海洋学研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 75-87.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2024.03.006
基于BP神经网络模型的哨兵SAR反演风速偏差校正
倪晗玥1,2( ), 董昌明3, 刘振波3, 杨劲松1,2,*(
), 董昌明3, 刘振波3, 杨劲松1,2,*( ), 李晓辉2, 任林2
), 李晓辉2, 任林2
- 1.上海交通大学 海洋学院,上海 200240
2.自然资源部第二海洋研究所 卫星海洋环境动力学国家重点实验室,浙江 杭州 310012
3.南京信息工程大学 海洋科学学院,江苏 南京 210044
-
收稿日期:2023-12-26修回日期:2024-03-26出版日期:2024-09-15发布日期:2024-11-25 -
通讯作者:*杨劲松(1969—),男,研究员,主要从事海洋微波遥感与卫星海洋学研究,E-mail:jsyang@sio.org.cn。 -
作者简介:倪晗玥(2000—),女,江苏省苏州市人,主要从事海洋微波遥感研究,E-mail:nihanyue001126@163.com。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42306200);国家自然科学基金项目(42306216);国家重点研发计划项目(2022YFC3103101)
Calibration of Sentinel-1 SAR retrieved wind speed based on BP neural network model
NI Hanyue1,2( ), DONG Changming3, LIU Zhenbo3, YANG Jingsong1,2,*(
), DONG Changming3, LIU Zhenbo3, YANG Jingsong1,2,*( ), LI Xiaohui2, REN Lin2
), LI Xiaohui2, REN Lin2
- 1. School of Oceanography, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2. Second Institute of Oceanography, MNR, State Key Laboratory of Satellite Ocean Environment Dynamics, Hangzhou 310012, China
3. School of Marine Sciences, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2023-12-26Revised:2024-03-26Online:2024-09-15Published:2024-11-25
摘要:
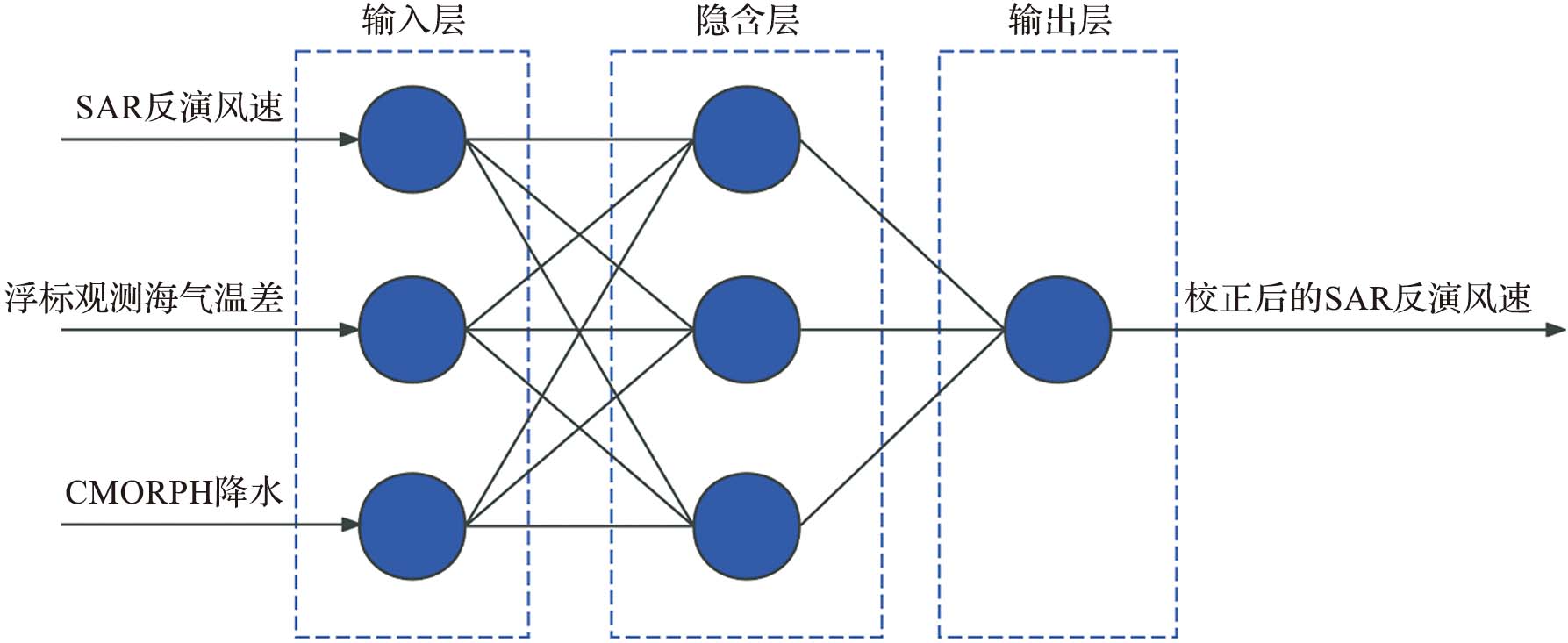
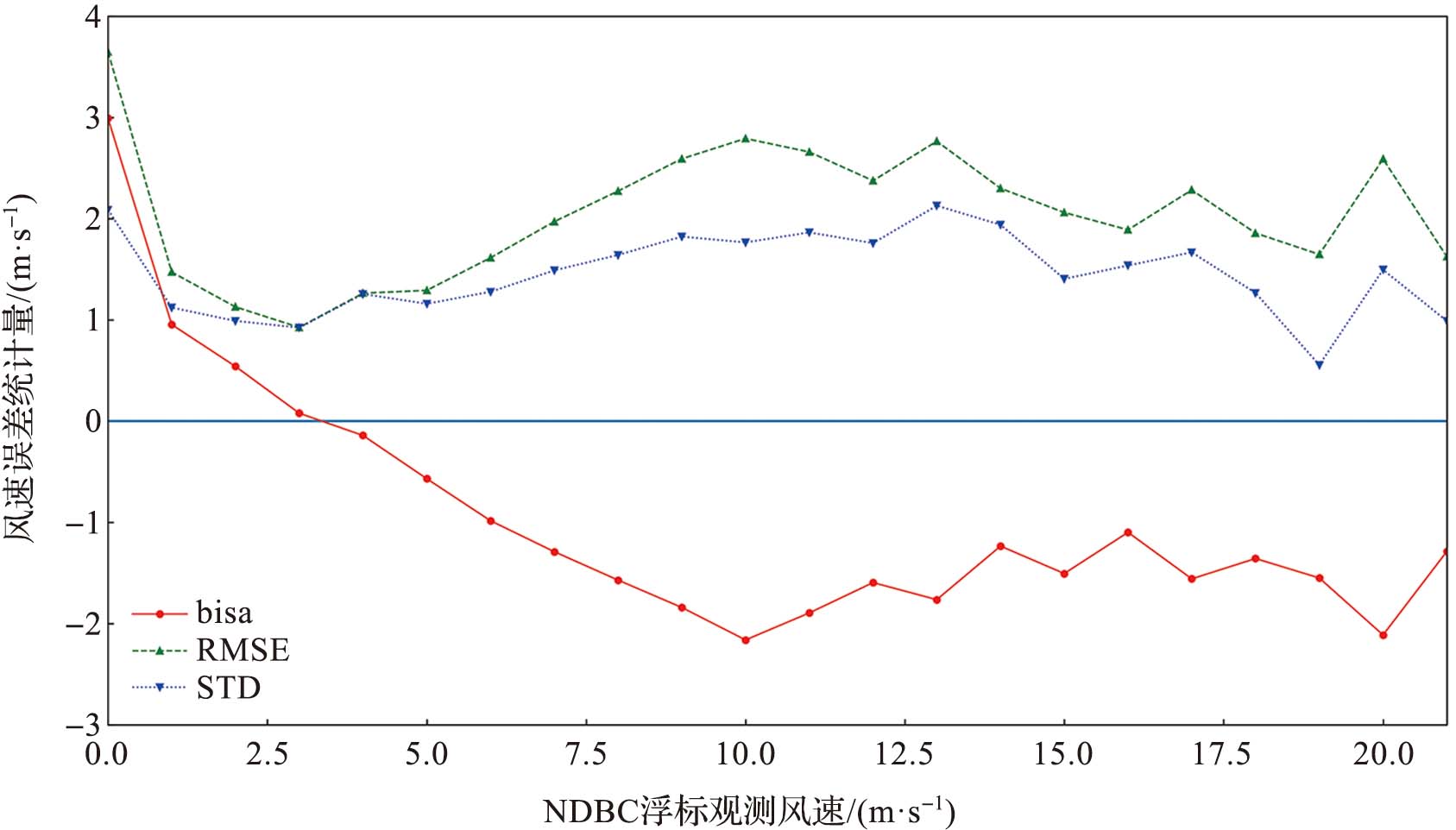
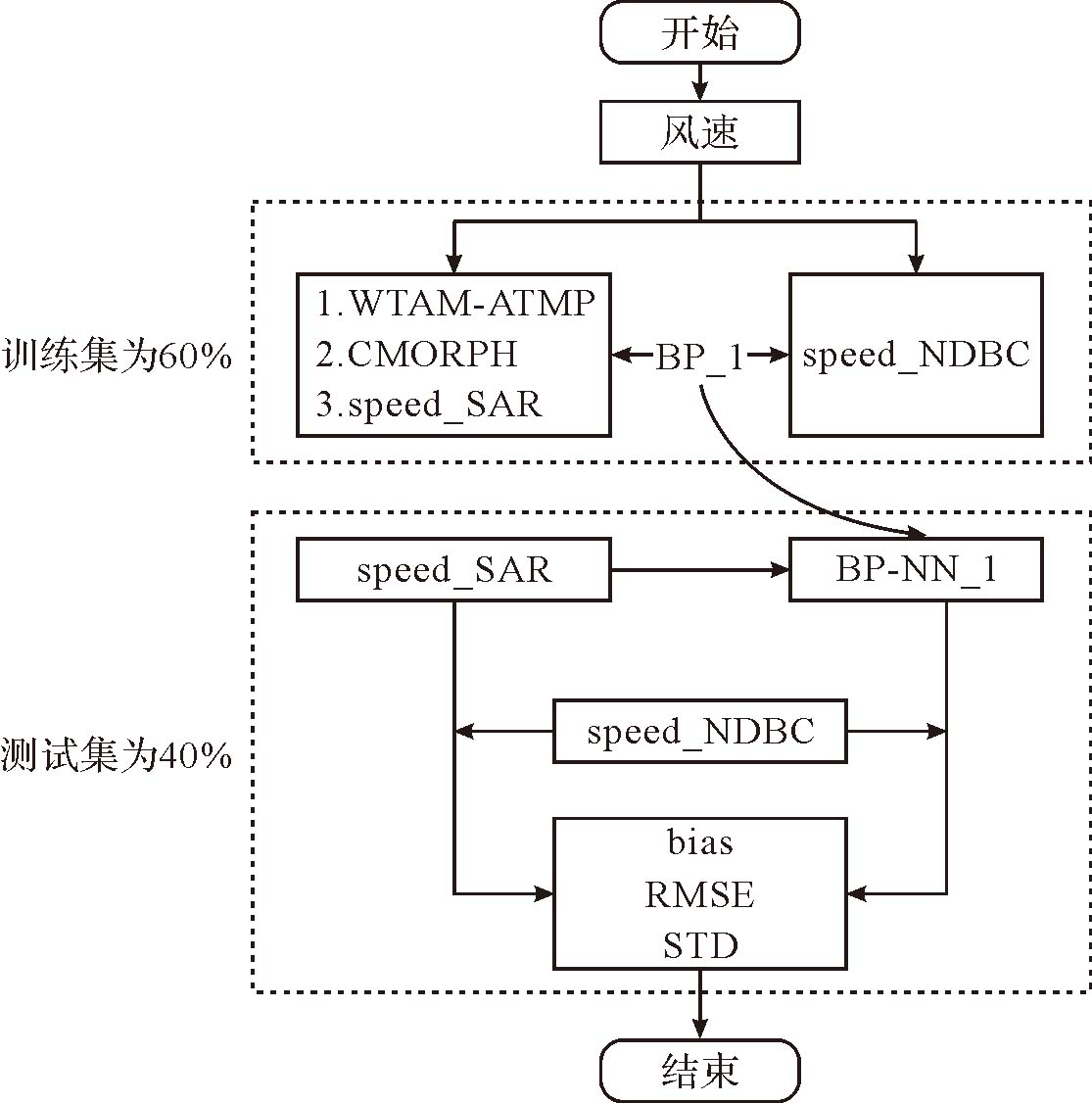
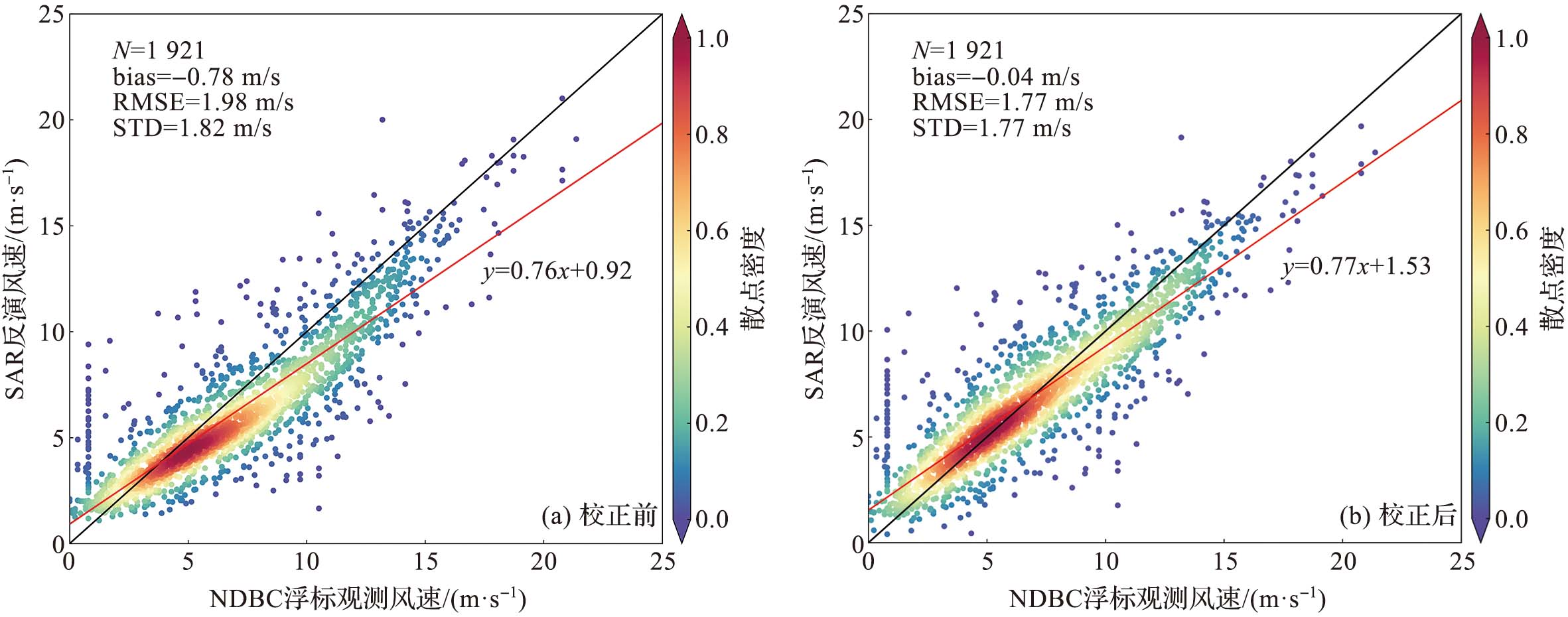
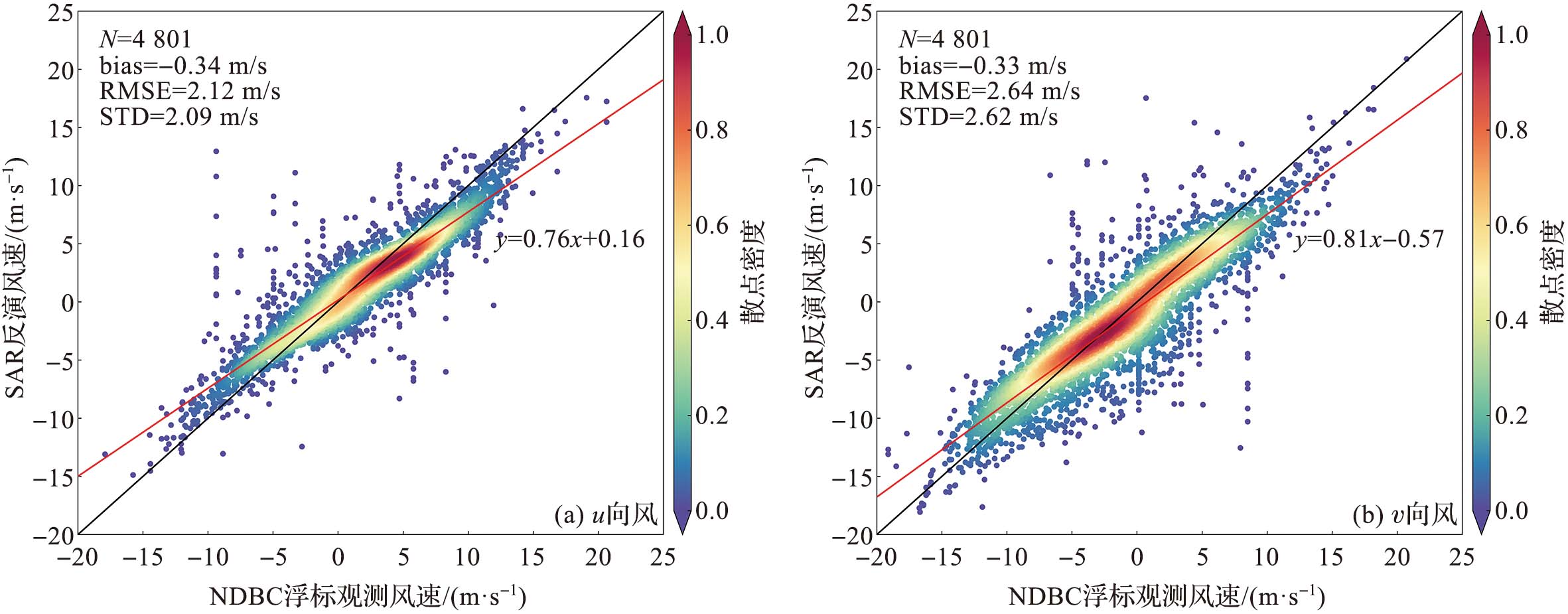
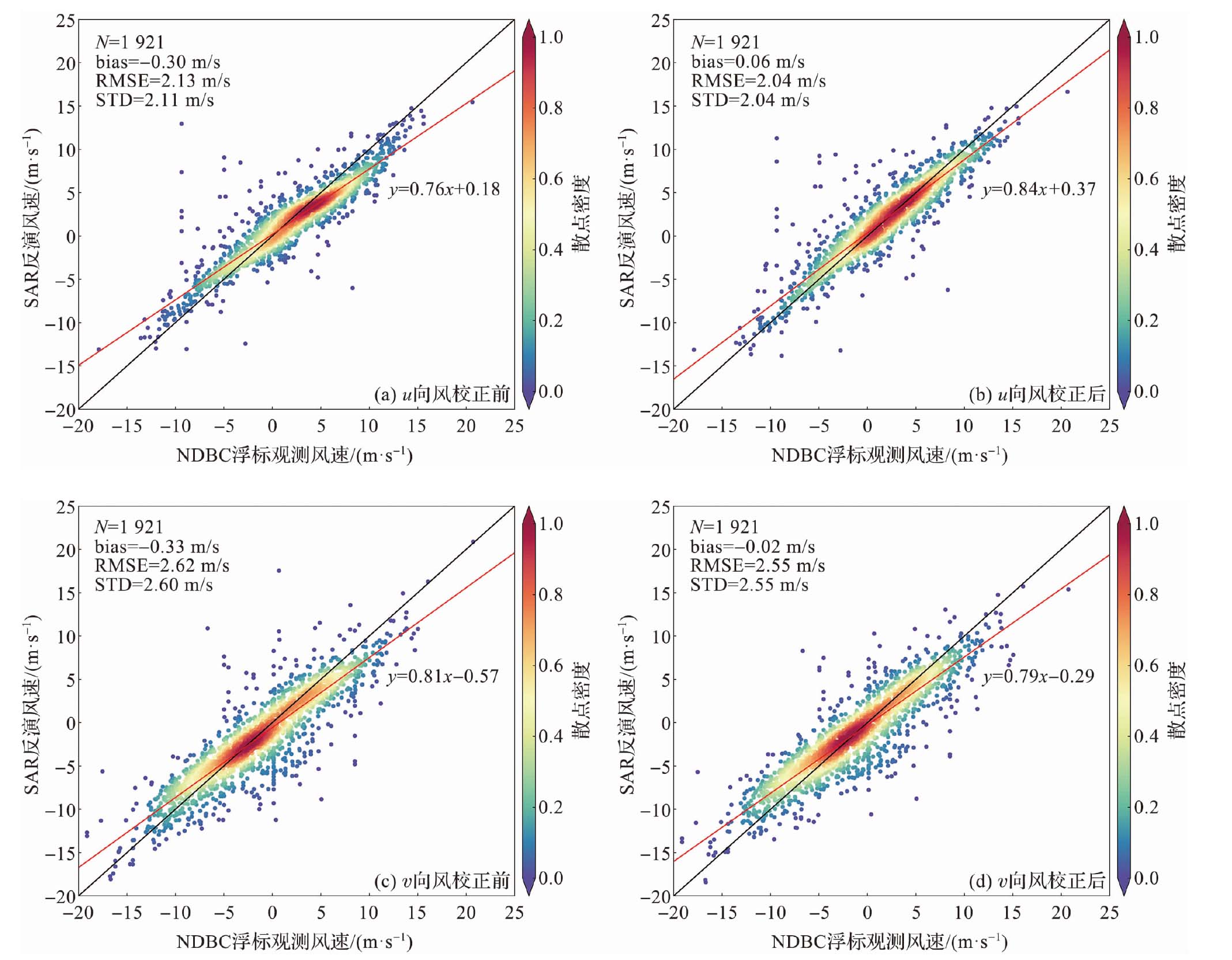
该文基于美国国家浮标资料中心(National Data Buoy Center,NDBC) 浮标观测数据对哨兵一号搭载的合成孔径雷达(synthetic aperture radar,SAR) 反演风速数据进行精度分析,并利用BP神经网络 (back propagation neural network) 对SAR反演风速的偏差进行校正;同时针对环境要素、BP神经网络训练输入的样本量以及神经网络结构参数设计了敏感性试验;最后将SAR标量风场数据转换为用u、v矢量表示的风场数据,并对u向风和v向风分别进行了精度分析和校正。实验结果表明:SAR反演风速相较于浮标观测数据出现了低估现象;经过BP神经网络校正后,SAR反演风速数据的精度得到了改善,风速的平均偏差绝对值从0.78 m/s下降到0.04 m/s,均方根误差从1.98 m/s下降到了1.77 m/s;敏感性试验表明输入质量较差的环境要素数据时BP神经网络的校正效果有所下降,而增加训练集样本量能改善校正效果;将标量风场数据转换为u、v矢量风场数据后的校正结果也显示BP神经网络具有较好的校正效果。
中图分类号:
引用本文
倪晗玥, 董昌明, 刘振波, 杨劲松, 李晓辉, 任林. 基于BP神经网络模型的哨兵SAR反演风速偏差校正[J]. 海洋学研究, 2024, 42(3): 75-87.
NI Hanyue, DONG Changming, LIU Zhenbo, YANG Jingsong, LI Xiaohui, REN Lin. Calibration of Sentinel-1 SAR retrieved wind speed based on BP neural network model[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2024, 42(3): 75-87.
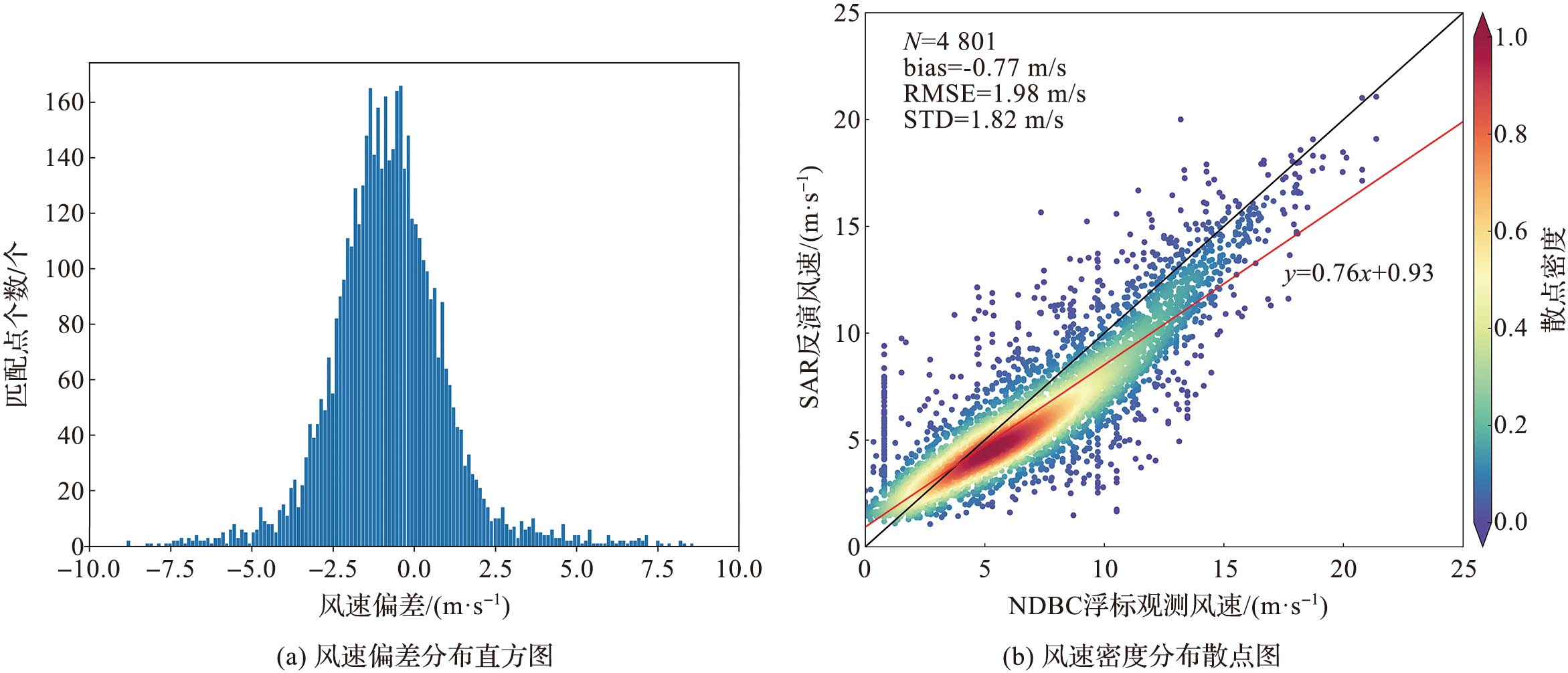
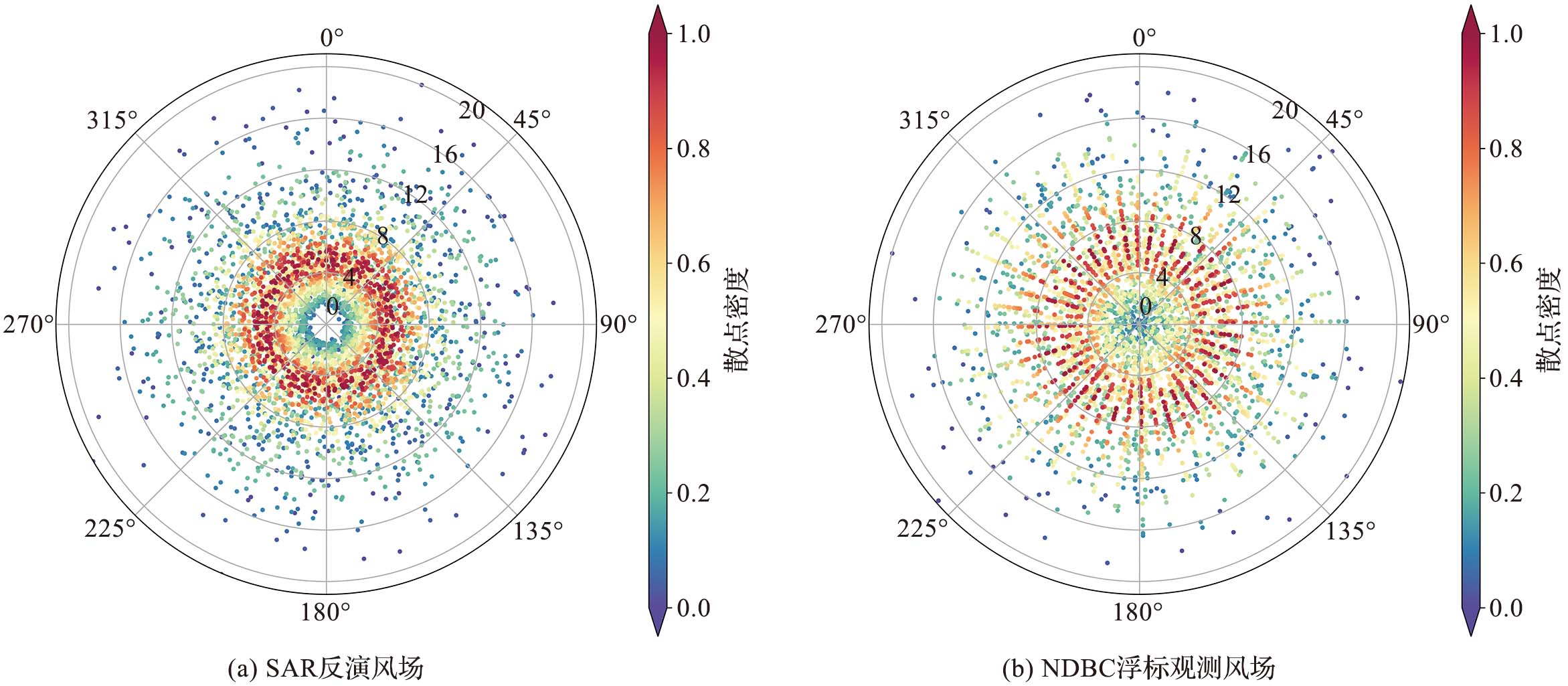
图2 SAR反演风速精度分析 (图b中的黑线为1∶1对角线,红线表示拟合后的一次函数。后文同此。)
Fig.2 Accuracy analysis of SAR-derived wind speed (In fig.b, the black line is a 1∶1 diagonal line, and the red line is the fitted linear function, similarly hereinafter. )
| 统计量 | 同时输入降水数据 和海气温差数据 | 只输入降 水数据 | 只输入海气 温差数据 |
|---|---|---|---|
| bias/(m·s-1) | -0.04 | -0.05 | -0.04 |
| RMSE/(m·s-1) | 1.77 | 1.79 | 1.77 |
| STD/(m·s-1) | 1.77 | 1.79 | 1.77 |
表1 环境要素对风速校正的敏感性试验结果
Tab.1 Sensitivity experiment results of environmental factors on wind speed calibration
| 统计量 | 同时输入降水数据 和海气温差数据 | 只输入降 水数据 | 只输入海气 温差数据 |
|---|---|---|---|
| bias/(m·s-1) | -0.04 | -0.05 | -0.04 |
| RMSE/(m·s-1) | 1.77 | 1.79 | 1.77 |
| STD/(m·s-1) | 1.77 | 1.79 | 1.77 |
| 实验模型 | bias/(m·s-1) | RMSE/(m·s-1) | STD/(m·s-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原BP神经网络模型 | -0.04 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| 参数调整后的BP 神经网络模型 | 训练集数量为70% | 0.00 | 1.80 | 1.80 |
| 训练集数量为50% | 0.12 | 1.79 | 1.78 | |
| 训练批次数量为2 000 | -0.05 | 1.76 | 1.76 | |
| 训练批次数量为2 500 | -0.05 | 1.76 | 1.75 | |
| 隐含层神经元数量为50 | -0.04 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| 隐含层神经元数量为150 | -0.05 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| 学习率为0.01 | -0.05 | 1.77 | 1.76 | |
| 学习率为0.001 | -0.04 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
表2 BP神经网络参数对风速校正的敏感性试验结果
Tab.2 Sensitivity experiment results of BP neural network parameters on wind speed calibration
| 实验模型 | bias/(m·s-1) | RMSE/(m·s-1) | STD/(m·s-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原BP神经网络模型 | -0.04 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| 参数调整后的BP 神经网络模型 | 训练集数量为70% | 0.00 | 1.80 | 1.80 |
| 训练集数量为50% | 0.12 | 1.79 | 1.78 | |
| 训练批次数量为2 000 | -0.05 | 1.76 | 1.76 | |
| 训练批次数量为2 500 | -0.05 | 1.76 | 1.75 | |
| 隐含层神经元数量为50 | -0.04 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| 隐含层神经元数量为150 | -0.05 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| 学习率为0.01 | -0.05 | 1.77 | 1.76 | |
| 学习率为0.001 | -0.04 | 1.77 | 1.77 | |
| [1] | 蒋兴伟, 林明森, 张有广. 中国海洋卫星及应用进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(5):1185-1198. |
| JIANG X W, LIN M S, ZHANG Y G. Progress and prospect of Chinese ocean satellites[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(5): 1185-1198. | |
| [2] | 方贺, 杨劲松, 樊高峰, 等. 组合表面Bragg散射模型共极化SAR海表面风速反演[J]. 遥感学报, 2022, 26(6):1274-1287. |
| FANG H, YANG J S, FAN G F, et al. Ocean surface wind speed retrieve from co-polarized SAR using composite surface Bragg scattering model[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2022, 26(6): 1274-1287. | |
| [3] | 蔡树群, 张文静, 王盛安. 海洋环境观测技术研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2007, 26(3):76-81. |
| CAI S Q, ZHANG W J, WANG S A. An advance in marine environment observation technology[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2007, 26(3): 76-81. | |
| [4] | 徐文, 鄢社锋, 季飞, 等. 海洋信息获取、传输、处理及融合前沿研究评述[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2016, 46(8):1053-1085. |
| XU W, YAN S F, JI F, et al. Marine information gathering, transmission, processing, and fusion: Current status and future trends[J]. Scientia Sinica: Informationis, 2016, 46(8): 1053-1085. | |
| [5] | 范开国, 徐青, 徐东洋, 等. 星载SAR海面风场遥感研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(5):1807-1817. |
| FAN K G, XU Q, XU D Y, et al. Review of remote sensing of sea surface wind field by space-borne SAR[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(5): 1807-1817. | |
| [6] | 邓云凯, 赵凤军, 王宇. 星载SAR技术的发展趋势及应用浅析[J]. 雷达学报, 2012, 1(1):1-10. |
| DENG Y K, ZHAO F J, WANG Y. Brief analysis on the development and application of spaceborne SAR[J]. Journal of Radars, 2012, 1(1): 1-10. | |
| [7] | 张康宇. 基于C波段SAR的海面风场反演方法与近海风能资源评估[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. |
| ZHANG K Y. Sea surface wind field retrieval and offshore wind energy resource assessment based on C-band SAR data[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019. | |
| [8] | 张璇. C波段全极化SAR图像海面风场反演研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG X. Research of ocean wind retrival from C-band quad-polarization SAR images[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2018. | |
| [9] | 欧阳伦曦, 李新情, 惠凤鸣, 等. 哨兵卫星Sentinel-1A数据特性及应用潜力分析[J]. 极地研究, 2017, 29(2):286-295. |
| OU-YANG L X, LI X Q, HUI F M, et al. Sentinel-1A data products’ characteristics and the potential applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Polar Research, 2017, 29(2): 286-295. | |
| [10] | 朱良, 郭巍, 禹卫东. 合成孔径雷达卫星发展历程及趋势分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2009, 31(4):5-10. |
| ZHU L, GUO W, YU W D. Analysis of SAR satellite development history and tendency[J]. Modern Radar, 2009, 31(4): 5-10. | |
| [11] | 孙佳. 国外合成孔径雷达卫星发展趋势分析[J]. 装备指挥技术学院学报, 2007, 18(1):67-70. |
| SUN J. Analysis of the SAR satellite development tendency in the world[J]. Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command & Technology, 2007, 18(1): 67-70. | |
| [12] | LIN H, XU Q, ZHENG Q A. An overview on SAR measurements of sea surface wind[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2008, 18(8): 913-919. |
| [13] | FREILICH M H, DUNBAR R S. The accuracy of the NSCAT 1 vector winds: Comparisons with National Data Buoy Center buoys[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1999, 104(C5): 11231-11246. |
| [14] | WAN Y, GUO S, LI L G, et al. Data quality evaluation of Sentinel-1 and GF-3 SAR for wind field inversion[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): 3723. |
| [15] | PENSIERI S, BOZZANO R, SCHIANO M E. Comparison between QuikSCAT and buoy wind data in the Ligurian Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2010, 81(4): 286-296. |
| [16] | 代彭坤. 基于Sentinel-1的SAR台风风场反演研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2018. |
| DAI P K. Research of retrieving typhoon wind field based on Sentinel-1 SAR images[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2018. | |
| [17] | 许素芹, 李婷婷, 陈捷, 等. 海洋温度锋区后向散射系数仿真与特性研究[J]. 计算机仿真, 2019, 36(10):214-218,297. |
| XU S Q, LI T T, CHEN J, et al. Research and simulation of backscattering coefficient characteristic across ocean thermal fronts[J]. Computer Simulation, 2019, 36(10): 214-218, 297. | |
| [18] | 丁赟. 风浪状态对海面风应力的影响[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2005. |
| DING Y. The influence of wind sea state on wind stress[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2005. | |
| [19] | 殷实. 西北太平洋海面粗糙度分布与变化的初步研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009. |
| YIN S. Temporal and spatial variation of the sea surface roughness over the northwest Pacific Ocean[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009. | |
| [20] | 余水, 杨劲松, 贺双颜, 等. 降雨对SAR风场反演的影响及校正[J]. 海洋学报, 2017, 39(9):40-50. |
| YU S, YANG J S, HE S Y, et al. The correction of rain effect on SAR wind field retrieval[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2017, 39(9): 40-50. | |
| [21] | BENTAMY A, GRODSKY S A, CARTON J A, et al. Matching ASCAT and QuikSCAT winds[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2012, 117: C02011. |
| [22] | MONALDO F, JACKSON C, PICHEL W, et al. Early validation of operational SAR wind retrievals from Sentinel-1A[C]//2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), July 26-31, 2015, Milan, Italy. IEEE, 2015: 1223-1226. |
| [23] | 徐天真, 徐静琦, 楼顺里. 海面风垂直分布的计算方法[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1988, 10(4):1-6. |
| XU T Z, XU J Q, LOU S L. A method for calculating the wind variation with height in the marine atmospheric surface layer[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 1988, 10(4): 1-6. | |
| [24] | 陈永利, 赵永平, 张必成, 等. 海上不同高度风速换算关系的研究[J]. 海洋科学, 1989, 13(3):27-31. |
| CHEN Y L, ZHAO Y P, ZHANG B C, et al. The study of the relations of wind velocity at different heights over the sea[J]. Marine Sciences, 1989, 13(3): 27-31. | |
| [25] | ATLAS R, BUSALACCHI A J, GHIL M, et al. Global surface wind and flux fields from model assimilation of Seasat data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1987, 92(C6): 6477-6487. |
| [26] | LIU W T, KATSAROS K B, BUSINGER J A. Bulk parameterization of air-sea exchanges of heat and water vapor including the molecular constraints at the interface[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1979, 36(9): 1722-1735. |
| [27] | JOHNSON H K. Simple expressions for correcting wind speed data for elevation[J]. Coastal Engineering, 1999, 36(3): 263-269. |
| [28] | LIU W T, TANG W. Equivalent neutral winds[R]. Pasadena, CA: Jet Propulsion Laboratory, 1996. |
| [29] | FAIRALL C W, BRADLEY E F, HARE J E, et al. Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes: Updates and verification for the COARE algorithm[J]. Journal of Climate, 2003, 16(4): 571-591. |
| [30] |
陈克海, 解学通, 张金兰, 等. HY-2B卫星散射计海面风场产品质量分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(6):30-40.
DOI |
|
CHEN K H, XIE X T, ZHANG J L, et al. Accuracy analysis of the retrieved wind from HY-2B scatterometer[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 30-40.
DOI |
|
| [31] | DINKU T, RUIZ F, CONNOR S J, et al. Validation and intercomparison of satellite rainfall estimates over Colombia[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2010, 49(5): 1004-1014. |
| [32] | JAMANDRE C A, NARISMA G T. Spatio-temporal validation of satellite-based rainfall estimates in the Philippines[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2013, 122: 599-608. |
| [33] | SALIO P, HOBOUCHIAN M P, GARCÍA SKABAR Y, et al. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates over southern South America using a dense rain gauge network[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2015, 163: 146-161. |
| [34] | XING J Y, SHI J C, LEI Y H, et al. Evaluation of HY-2A scatterometer wind vectors using data from buoys, ERA-interim and ASCAT during 2012-2014[J]. Remote Sensing, 2016, 8(5): 390. |
| [35] |
朱金台, 董晓龙, 云日升. 利用浮标和NWP风场对HY-2散射计联合定标验证[J]. 电子学报, 2015, 43(11):2237-2242.
DOI |
| ZHU J T, DONG X L, YUN R S. Calibration and validation of HY-2 scatterometer using NWP and buoy data[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2015, 43(11): 2237-2242. | |
| [36] |
孙乾洋, 周利, 丁仕风, 等. 基于人工神经网络的极地船舶冰阻力预报方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2024, 58(2):156-165.
DOI |
| SUN Q Y, ZHOU L, DING S F, et al. An artificial neural network-based method for prediction of ice resistance of polar ships[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2024, 58(2): 156-165. | |
| [37] | 王煦莹, 沈红波, 徐兴周. 基于人工神经网络的金融信息系统风险评价[J]. 信息安全研究, 2022, 8(11):1055-1060. |
| WANG X Y, SHEN H B, XU X Z. Financial information system risk assessment based on artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Information Security Research, 2022, 8(11): 1055-1060. | |
| [38] | 郭晓萌, 方秀琴, 杨露露, 等. 基于人工神经网络的西辽河流域根区土壤湿度估算[J]. 自然资源遥感, 2023, 35(2):193-201. |
| GUO X M, FANG X Q, YANG L L, et al. Artificial neural network-based estimation of root zone soil moisture in the western Liaohe Rriver Basin[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2023, 35(2): 193-201. | |
| [39] | 刘志丰, 丁锋. 基于人工神经网络的沿海风速多步预测研究[J]. 气象科技, 2022, 50(6):851-858. |
| LIU Z F, DING F. Research on application of artificial neural network for sea surface wind speed forecasting[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2022, 50(6): 851-858. | |
| [40] | 蒋晨凯, 章四龙. 基于贝叶斯优化与人工神经网络的秦淮河流域水位预报[J]. 水电能源科学, 2022, 40(9):48-51,60. |
| JIANG C K, ZHANG S L. Water level forecasting of Qinhuaihe River Basin based on Bayesian optimization and artificial neural network[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2022, 40(9): 48-51, 60. | |
| [41] | 曹若馨, 张可欣, 曾维华, 等. 基于BP神经网络的水环境承载力预警研究:以北运河为例[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(5):2005-2017. |
| CAO R X, ZHANG K X, ZENG W H, et al. Research on the early-warning method of water environment carrying capacity based on BP neural network: A case study of Beiyunhe River Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(5): 2005-2017. | |
| [42] | 张秀菊, 王柳林, 李秀平, 等. 基于BP神经网络的潇河流域水质预测[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2021, 32(5):19-26. |
| ZHANG X J, WANG L L, LI X P, et al. Water quality prediction of the Xiaohe River Basin based on BP neural network model[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Water Engineering, 2021, 32(5): 19-26. | |
| [43] | 安慧, 范历娟, 吴海林, 等. 基于BP神经网络的淮河流域水生态足迹分析与预测[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2021, 30(5):1076-1087. |
| AN H, FAN L J, WU H L, et al. Analysis and prediction of water ecological footprint of Huaihe River Basin based on BP neural network[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2021, 30(5): 1076-1087. |
| [1] | 张勇勇. 基于GF5-AHSI遥感数据的横沙浅海水深反演[J]. 海洋学研究, 2022, 40(2): 93-101. |
| [2] | 胡昊, 许冬, 龙江平, 周勐佳, 唐博, 金路. 北部湾海底沉积物稀土元素与影响因子关系的BP神经网络定量分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2016, 34(1): 18-26. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||