海洋学研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 90-106.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2025.01.009
春季典型亚热带珊瑚礁海域海水pCO2的变化特征及其调控机制
杨波1,2,3,4( ), 张卓5, 周进4, 林子燚1, 谢子强6, 郑惠娜1,7, 廖宝林1, 肖宝华1,*(
), 张卓5, 周进4, 林子燚1, 谢子强6, 郑惠娜1,7, 廖宝林1, 肖宝华1,*( )
)
- 1.广东海洋大学 深圳研究院,广东 深圳 518108
2.广西北部湾海洋资源环境与可持续发展重点实验室,广西 北海 536015
3.江苏海洋大学 海洋科学与水产学院,江苏 连云港 222006
4.清华大学 深圳国际研究生院, 广东 深圳518055
5.广东海洋大学 水产学院,广东 湛江 524088
6.深圳市碧海蓝天海洋科技有限公司, 广东 深圳 518108
7.广东海洋大学 食品科技学院,广东 湛江 524088
-
收稿日期:2023-08-17修回日期:2023-11-16出版日期:2025-03-15发布日期:2025-05-30 -
通讯作者:*肖宝华(1978—),男,教授级高级工程师,主要从事珊瑚礁生态调查研究,E-mail: xiaobh@gdou.edu.cn。 -
作者简介:杨波(1990—),男,山东省青岛市人,讲师,主要从事近海碳循环方面的研究,E-mail:sdqdyb123@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(42406039);广东省基础与应用基础研究基金项目(2023A1515012204);广东省基础与应用基础研究基金项目(2022A1515110345);广西北部湾海洋资源环境与可持续发展重点实验室开放基金项目(MRESD-2024-B02);深圳市可持续发展专项(KCXFZ20211020165547011)
Variation characteristics and regulation mechanism of pCO2 in typical subtropical coral reefs area in spring
YANG Bo1,2,3,4( ), ZHANG Zhuo5, ZHOU Jin4, LIN Ziyi1, XIE Ziqiang6, ZHENG Huina1,7, LIAO Baolin1, XIAO Baohua1,*(
), ZHANG Zhuo5, ZHOU Jin4, LIN Ziyi1, XIE Ziqiang6, ZHENG Huina1,7, LIAO Baolin1, XIAO Baohua1,*( )
)
- 1. Shenzhen Institute of Guangdong Ocean University, Shenzhen 518108, China
2. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Beibu Gulf Marine Resources, Environment and Sustainable Development, Beihai 536015, China
3. College of Marine Science and Fisheries, Jiangsu Ocean University, Lianyungang 222006, China
4. Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University, Shenzhen 518055, China
5. College of Fisheries, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang 524088, China
6. Shenzhen Blue Sea Blue Sky Marine Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen 518108, China
7. College of Food Science and Technology, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang 524088, China
-
Received:2023-08-17Revised:2023-11-16Online:2025-03-15Published:2025-05-30
摘要:
由于存在极高的初级生产和高效的碳代谢速率, 珊瑚礁海域二氧化碳(CO2)的汇/源属性仍存有争议。为了明晰我国亚热带珊瑚礁海域CO2的源、汇特征及驱动因素,基于2023年5月的海上调查结果并结合室内培养实验数据,本文探究了春季大澳湾(珊瑚礁海域)海水CO2分压(pCO2)的分布特征及主要控制机制。结果表明:春季大澳湾海水pCO2的范围为412.9~555.7 μatm,主要表现为大气CO2的源,平均释放通量为0.53±0.90 mmol·m-2·d-1。调查期间,pCO2整体呈现近岸高于远岸的分布特征,这主要受到生物活动(净呼吸)和陆源淡水输入的共同控制。此外,海水pCO2的日周期变化显著,其差值最高可达168 μatm。生物活动(光合和呼吸作用)的昼夜差异是导致pCO2日变化的主要因素,在礁区和非礁区对pCO2日变化的贡献分别为89.4%和66.4%。物理过程(温度和潮汐作用)对pCO2昼夜变化的影响较小,其中温度变化在礁区和非礁区的贡献分别为12.7%和21.5%,其作用远低于生物过程。此外,近岸珊瑚的代谢过程可能会显著提升大澳湾局部(礁区)的pCO2,增强海域的CO2源属性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨波, 张卓, 周进, 林子燚, 谢子强, 郑惠娜, 廖宝林, 肖宝华. 春季典型亚热带珊瑚礁海域海水pCO2的变化特征及其调控机制[J]. 海洋学研究, 2025, 43(1): 90-106.
YANG Bo, ZHANG Zhuo, ZHOU Jin, LIN Ziyi, XIE Ziqiang, ZHENG Huina, LIAO Baolin, XIAO Baohua. Variation characteristics and regulation mechanism of pCO2 in typical subtropical coral reefs area in spring[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2025, 43(1): 90-106.
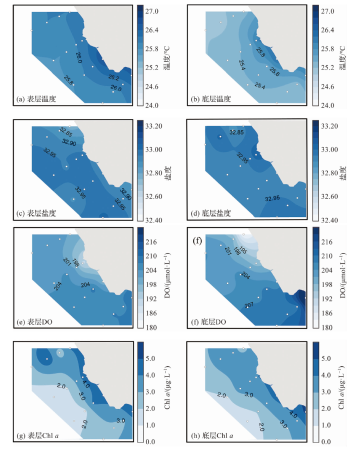
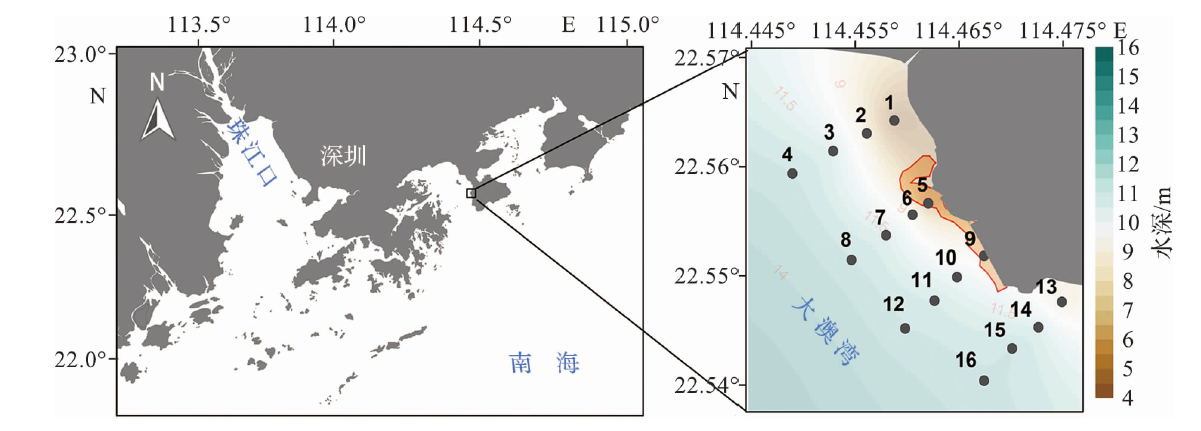
图2 表、底层海水温度、盐度、DO和Chl a的水平分布特征
Fig.2 The horizontal distribution characteristics of temperature, salinity, DO and Chl a in the surface and bottom seawater

图4 珊瑚礁区和非珊瑚礁区表、底层海水温度、DO和AOU的日变化特征
Fig.4 Diurnal variation characteristics of temperature, DO and AOU in the surface and bottom water in coral reef and non-reef areas
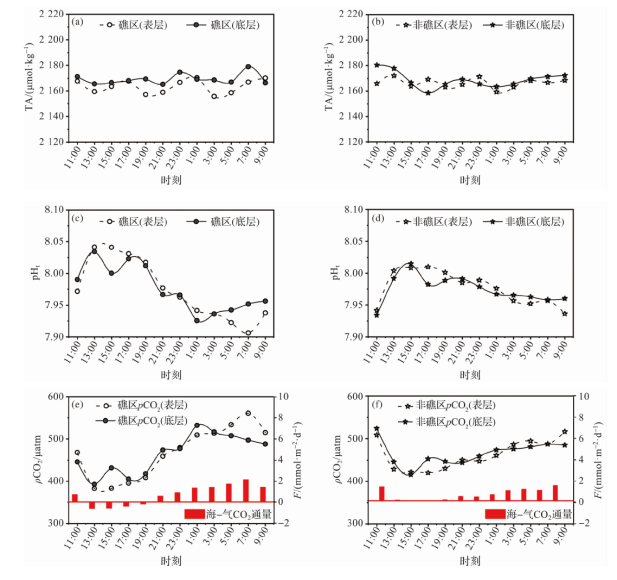
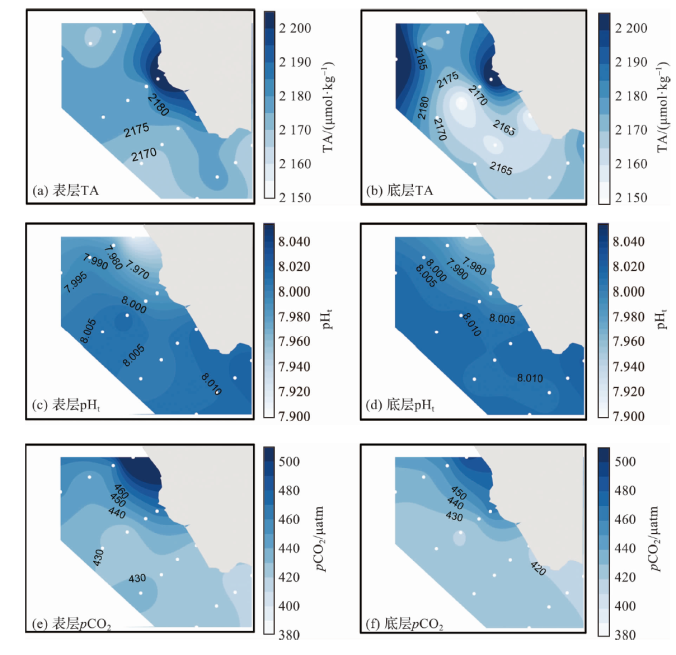
图5 珊瑚礁区和非珊瑚礁区表、底层海水TA、pHt、pCO2和海-气CO2通量的日变化特征
Fig.5 Diurnal variation characteristics of TA, pHt, pCO2 and air-sea CO2 flux in the surface and bottom water in coral reef and non-reef areas
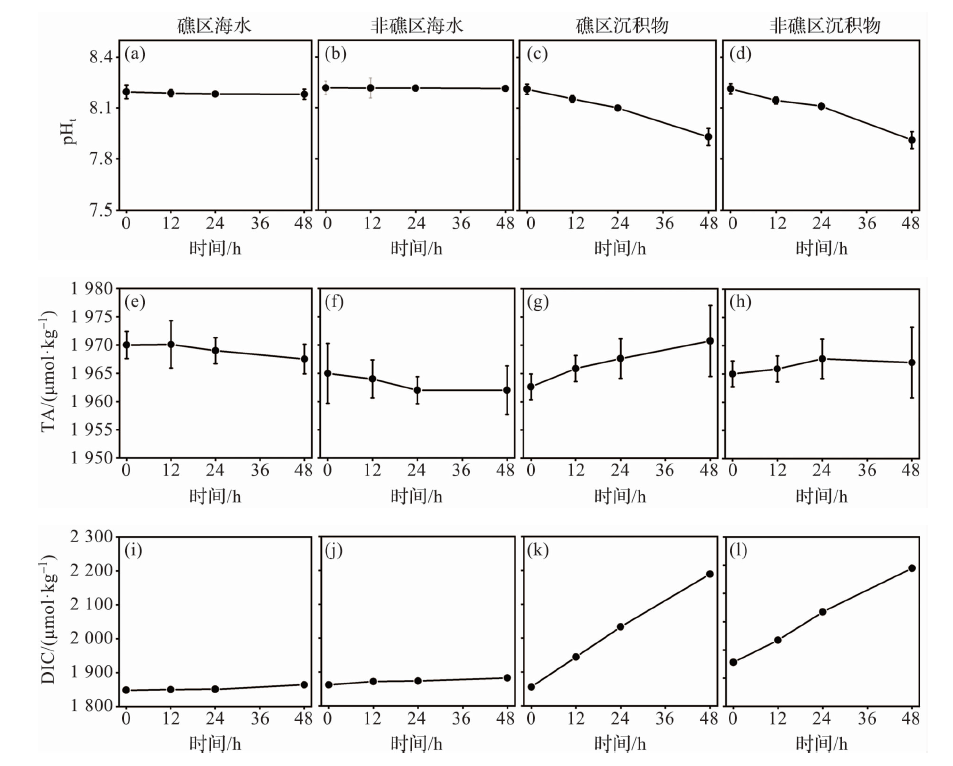
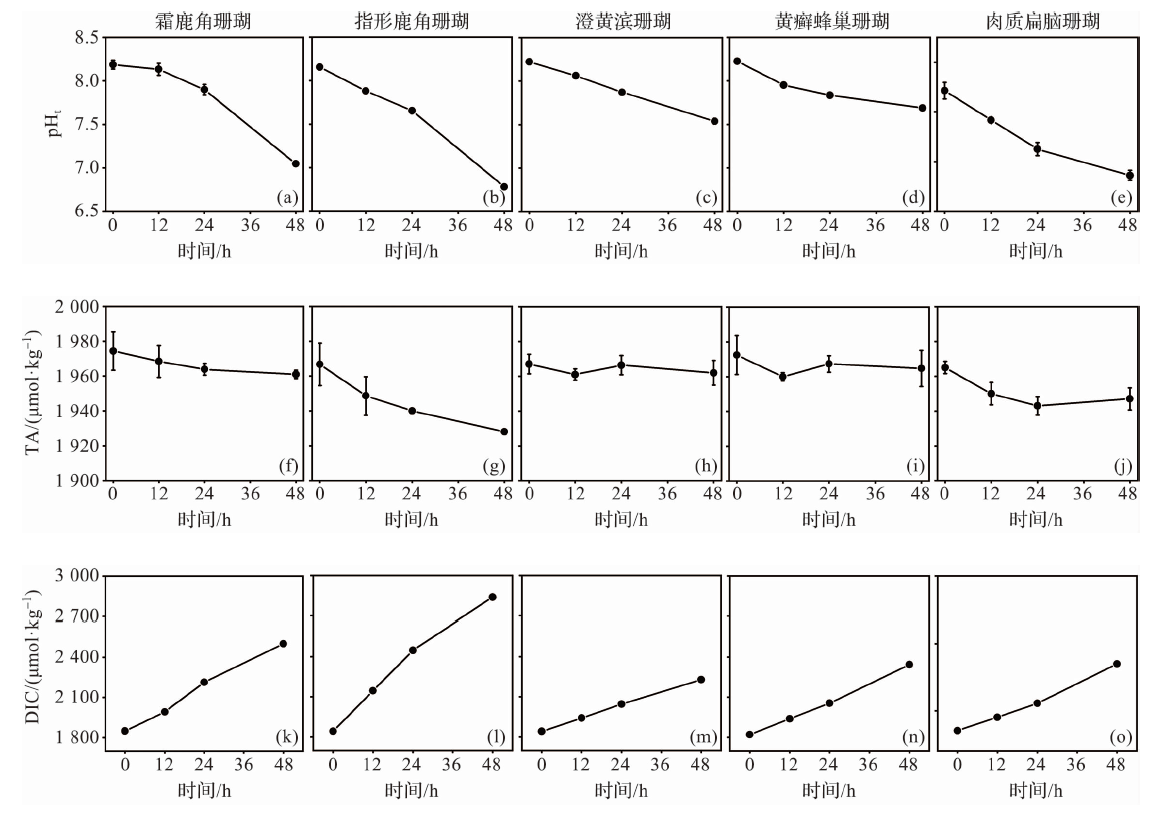
图7 室内模拟实验中pHt、TA和DIC的变化(海水和沉积物微生物代谢)
Fig.7 Changes in pHt, TA and DIC during indoor simulation experiments (microbial metabolism in seawater and sediment)

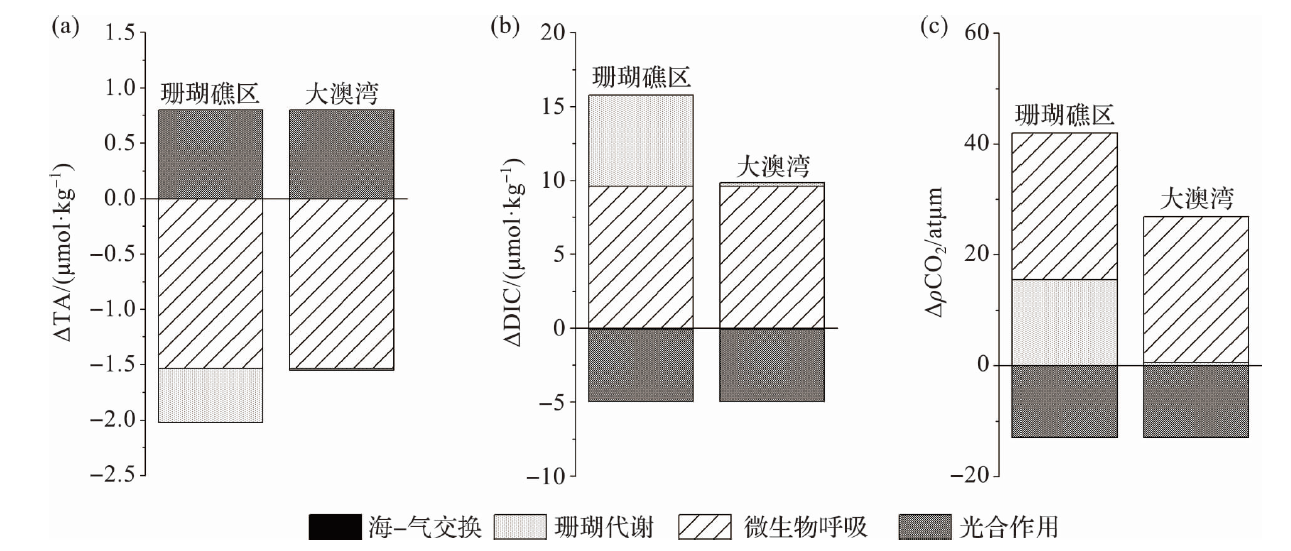
图8 海水微生物代谢、沉积物释放以及珊瑚代谢过程中DIC和TA的平均释放通量
Fig.8 The average release fluxes of DIC and TA during the seawater microbial metabolism, sediment release, and the coral metabolism
| 项目 | 释放通量 | 研究区域(目标) | 数据来源 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIC | TA | |||
| 海水微生物代谢 /(μmol·kg-1·d-1) | 13.01±2.95 | -1.40±0.36 | 胶州湾(海水) | 文献[ |
| 4.95±0.41 | 路易斯安那大陆架(海水) | 文献[ | ||
| 14.21±1.31 | 墨西哥湾(海水) | 文献[ | ||
| 沉积物释放 /(mmol·m-2·d-1) | 6.05±1.58 | 北黄海(沉积物) | 文献[ | |
| 6.94±4.90 | 南黄海(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 0.82±0.02 | 博滕海(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 2.12±0.07 | 博恩霍尔姆岛沿岸(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 9.32±3.52 | 英国北海(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 31.14±22.01 | 29.06±21.39 | 墨西哥湾(沉积物) | 文献[ | |
| 9.70±2.88 | 3.84±2.77 | 蒙特利湾(沉积物) | 文献[ | |
| 17.23±1.70 | 路易斯安那大陆架(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 珊瑚代谢 /(mmol·cm-2·d-1) | -27.12±2.33 | 指形鹿角珊瑚 | 文献[ | |
| -16.60±0.70 | 美丽鹿角珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| -54 | 铁星珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| -0.38±1.26 | 板叶角蜂巢珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| 13.82 | 风信子鹿角珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| 0.53 | 丛生盔形珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
表1 全球近海/河口区海水微生物代谢、沉积物释放和珊瑚代谢过程中DIC和TA的释放通量
Tab.1 The release fluxes of DIC and TA during the seawater microbial metabolism, sediment release, and the coral metabolism in other offshore/estuarine areas of the world
| 项目 | 释放通量 | 研究区域(目标) | 数据来源 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIC | TA | |||
| 海水微生物代谢 /(μmol·kg-1·d-1) | 13.01±2.95 | -1.40±0.36 | 胶州湾(海水) | 文献[ |
| 4.95±0.41 | 路易斯安那大陆架(海水) | 文献[ | ||
| 14.21±1.31 | 墨西哥湾(海水) | 文献[ | ||
| 沉积物释放 /(mmol·m-2·d-1) | 6.05±1.58 | 北黄海(沉积物) | 文献[ | |
| 6.94±4.90 | 南黄海(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 0.82±0.02 | 博滕海(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 2.12±0.07 | 博恩霍尔姆岛沿岸(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 9.32±3.52 | 英国北海(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 31.14±22.01 | 29.06±21.39 | 墨西哥湾(沉积物) | 文献[ | |
| 9.70±2.88 | 3.84±2.77 | 蒙特利湾(沉积物) | 文献[ | |
| 17.23±1.70 | 路易斯安那大陆架(沉积物) | 文献[ | ||
| 珊瑚代谢 /(mmol·cm-2·d-1) | -27.12±2.33 | 指形鹿角珊瑚 | 文献[ | |
| -16.60±0.70 | 美丽鹿角珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| -54 | 铁星珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| -0.38±1.26 | 板叶角蜂巢珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| 13.82 | 风信子鹿角珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| 0.53 | 丛生盔形珊瑚 | 文献[ | ||
| 层位 | 温度 | 盐度 | AOU | Chl a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表层 | -0.111 | -0.596* | 0.476* | 0.225 |
| 底层 | -0.088 | 0.200 | 0.826** | -0.069 |
表2 大澳湾表、底层海水中pCO2与环境因子的相关性(n=16)
Tab.2 Correlation between pCO2 and environmental factors in the surface and bottom waters of Daao Bay (n=16)
| 层位 | 温度 | 盐度 | AOU | Chl a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 表层 | -0.111 | -0.596* | 0.476* | 0.225 |
| 底层 | -0.088 | 0.200 | 0.826** | -0.069 |
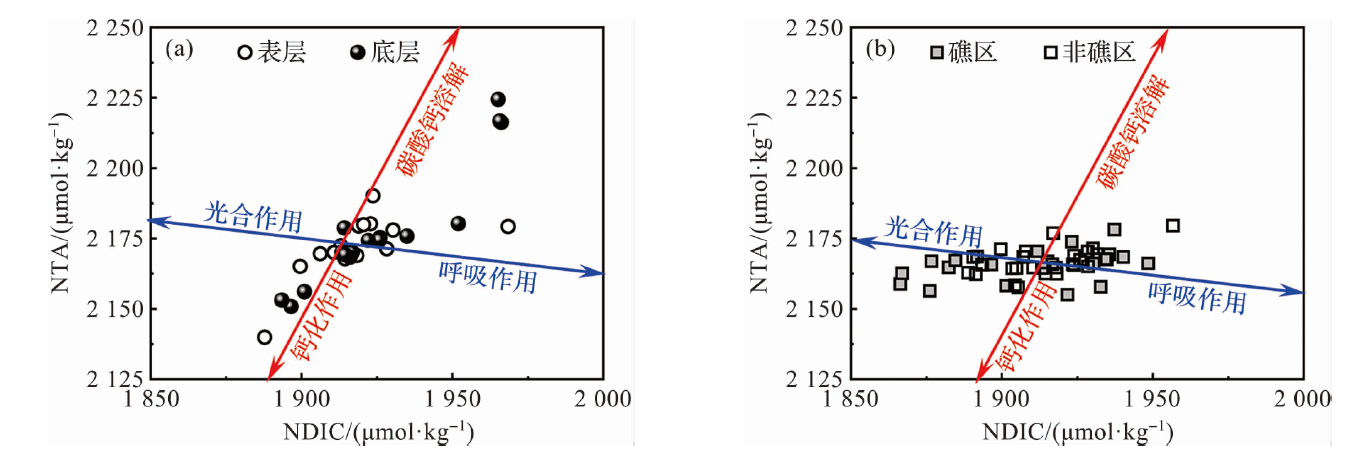
图9 不同调查站位(a)和24 h定点连续观测站位(b)海水中NTA和NDIC的关系 (红色线和蓝色线的交点为海水样本NTA和NDIC的平均值。)
Fig.9 The relationship between NTA and NDIC of seawater in different survey stations (a) and 24 h fixed-point continuous observation stations (b) (The intersection of the red and blue line is the average of NTA and NDIC for seawater samples.)
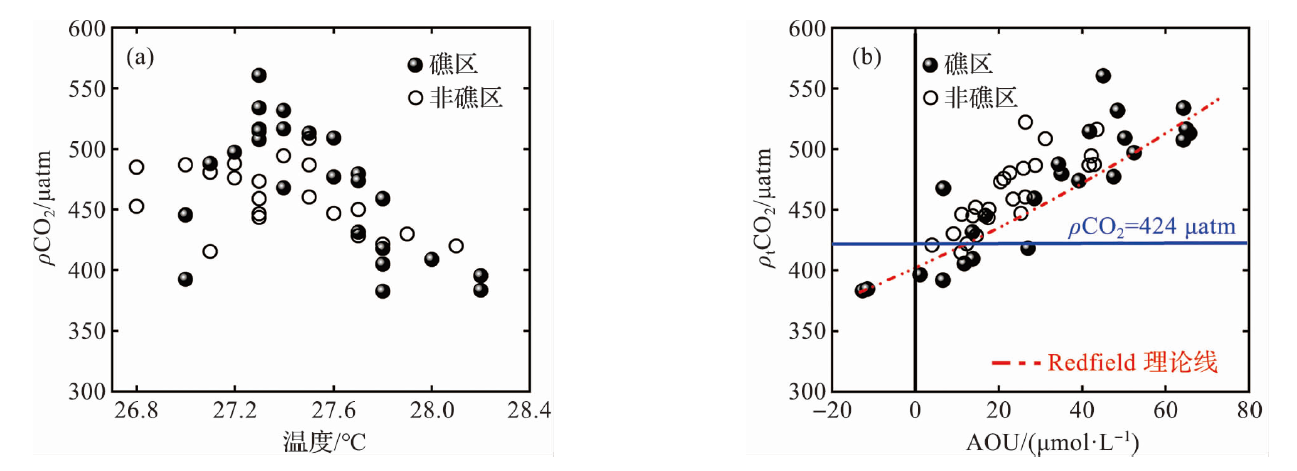
图10 24 h定点连续观测站位海水中pCO2与温度(a)和ptCO2与AOU(b)的关系
Fig.10 The relationship between pCO2 and temperature (a), ptCO2 and AOU (b) in seawater in the 24 h fixed-point continuous observation stations
| [1] |
张双, 祁第, 吴瀛旭, 等. 南大洋人为二氧化碳的吸收、分布、储存与输运研究进展[J]. 极地研究, 2024, 36(3):391-405.
DOI |
| ZHANG S, QI D, WU Y X, et al. Research and prospects of anthropogenic carbon dioxide uptake, distribution, storage and transport in the Southern Ocean[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2024, 36(3): 391-405. | |
| [2] |
SABINE C L, FEELY R A, GRUBER N, et al. The oceanic sink for anthropogenic CO2[J]. Science, 2004, 305(5682): 367-371.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | FRIEDLINGSTEIN P, O’SULLIVAN M, JONES M W, et al. Global carbon budget 2020[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2020, 12(4): 3269-3340. |
| [4] | SIEGENTHALER U, SARMIENTO J L. Atmospheric carbon dioxide and the ocean[J]. Nature, 1993, 365(6442): 119-125. |
| [5] | ORR J C, FABRY V J, AUMONT O, et al. Anthropogenic ocean acidification over the twenty-first century and its impact on calcifying organisms[J]. Nature, 2005, 437(7059): 681-686. |
| [6] | BATES N R, ASTOR Y M, TTHEW J, et al. A time-series view of changing ocean chemistry due to ocean uptake of anthropogenic CO2 and ocean acidification[J]. Oceanography, 2014, 27(1): 126-141. |
| [7] | LAUVSET S K, GRUBER N, LANDSCHÜTZER P, et al. Trends and drivers in global surface ocean pH over the past 3 decades[J]. Biogeosciences, 2015, 12(5): 1285-1298. |
| [8] | GATTUSO J P, FRANKIGNOULLE M, WOLLAST R. Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystems[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 1998, 29: 405-434. |
| [9] | BORGES A V. Do we have enough pieces of the jigsaw to integrate CO2 fluxes in the coastal ocean?[J]. Estuaries, 2005, 28(1): 3-27. |
| [10] | YANG B, GAO X L, ZHAO J M, et al. Massive shellfish farming might accelerate coastal acidification: A case study on carbonate system dynamics in a bay scallop (Argopecten irradians) farming area, North Yellow Sea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 798: 149214. |
| [11] | YANG B, ZHANG Z, CUI Z P, et al. Multiple factors driving carbonate system in subtropical coral community environments along Dapeng peninsula, South China Sea[J]. Atmosphere, 2023, 14(4): 688. |
| [12] | 李德望, 林华, 陈思杨, 等. 2017年春季长江口-东海连续体pCO2的空间分布特征及其控制因素[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(4):52-62. |
| LI D W, LIN H, CHEN S Y, et al. Distributions and controlling factors of pCO2 in the Changjiang(Yangtze River) Estuary-East China Sea continuum in spring of 2017[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2021, 39(4): 52-62. | |
| [13] | 杨旭锋, 于培松, 潘建明, 等. 2019年夏末长江口及其邻近海域走航pCO2变化及控制机制[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(4):63-72. |
| YANG X F, YU P S, PAN J M, et al. Spatial variation of underway surface pCO2 and its controls in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary and adjacent sea area in late summer of 2019[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2021, 39(4): 63-72. | |
| [14] |
许欣, 于培松, 蔡小霞, 等. 南海西部秋季海表pCO2分布与海-气CO2通量[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2016, 35(3):55-64.
DOI |
| XU X, YU P S, CAI X X, et al. Distributions of partial pressure of carbon dioxide and sea-air CO2 flux in the western South China Sea in autumn[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(3): 55-64. | |
| [15] | 谢勇琪, 蓝军南, 朱鸣, 等. 深圳大鹏湾海域水质状况调查分析[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2021, 39(11):118-123. |
| XIE Y Q, LAN J N, ZHU M, et al. Analysis of water quality investigation in Dapeng Bay of Shenzhen[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2021, 39(11): 118-123. | |
| [16] | 马方方, 冷科明, 周秋伶, 等. 近40年深圳大鹏湾海域赤潮发生规律及其演变机制分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2021, 40(2):263-271. |
| MA F F, LENG K M, ZHOU Q L, et al. Analysis on the occurrences and evolution mechanism of HABs in Dapeng bay, Shenzhen in the last 40 years[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2021, 40(2): 263-271. | |
| [17] | 贾春斌, 王佳美, 唐振朝. 深圳东部海域珊瑚群落分布特征[J]. 渔业研究, 2020, 42(6):590-597. |
| JIA C B, WANG J M, TANG Z Z. Distribution of coral communities in eastern sea area of Shenzhen[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2020, 42(6): 590-597. | |
| [18] | 黄小平, 岳维忠, 李颖虹, 等. 大鹏湾平洲岛附近海域生态环境特征及其演变过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2004, 23(5):72-80. |
| HUANG X P, YUE W Z, LI Y H, et al. Environmental characteristics and evolvement in sea area around Pingzhou island of Dapeng bay, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2004, 23(5): 72-80. | |
| [19] | 郭峰, 肖家光, 田鹏, 等. 大亚湾及大鹏半岛沿岸造礁石珊瑚现状与生态脆弱性评价[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2022, 41(4):568-582. |
| GUO F, XIAO J G, TIAN P, et al. Status of scleractinian corals in Daya Bay and along the coast of Dapeng Peninsula and ecological vulnerability assessment[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 568-582. | |
| [20] | DICKSON A, SABINE C L, CHRISTIAN J R. Guide to best practices for ocean CO2 measurements[M]. [S.l.]: PICES, 2007. |
| [21] | GRASSHOFF K, KREMLING K, EHRHARDT M. Methods of seawater analysis[M]. third edition. [S.l.]: Wiley-VCH, 1999: 632. |
| [22] | HAMME R C, EMERSON S R. The solubility of neon, nitrogen and argon in distilled water and seawater[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2004, 51(11): 1517-1528. |
| [23] | CADÉE G C, HEGEMAN J. Primary production of phytoplankton in the Dutch wadden sea[J]. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research, 1974, 8(2/3): 240-259. |
| [24] | LUEKER T J, DICKSON A G, KEELING C D. Ocean pCO2 calculated from dissolved inorganic carbon, alkalinity, and equations for K1 and K2: Validation based on laboratory measurements of CO2 in gas and seawater at equilibrium[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2000, 70(1/2/3): 105-119. |
| [25] | DICKSON A G. Standard potential of the reaction: AgCl(s)+$\frac{1}{2}$H2(g)=Ag(s)+HCl(aq), and the standard acidity constant of the ion $\mathrm{HSO}_4^{-}$ in synthetic sea water from 273.15 to 318.15 K[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 1990, 22: 113-127. |
| [26] | LEE K, KIM T W, BYRNE R H, et al. The universal ratio of boron to chlorinity for the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(6): 1801-1811. |
| [27] | SWEENEY C, GLOOR E, JACOBSON A R, et al. Constraining global air-sea gas exchange for CO2 with recent bomb14C measurements[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2007, 21(2): GB2015. |
| [28] | WANNINKHOF R. Relationship between wind speed and gas exchange over the ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1992, 97(C5): 7373-7382. |
| [29] |
HAN P, LI Y X, YANG X F, et al. Effects of aerobic respiration and nitrification on dissolved inorganic nitrogen and carbon dioxide in human-perturbed eastern Jiaozhou Bay, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2017, 124(1): 449-458.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | MURRELL M C, LEHRTER J C. Sediment and lower water column oxygen consumption in the seasonally hypoxic region of the Louisiana continental shelf[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2011, 34(5): 912-924. |
| [31] | BERELSON W M, MCMANUS J, SEVERMANN S, et al. Benthic fluxes from hypoxia-influenced Gulf of Mexico sediments: Impact on bottom water acidification[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2019, 209: 94-106. |
| [32] | YANG B, GAO X L, ZHAO J M, et al. Potential linkage between sedimentary oxygen consumption and benthic flux of biogenic elements in a coastal scallop farming area, North Yellow Sea[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 273: 129641. |
| [33] | REN J H, ZHU M X, WANG D Y, et al. Organic carbon mineralization pathways in the muddy sediments of the South Yellow Sea: Insights from steady-state modeling of porewater[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2022, 138: 105237. |
| [34] | WINOGRADOW A, PEMPKOWIAK J. Organic carbon burial rates in the Baltic Sea sediments[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 138: 27-36. |
| [35] | DE BORGER E, BRAECKMAN U, SOETAERT K. Rapid organic matter cycling in North Sea sediments[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2021, 214: 104327. |
| [36] | BERELSON W, MCMANUS J, COALE K, et al. A time series of benthic flux measurements from Monterey Bay, CA[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2003, 23(5): 457-481. |
| [37] | BERELSON W M, MCMANUS J, SEVERMANN S, et al. Benthic flux of oxygen and nutrients across Oregon/California shelf sediments[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2013, 55: 66-75. |
| [38] | NISHIDA K, ISHIKAWA K, IGUCHI A, et al. Skeletal oxygen and carbon isotope compositions of Acropora coral primary polyps experimentally cultured at different temperatures[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(7): 2840-2849. |
| [39] | CHAN W Y, EGGINS S M. Calcification responses to diurnal variation in seawater carbonate chemistry by the coral Acropora formosa[J]. Coral Reefs, 2017, 36(3): 763-772. |
| [40] | KUFFNER I B, HICKEY T D, MORRISON J M. Calcifi-cation rates of the massive coral Siderastrea siderea and crustose coralline algae along the Florida Keys (USA) outer-reef tract[J]. Coral Reefs, 2013, 32(4): 987-997. |
| [41] |
郭亚娟, 周伟华, 袁翔城, 等. 两种造礁石珊瑚对海水酸化和溶解有机碳加富的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(1):57-63.
DOI |
| GUO Y J, ZHOU W H, YUAN X C, et al. Responses of two species of reef-building corals to acidification and dissolved organic carbon enrichment[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(1): 57-63. | |
| [42] | 赵贺, 张峻菱, 王浩, 等. 两种造礁石珊瑚固碳能力初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3):146-154. |
| ZHAO H, ZHANG J L, WANG H, et al. Preliminary study on carbon sequestration capacity of two hermatypic corals[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 146-154. | |
| [43] | XUE L, CAI W J, HU X P, et al. Sea surface carbon dioxide at the Georgia time series site (2006-2007): Air-sea flux and controlling processes[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2016, 140: 14-26. |
| [44] | XUE L, XUE M, ZHANG L J, et al. Surface partial pressure of CO2 and air-sea exchange in the northern Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2012, 105: 194-206. |
| [45] | CAI W J, DAI M H, WANG Y C. Air-sea exchange of carbon dioxide in ocean margins: A province-based synthesis[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2006, 33(12): L12603. |
| [46] | ZHAI W D, CHEN J F, JIN H Y, et al. Spring carbonate chemistry dynamics of surface waters in the northern East China Sea: Water mixing, biological uptake of CO2, and chemical buffering capacity[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2014, 119(9): 5638-5653. |
| [47] | 邱爽, 龚信宝, 张继红, 等. 桑沟湾养殖区春季pCO2分布特征及影响机制[J]. 渔业科学进展, 2013, 34(1):31-37. |
| QIU S, GONG X B, ZHANG J H, et al. Distribution and affecting factors of pCO2 in aquaculture areas of Sanggou Bay during spring[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 2013, 34(1): 31-37. | |
| [48] | 严宏强, 余克服, 施祺, 等. 南海珊瑚礁夏季是大气CO2的源[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(6):414-422. |
| YAN H Q, YU K F, SHI Q, et al. Coral reefs in the South China Sea are the source of atmospheric CO2 in summer[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(6): 414-422. | |
| [49] | JIANG Z P, LÜ J C, LI Q L, et al. Tidal-driven submarine groundwater discharge and its influences on the carbonate system of a coastal coral reef in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2021,126: e2021JC017203. |
| [50] | 张志荣. 东海近岸水体CO2变化特征及调控机制研究:基于浮标观测[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG Z R. Study on the variation characteristics and regulation mechanism of CO2 in the coastal waters of the East China Sea: Based on buoy observation[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2018. | |
| [51] | 许欣, 王翔, 胡慧娜, 等. 北部湾东北部春、夏季表层海水CO2分压的24 h变化及其调控机制研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2023, 45(3):14-26. |
| XU X, WANG X, HU H N, et al. Hourly variations of partial pressure of CO2 in surface sea water and its controlling mechanisms in the northeastern Beibu Gulf in spring and summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2023, 45(3): 14-26. | |
| [52] | DAI M H, LU Z M, ZHAI W D, et al. Diurnal variations of surface seawater pCO2 in contrasting coastal environments[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2009, 54(3): 735-745. |
| [53] | REDFIELD A C. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment[J]. American Scientist, 1958, 46(3): 205-221. |
| [54] | 杨威, 郭香会, 曹知勉, 等. 南海西北部海域夏季碳酸盐系统动态变化特征及调控机制:沿岸上升流、河流冲淡水及地下水输入的共同作用[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2022, 52(12):2373-2390. |
| YANG W, GUO X H, CAO Z M, et al. Carbonate dynamics in a tropical coastal system in the South China Sea featuring upwelling, river plumes and submarine groundwater discharge[J]. Scientia Sinica: Terrae, 2022, 52(12): 2373-2390. | |
| [55] | WRIGHT R M, STRADER M E, GENUISE H M, et al. Effects of thermal stress on amount, composition, and antibacterial properties of coral mucus[J]. PeerJ, 2019, 7: e6849. |
| [1] | 王洋, 全鑫, 庄雅, 赵化德, 苏剑钟. 热带红树林河口海-气CO2通量季节变化及控制因素——以海南东寨港为例[J]. 海洋学研究, 2025, 43(1): 79-89. |
| [2] | 周学杭, 张洪海, 马昕, 陈朝晖. 基于浮标观测的春季青岛近岸海水pCO2变化及海-气CO2通量研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2023, 41(3): 14-21. |
| [3] | 刘婷宇, 白雁, 朱伯仲, 李腾, 龚芳. 高空间分辨率海表CO2分压的卫星遥感反演算法:机器学习在秋季象山港的应用[J]. 海洋学研究, 2023, 41(1): 82-95. |
| [4] | 苗燕熠, 王斌, 李德望, 金海燕, 江志兵, 马晓, 于培松, 陈建芳, 王俊洋. 大风事件对长江口及邻近海域海-气CO2通量的影响[J]. 海洋学研究, 2020, 38(1): 42-49. |
| [5] | 李熠, 何海伦, 陈大可. 基于海水环境和气象参数经验公式估算的东海海-气CO2通量[J]. 海洋学研究, 2012, 30(3): 30-40. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||