海洋学研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 14-21.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2025.01.002
国产深海HM4000型剖面浮标盐度数据校正
张璇1,2( ), 刘增宏1,2,*(
), 刘增宏1,2,*( ), 陈朝晖3, 任翀4, 熊海霞4, 高志远3, 严啸峦5, 张林林5
), 陈朝晖3, 任翀4, 熊海霞4, 高志远3, 严啸峦5, 张林林5
- 1.自然资源部第二海洋研究所,浙江 杭州 310012
2.卫星海洋环境监测预警全国重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310012
3.中国海洋大学 物理海洋教育部重点实验室,山东 青岛 266100
4.崂山实验室,山东 青岛 266237
5.中国科学院海洋研究所,山东 青岛 266071
Calibration of salinity data of a domestically-produced HM4000 deep profiling float
ZHANG Xuan1,2( ), LIU Zenghong1,2,*(
), LIU Zenghong1,2,*( ), CHEN Zhaohui3, REN Chong4, XIONG Haixia4, GAO Zhiyuan3, YAN Xiaoluan5, ZHANG Linlin5
), CHEN Zhaohui3, REN Chong4, XIONG Haixia4, GAO Zhiyuan3, YAN Xiaoluan5, ZHANG Linlin5
- 1. Second Institute of Oceanography, MNR, Hangzhou 310012, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Satellite Ocean Environment Dynamics, Hangzhou 310012, China
3. Key Laboratory of Physical Oceanography, MOE, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
4. Laoshan Laboratory, Qingdao 266237, China
5. Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
摘要:
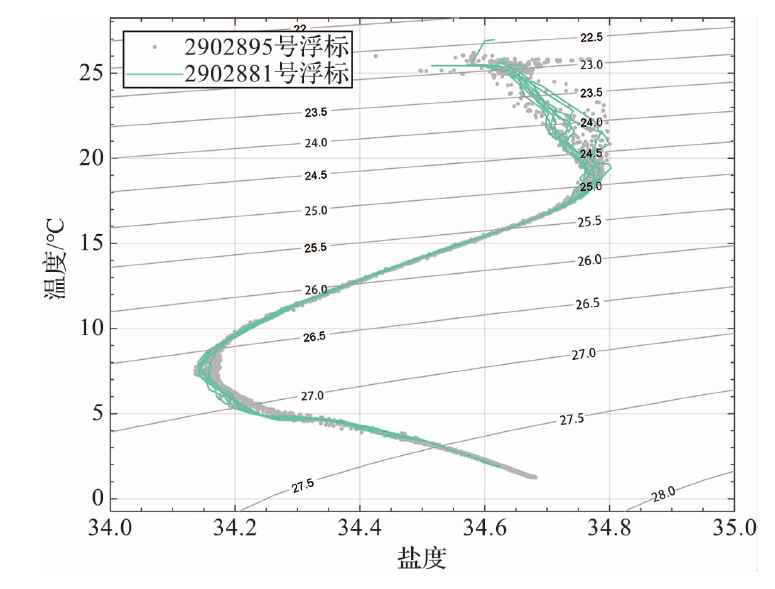
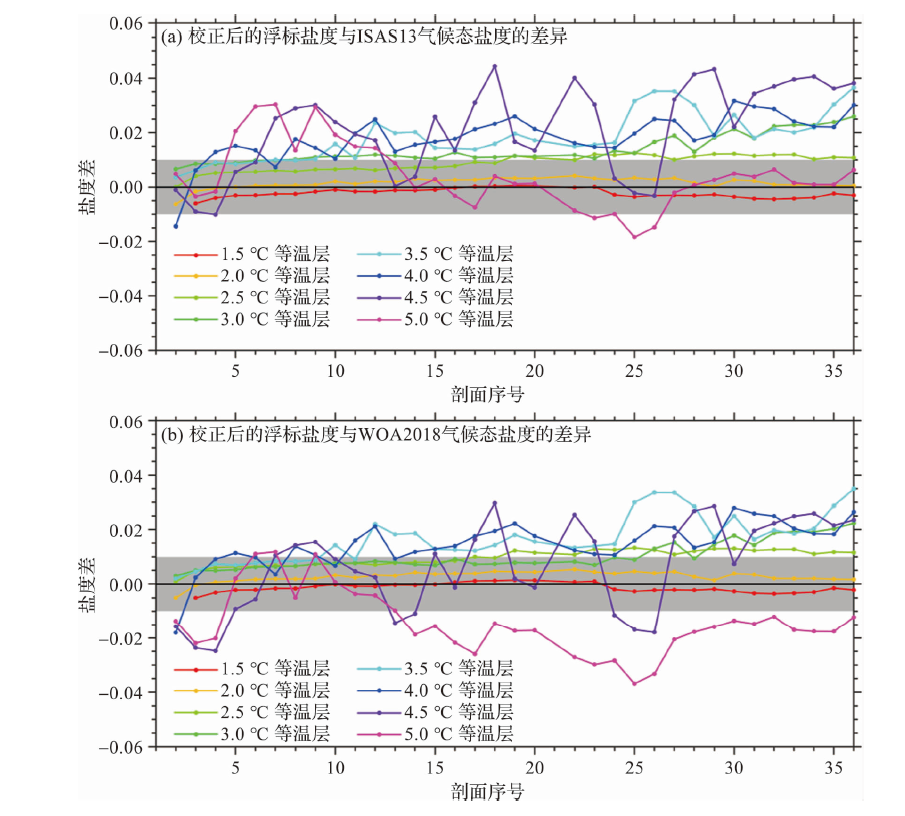
2023年12月,崂山实验室“深海Argo区域观测网建设”项目在菲律宾海盆布放了1台国产4 000 m级HM4000型剖面浮标(世界气象组织编号为2902895),该浮标携带了加拿大RBR公司生产的RBRargo3 deep 6k CTD传感器(以下简称RBR CTD)。布放后发现,该浮标返回的盐度观测数据与船载CTD结果以及气候态盐度值相比存在系统性的偏差。为了校正浮标盐度数据,使用现场盐度计分析结果和船载CTD测量的盐度,计算了RBR CTD电导率的偏移率,进而对浮标盐度剖面进行了校正。经检验,校正后的结果与邻近浮标和气候态盐度数据基本一致。随着我国 “深海Argo区域观测网建设”项目的启动实施,越来越多的国产深海Argo浮标将被布放,相比观测水深为0~2 000 m范围内的核心Argo(Core-Argo,仅观测海水温度和盐度),深海Argo(Deep-Argo)需要更高的观测精度才能分辨出深海更小的变化。当前,Deep-Argo使用的CTD传感器仍存在技术问题,一些浮标和传感器在存储、运输和使用过程中难免会存在不当操作,导致观测数据特别是盐度数据存在较大误差。为此,本文提出了一种使用现场比测资料对深海Argo浮标观测资料进行校正的方法,可为我国深海Argo区域观测网资料质量控制提供重要的技术支撑。
中图分类号: