon: Toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 2011, 9(10): 552-560.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
PHANG V X H, CHOU L M, FRIESS D A. Ecosystem carbon stocks across a tropical intertidal habitat mosaic of mangrove forest, seagrass meadow, mudflat and sandbar[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2015, 40(10): 1387-1400.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
SASMITO S D, KUZYAKOV Y, LUBIS A A, et al. Organic carbon burial and sources in soils of coastal mudflat and mangrove ecosystems[J]. CATENA, 2020, 187: 104414.
DOI URL |
| [10] | HORI M, BAYNE C J, KUWAE T. Blue carbon: Characteristics of the ocean’s sequestration and storage ability of carbon dioxide[M]//KUWAE T, HORI M. Blue carbon in shallow coastal ecosystems. Singapore: Springer, 2019: 1-31. |
| [11] |
SCHEFFOLD M I E, HENSE I. Quantifying contemporary organic carbon stocks of the Baltic Sea ecosystem[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2020, 7: 571956.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
OUYANG X G, LEE S Y. Improved estimates on global carbon stock and carbon pools in tidal wetlands[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 317.
DOI PMID |
| [13] |
JANAS U, BURSKA D, KENDZIERSKA H, et al. Importance of benthic macrofauna and coastal biotopes for ecosystem functioning—Oxygen and nutrient fluxes in the coastal zone[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2019, 225: 106238.
DOI URL |
| [14] | ROSSI S, COPPARI M, VILADRICH N. Benthic-pelagic coupling: New perspectives in the animal forests[M]//ROSSI S, BRAMANTI L, GORI A, et al. Marine animal forests. Cham: Springer, 2017: 855-885. |
| [15] | ROSSI S, RIZZO L. Marine animal forests as carbon immobilizers or why we should preserve these three-dimensional alive structures[M]//ROSSI S, BRAMANTI L. Perspectives on the marine animal forests of the world. Cham: Springer, 2020: 333-400. |
| [16] | 台州史志网. 台州地区志[EB/OL].(2019-01-14)[2022-08-01]. http://tzsz.zjtz.gov.cn/art/2019/1/14/art_1229206642_54283679.html. |
| Taizhou Historical Record Website. Taizhou local chronicles[EB/OL]. (2019-01-14)[2022-08-01]. http://tzsz.zjtz.gov.cn/art/2019/1/14/art_1229206642_54283679.html. | |
| [17] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋调查规范第6部分: 海洋生物调查:GB/T 12763.6-2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standar-dization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: Marine biological survey: GB/T 12763.6—2007[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2007. | |
| [18] |
BOESCH D F. Classification and community structure of macrobenthos in the Hampton Roads area, Virginia[J]. Marine Biology, 1973, 21(3): 226-244.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
廖一波, 寿鹿, 曾江宁, 等. 浙江西门岛海洋特别保护区大型底栖动物功能群特征及其与环境的关系[J]. 生物多样性, 2013, 21(1):3-10.
DOI |
|
LIAO Y B, SHOU L, ZENG J N, et al. Functional groups of marine macrobenthos in relation to environmental factors around the Ximen Island National Marine Special Reserve, Zhejiang[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2013, 21(1): 3-10.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 袁健美, 张虎, 汤晓鸿, 等. 江苏南部潮间带大型底栖动物功能群研究[J]. 海洋渔业, 2019, 41(1):43-52. |
| YUAN J M, ZHANG H, TANG X H, et al. Macrozoo-benthic functional groups in intertidal zone of southern Jiangsu Province[J]. Marine Fisheries, 2019, 41(1): 43-52. | |
| [21] | 龚堃, 鲍毅新, 任鹏, 等. 漩门湾围垦区外滩涂不同生境大型底栖动物功能群及其变化[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(24):8214-8223. |
| GONG K, BAO Y X, REN P, et al. Macrobenthic functional groups in different habitats in the reclaimed wetland Xuanmen Bay[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(24): 8214-8223. | |
| [22] |
GAMITO S, PATRÍCIO J, NETO J M, et al. Feeding diversity index as complementary information in the assessment of ecological quality status[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2012, 19: 73-78.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LÜ W W, ZHOU W Z, ZHAO Y L. Macrobenthos functional groups as indicators of ecological restoration in reclaimed intertidal wetlands of China’s Yangtze Estuary[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2018, 22: 93-100.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
STUDDS C E, KENDALL B E, MURRAY N J, et al. Rapid population decline in migratory shorebirds relying on Yellow Sea tidal mudflats as stopover sites[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8: 14895.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
XIE X F, PU L J, ZHU M, et al. Differential effects of various reclamation treatments on soil characteristics: An experimental study of newly reclaimed tidal mudflats on the East China coast[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 768: 144996.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LIAO Y B, SHOU L, TANG Y B, et al. Influence of two non-indigenous plants on intertidal macrobenthic commu-nities in Ximen Island Special Marine Protected Area, China[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2018, 112: 96-104.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
JACKSON M V, FULLER R A, GAN X J, et al. Dual threat of tidal flat loss and invasive Spartina alterniflora endanger important shorebird habitat in coastal mainland China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2021, 278: 111549.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MURRAY N J, MA Z J, FULLER R A. Tidal flats of the Yellow Sea: A review of ecosystem status and anthropogenic threats[J]. Austral Ecology, 2015, 40(4): 472-481.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZUO P, ZHAO S H, LIU C A, et al. Distribution of Spartina spp. along China’s coast[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 40: 160-166.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WANG M, GAO X Q, WANG W Q. Differences in burrow morphology of crabs between Spartina alterniflora marsh and mangrove habitats[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2014, 69: 213-219.
DOI URL |
| [31] | LU K L, HAN G X, WU H T. Effects of Spartina alterniflora invasion on the benthic invertebrate community in intertidal wetlands[J]. Ecosphere, 2022, 13(3): e3693. |
| [32] | 黄雅琴, 王建军, 何雪宝, 等. 三沙湾互花米草(Spartina alterniflora)入侵对大型底栖动物群落结构的影响[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020, 51(3):506-519. |
| HUANG Y Q, WANG J J, HE X B, et al. Effect of Spartina alterniflora invasion on community structure of macrobenthos in Sansha Bay, Fujian[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(3): 506-519. | |
| [33] | QIU J. Chinese survey reveals widespread coastal pollution[J]. Nature, 2012. DOI:10.1038/nature.2012.11743. |
| [34] | 彭欣, 谢起浪, 陈少波, 等. 南麂列岛潮间带底栖生物时空分布及其对人类活动的响应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2009, 40(5):584-589. |
| PENG X, XIE Q L, CHEN S B, et al. Distribution of intertidal benthos and the human impact in Nanji Islands, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2009, 40(5): 584-589. | |
| [35] | 张华伟, 彭欣, 刘俊峰, 等. 南麂列岛冬夏季潮间带大型底栖生物群落结构[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2018, 27(1):133-140. |
| ZHANG H W, PENG X, LIU J F, et al. Community structure of macrobenthos in the intertidal zones of Nanji Islands in winter and summer[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2018, 27(1): 133-140. | |
| [36] | 杨颖, 陈思思, 周红宏, 等. 长江口潮间带底栖生物生态及变化趋势[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(4):1606-1618. |
| YANG Y, CHEN S S, ZHOU H H, et al. Ecological evaluation and variation trend analysis of macrobenthos in intertidal zone of Changjiang Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(4): 1606-1618. | |
| [37] | 唐久, 郭刚强, 彭欣, 等. 三门湾潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构变化[J]. 科技通报, 2015, 31(11):97-104,123. |
| TANG J, GUO G Q, PENG X, et al. Community structure change of intertidal macrozoobenthos in Sanmen Bay[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2015, 31(11): 97-104, 123. | |
| [38] | 刘玉, 杨翼, 张文亮, 等. 湄洲湾潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构和多样性特征[J]. 湿地科学, 2014, 12(2):148-154. |
| LIU Y, YANG Y, ZHANG W L, et al. Characteristics of community structure and biodiversity of macrozoobenthos in intertidal zones in Meizhou Bay[J]. Wetland Science, 2014, 12(2): 148-154. | |
| [39] | 李慧峰, 杨文波, 袁立来, 等. 莱州湾南部胶莱河口潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 2018, 33(5):674-682. |
| LI H F, YANG W B, YUAN L L, et al. Intertidal macrozoobenthic community structural features in Jiaolai Estuary of South Laizhou Bay[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2018, 33(5): 674-682. | |
| [40] | 祝超文, 张虎, 袁健美, 等. 南黄海潮间带大型底栖动物群落组成及时空变化[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2022, 31(4):950-960. |
| ZHU C W, ZHANG H, YUAN J M, et al. Community composition and spatial and temporal changes of macrobenthos in intertidal zone of southern Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2022, 31(4): 950-960. | |
| [41] | HUANG X C, QIU J F, QI S J, et al. Impact of land reclamation in Aiwan Cove on marine water quality in Zhejiang Province, China[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 5th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environment Engineering (ICSEEE 2016). Paris: Atlantis Press, 2016: 456-459. |
| [42] |
STRICKLAND M S, HAWLENA D, REESE A, et al. Trophic cascade alters ecosystem carbon exchange[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(27): 11035-11038.
DOI PMID |
| [43] |
RODIL I F, LOHRER A M, ATTARD K M, et al. Positive contribution of macrofaunal biodiversity to secondary production and seagrass carbon metabolism[J]. Ecology, 2022, 103(4): e3648.
DOI PMID |
| [44] |
GITHAIGA M N, FROUWS A M, KAIRO J G, et al. Seagrass removal leads to rapid changes in fauna and loss of carbon[J]. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2019, 7: 62.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
MEDINA-CONTRERAS D, ARENAS F, CANTERA-KINTZ J, et al. Carbon sources supporting macrobenthic crustaceans in tropical eastern Pacific mangroves[J]. Food Webs, 2022, 30: e00219.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
AHMED N, BUNTING S W, GLASER M, et al. Can greening of aquaculture sequester blue carbon?[J]. Ambio, 2017, 46(4): 468-477.
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
TAMBURINI E, TUROLLA E, LANZONI M, et al. Manila clam and Mediterranean mussel aquaculture is sustainable and a net carbon sink[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 848: 157508.
DOI URL |
| [48] | ALI AKBER M, AZIZ A A, LOVELOCK C. Major drivers of coastal aquaculture expansion in Southeast Asia[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2020, 198: 105364. |
| [49] | 中华人民共和国农业农村部渔业渔政管理局. 2020中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020. |
| Bureau of Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. 2020 China fishery statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2020. | |
| [50] |
NAYLOR R L, HARDY R W, BUSCHMANN A H, et al. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture[J]. Nature, 2021, 591(7851): 551-563.
DOI |
| [51] |
MARIANI G, CHEUNG W W L, LYET A, et al. Let more big fish sink: Fisheries prevent blue carbon sequestration—Half in unprofitable areas[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6(44): eabb4848.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
WŁODARSKA-KOWALCZUK M, MAZURKIEWICZ M, GÓRSKA B, et al. Organic carbon origin, benthic faunal consumption, and burial in sediments of northern Atlantic and Arctic fjords (60-81°N)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 2019, 124(12): 3737-3751.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
ZWERSCHKE N, SANDS C J, ROMAN-GONZALEZ A, et al. Quantification of blue carbon pathways contributing to negative feedback on climate change following glacier retreat in West Antarctic fjords[J]. Global Change Biology, 2022, 28(1): 8-20.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
MENG W Q, FEAGIN R A, HU B B, et al. The spatial distribution of blue carbon in the coastal wetlands of China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2019, 222: 13-20.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
YU C X, GUAN D S, GANG W, et al. Development of ecosystem carbon stock with the progression of a natural mangrove forest in Yingluo Bay, China[J]. Plant and Soil, 2021, 460(1/2): 391-401.
DOI |
| [56] |
ZHANG Z M, WANG Y, ZHU Y K, et al. Carbon sequestration in soil and biomass under native and non-native mangrove ecosystems[J]. Plant and Soil, 2022, 479(1/2): 61-76.
DOI |
| [57] |
LIAO C Z, LUO Y Q, JIANG L F, et al. Invasion of Spartina alterniflora enhanced ecosystem carbon and nitrogen stocks in the Yangtze Estuary, China[J]. Ecosystems, 2007, 10(8): 1351-1361.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
OLSEN Y S, FOX S E, TEICHBERG M, et al. δ15N and δ13C reveal differences in carbon flow through estuarine benthic food webs in response to the relative availability of macroalgae and eelgrass[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 2011, 421: 83-96.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
GILLIES C L, STARK J S, JOHNSTONE G J, et al. Carbon flow and trophic structure of an Antarctic coastal benthic community as determined by δ13C and δ15N[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2012, 97: 44-57.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
ALLGEIER J E, WENGER S, LAYMAN C A. Taxonomic identity best explains variation in body nutrient stoichiometry in a diverse marine animal community[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10: 13718.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | DONG Di, HUANG Huamei, GAO Qing, CHEN Mianrun, YANG Xi. Conservation gap analysis of coastal blue carbon ecosystems: Taking Guangdong and Guangxi as examples [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2023, 41(1): 110-120. |
| [2] | JIA Haibo, CHAI Xiaoping, HUANG Bei. Effect of seasonal hypoxia on macrobenthic communities in the Yangtze Estuary from 2016 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2021, 39(2): 80-88. |
| [3] | LI Shuai, LÜ Teng-teng, HAN Qing-gong, ZHENG Jun-yong, HAN Qing-xi. Comparison of composition and structure of macrobenthic communities in the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea in May 2010 and June 2013 [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2017, 35(1): 86-94. |
| [4] | LI Li, ZHANG Jian-le, NIU Ji-zhu, SHI Wei-jie, MA Xin. Study on the community structural variation of macrobenthos and impact factors in the adjacent sea area of Qinhuangdao Estuary in summer [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2014, 32(4): 83-89. |
| [5] | JIANG Hai-hua, PENG Xin, XIAO Guo-qiang, ZHANG Yong-pu, ZHANG Jiong-ming, FANG Jun, CAI Jing-bo. Community structure of intertidal macrobenthos in islands of Wenling, Zhejiang, China [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2014, 32(3): 78-86. |
| [6] | GUO Feng-xia, QIU Jian-li, WU Song-hua, GUO Guo-ming. The EOF analysis on the profile change of tidal flat among groins [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2012, 30(4): 37-45. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||