Journal of Marine Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 69-78.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2025.01.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of the variation characteristics of the sea level in Zhoushan and the adjacent East China Sea from 1993 to 2021
JIN Jie( ), CHEN Yujie, YAO Yongheng, ZHANG Siyuan, HU Zhentao, DING Mengrong, JIA Bin*(
), CHEN Yujie, YAO Yongheng, ZHANG Siyuan, HU Zhentao, DING Mengrong, JIA Bin*( )
)
- College of Marine Science and Technology, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan 316022, China
-
Received:2024-05-09Revised:2024-10-14Online:2025-03-15Published:2025-05-30 -
Contact:JIA Bin
CLC Number:
Cite this article
JIN Jie, CHEN Yujie, YAO Yongheng, ZHANG Siyuan, HU Zhentao, DING Mengrong, JIA Bin. Analysis of the variation characteristics of the sea level in Zhoushan and the adjacent East China Sea from 1993 to 2021[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2025, 43(1): 69-78.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://hyxyj.sio.org.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2025.01.007
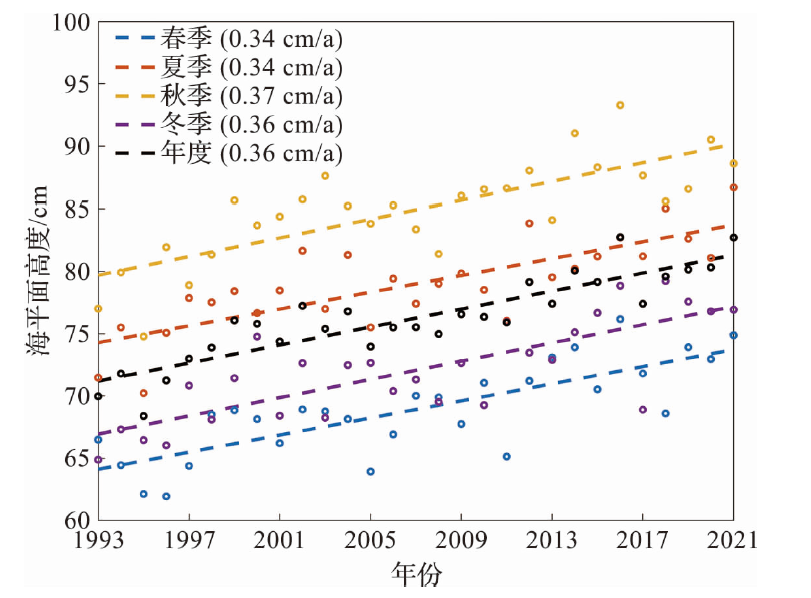
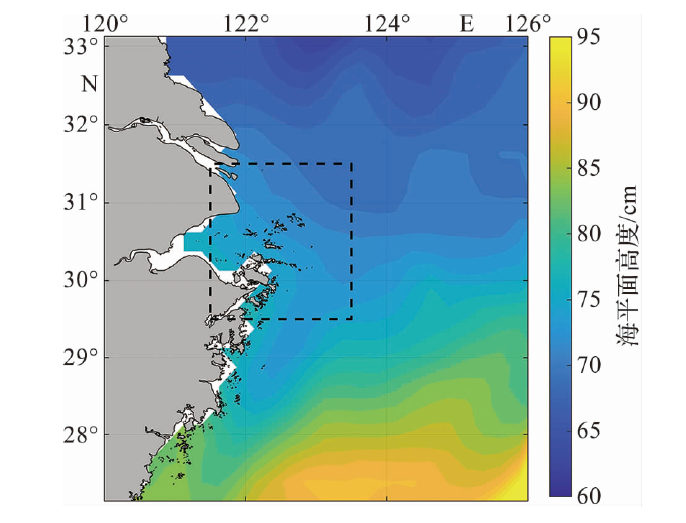
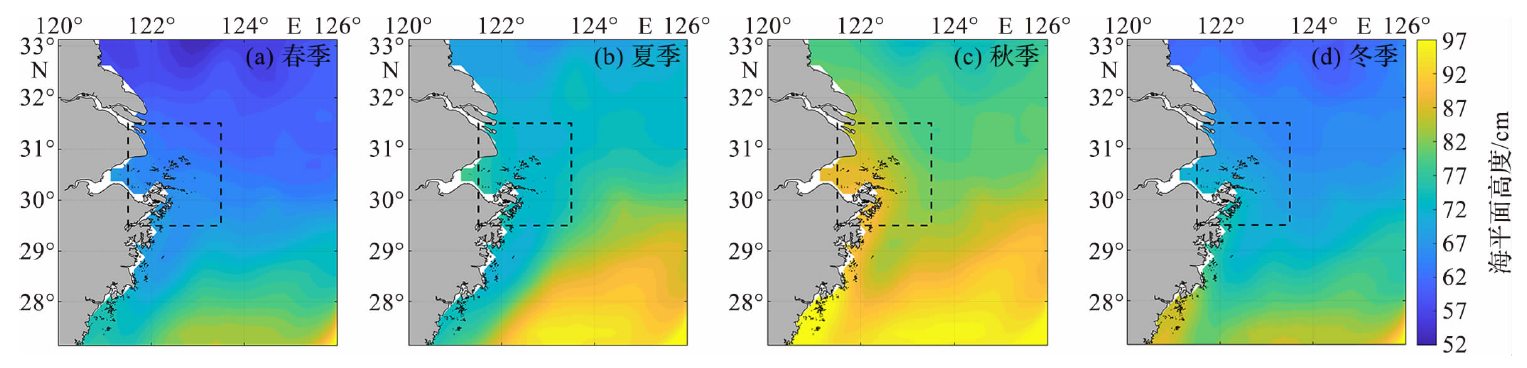
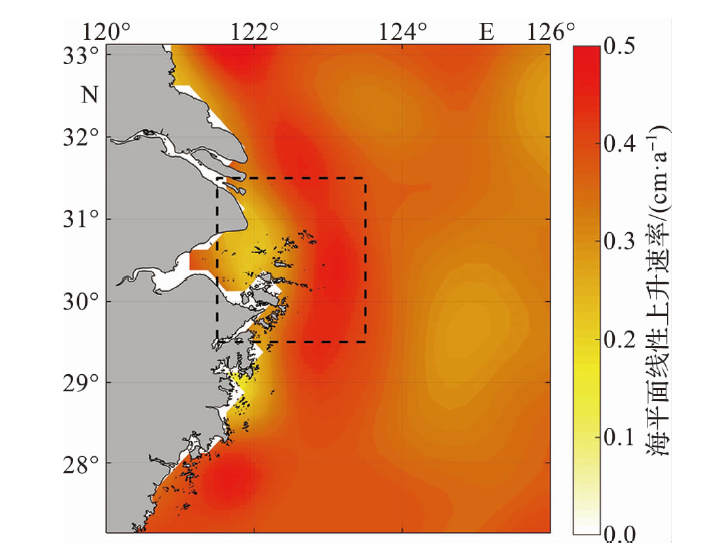
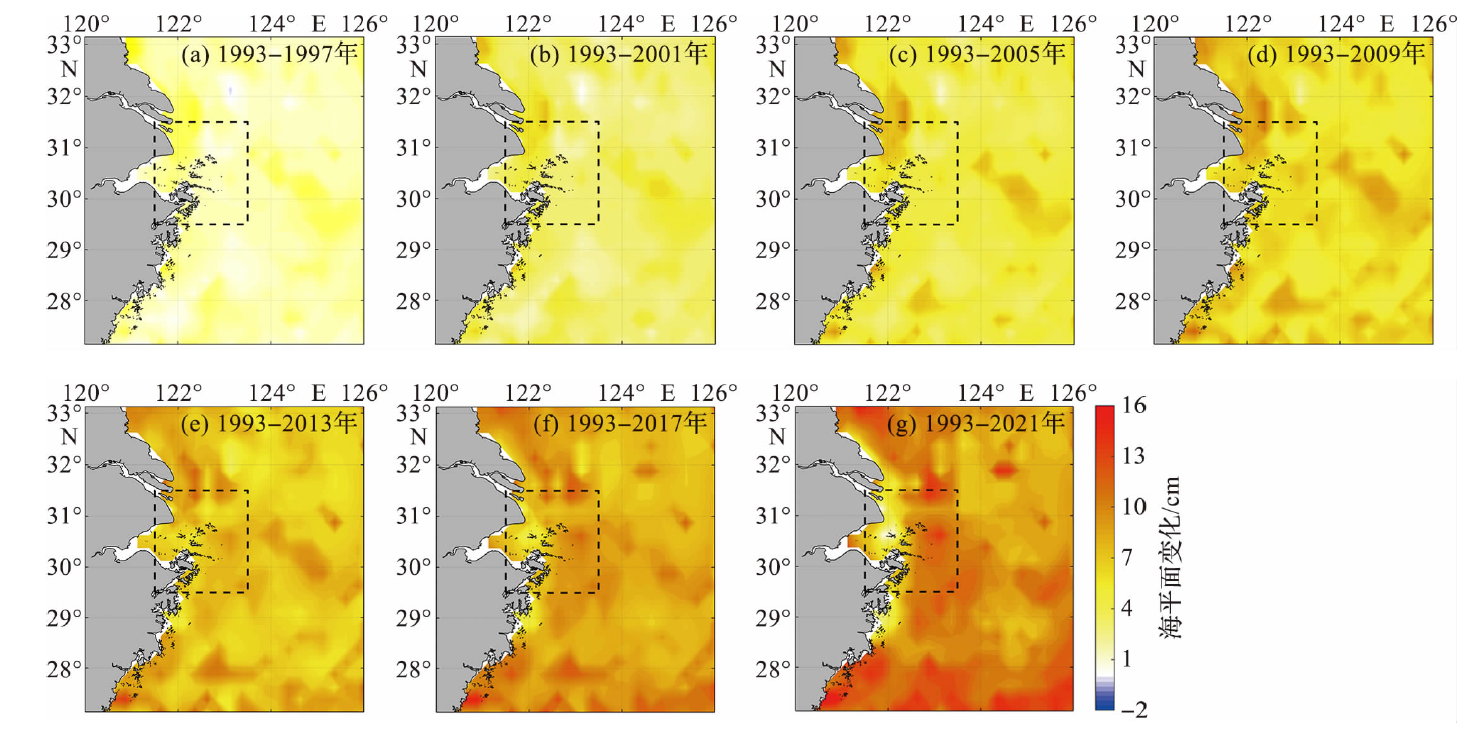
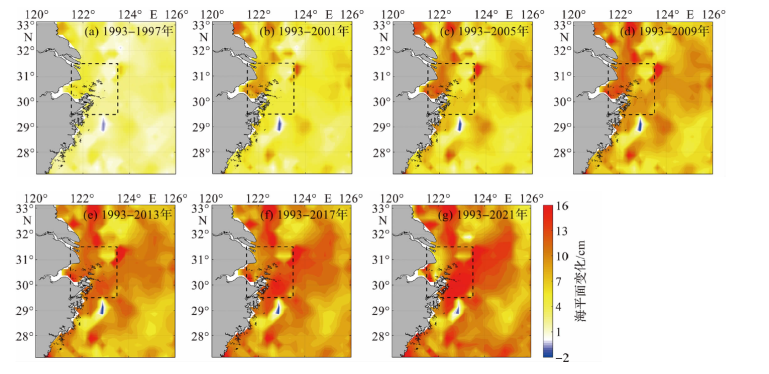
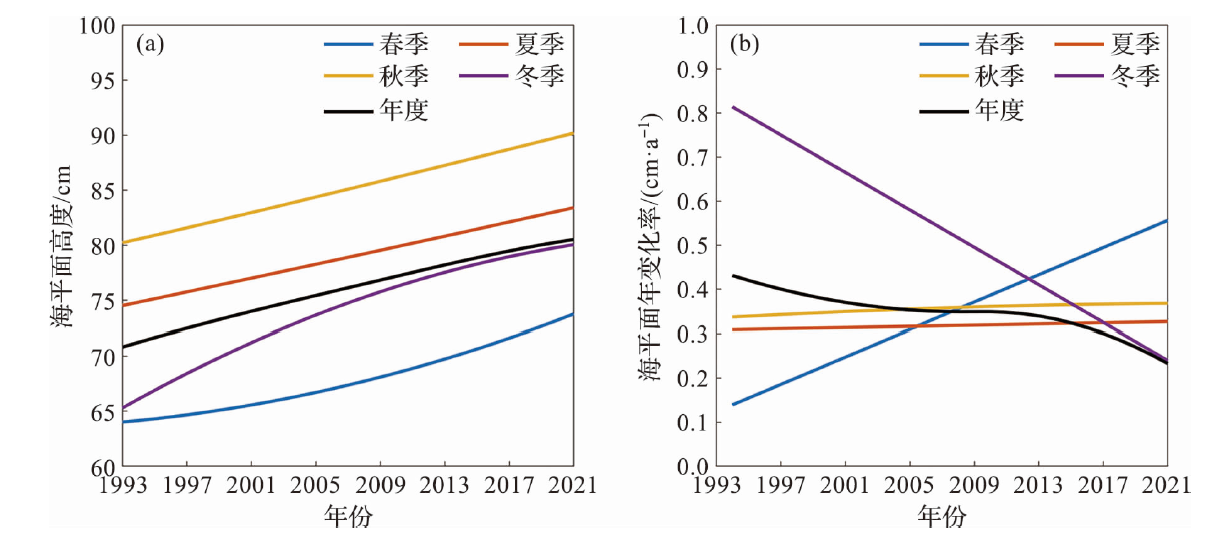
Fig.6 The linear change trend of the sea level in the study area during 1993-2021 (The dots represent the annual or seasonal mean sea level and the dashed lines represent the linear fitting results.)
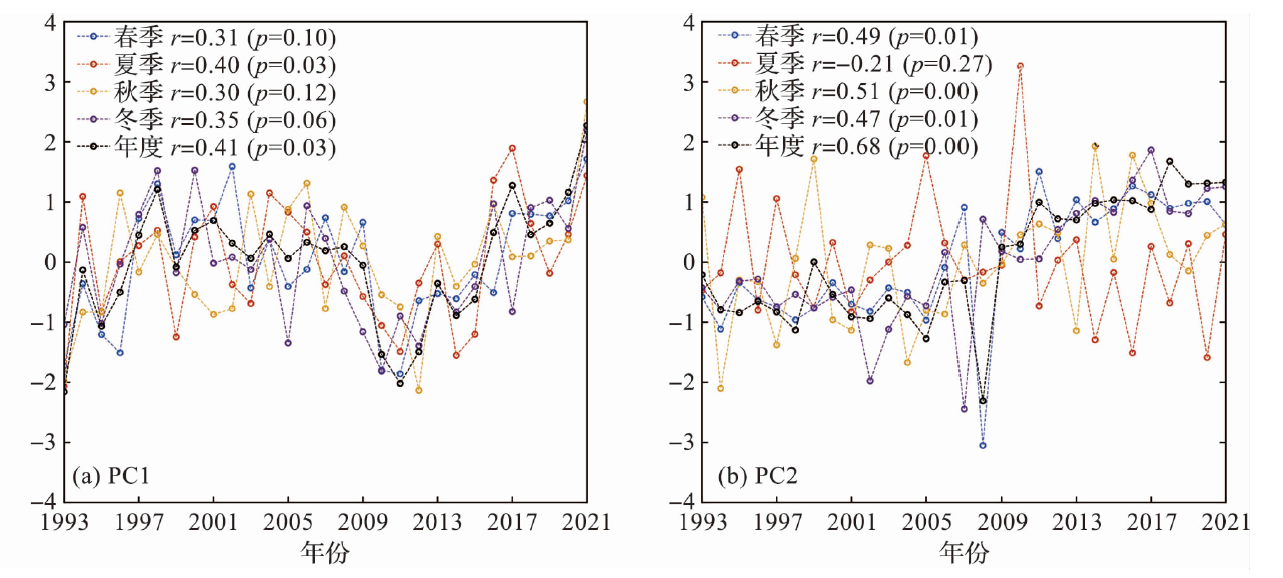
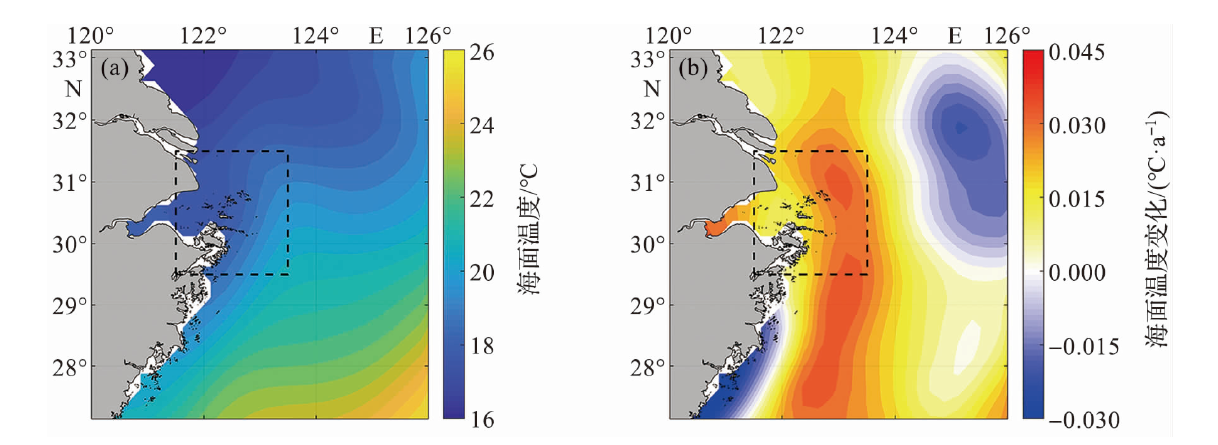
Fig.12 Time series of the first(a) and second principal component (b) for the empirical orthogonal decomposition of sea surface temperature during 1993-2021
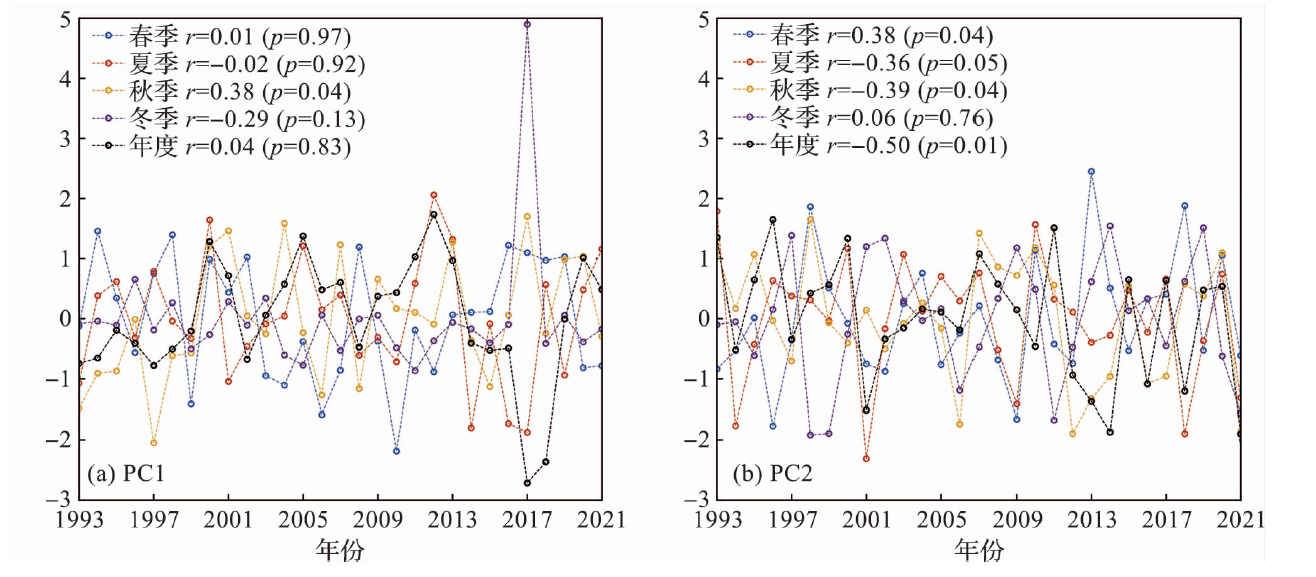
Fig.14 Time series of the first (a) and second principal component (b) for the empirical orthogonal decomposition of sea surface wind during 1993-2021
| [1] | 蔡榕硕, 谭红建. 海平面加速上升对低海拔岛屿、沿海地区及社会的影响和风险[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(2):163-171. |
| CAI R S, TAN H J. Impacts and risks of accelerating sea level rise on low lying islands, coasts and communities[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(2): 163-171. | |
| [2] | 王阳. 在稳定与公平之间:海平面上升对海洋边界的影响及其应对[J]. 中国海商法研究, 2022, 33(4):15-26. |
| WANG Y. Between stability and equality: The impact of sea level rise on maritime boundaries and its response[J]. Chinese Journal of Maritime Law, 2022, 33(4): 15-26. | |
| [3] | 李加林, 张殿发, 杨晓平, 等. 海平面上升的灾害效应及其研究现状[J]. 灾害学, 2005, 20(2):49-53. |
| LI J L, ZHANG D F, YANG X P, et al. Disaster effect of sea level rise in China and the research status in quo[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2005, 20(2): 49-53. | |
| [4] | 李杰, 杜凌, 张守文, 等. A1B气候情景下海平面变化对东中国海风暴潮的影响[J]. 海洋预报, 2014, 31(5):20-29. |
| LI J, DU L, ZHANG S W, et al. Impact of sea level variations on storm surge under SRES A1B scenario in the East China Sea[J]. Marine Forecasts, 2014, 31(5): 20-29. | |
| [5] |
孙鸿程, 蔡廷禄, 夏小明, 等. 舟山六横岛海域浅部地层结构与水下滑坡分布特征[J]. 海洋学研究, 2019, 37(1):59-66.
DOI |
| SUN H C, CAI T L, XIA X M, et al. Distribution characteristics of subaqueous landslides in the sea area of Liuheng Island, Zhoushan[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2019, 37(1): 59-66. | |
| [6] | 羊天柱, 应仁方, 张俊彪, 等. 浙江沿岸海平面研究和变化预测[J]. 东海海洋, 1999, 17(4):1-11. |
| YANG T Z, YING R F, ZHANG J B, et al. The research and prediction of the sea level along the coast of Zhejiang Province[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 1999, 17(4):1-11. | |
| [7] | 乔新, 陈戈. 基于11年高度计数据的中国海海平面变化初步研究[J]. 海洋科学, 2008, 32(1): 60-64. |
| QIAO X, CHEN G. A preliminary analysis on the China Sea level using 11 years’ TOPEX/Poseidon altimeter data[J]. Marine Science, 2008, 32(1):60-64. | |
| [8] | 詹金刚, 王勇, 许厚泽, 等. 我国近海1992-2006年海平面变化的小波分析[J]. 测绘学报, 2008, 37(4):438-443. |
| ZHAN J G, WANG Y, XU H Z, et al. The wavelet analysis of sea level change in China Sea during 1992-2006[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2008, 37(4): 438-443. | |
| [9] | 自然资源部. 2023年中国海平面公报[R]. https://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202404/t20240429_2844012.html. |
| Ministry of Natural Resources. China Sea Level Bulletin 2023[R]. https://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202404/t20240429_2844012.html. | |
| [10] | 王慧, 全梦媛, 徐卫青, 等. 中国沿海和近海海平面上升预测[J]. 海洋学报, 2023, 45(8):1-10. |
| WANG H, QUAN M Y, XU W Q, et al. Sea level rise projection in China’s coastal and offshore areas[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2023, 45(8): 1-10. | |
| [11] | 王龙, 王晶, 杨俊钢. 东海海平面变化的综合分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(1):28-37. |
| WANG L, WANG J, YANG J G. The Comprehensive analysis of sea level change in the East China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2014, 36(1): 28-37. | |
| [12] | 杨洋, 孙群, 杨敏, 等. 东中国海海平面高度的时空变化特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2018, 49(3):481-489. |
| YANG Y, SUN Q, YANG M, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of sea level of the East China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2018, 49(3): 481-489. | |
| [13] |
TABURET G, SANCHEZ-ROMAN A, BALLAROTTA M, et al. DUACS DT2018: 25 years of reprocessed sea level altimetry products[J]. Ocean Science, 2019, 15(5): 1207-1224.
DOI |
| [14] | HUANG B Y, LIU C Y, BANZON V, et al. Improvements of the Daily Optimum Interpolation Sea Surface Temperature (DOISST) Version 2.1[J]. Journal of Climate, 2021, 34(8): 2923-2939. |
| [15] | WENTZ F J, SCOTT J, HOFFMAN R, et al. Remote Sensing Systems Cross-Calibrated Multi-Platform (CCMP) 6-hourly ocean vector wind analysis product on 0.25 deg grid, Version 2.0.[EB/OL]. https://remss.com/measurements/ccmp/. |
| [16] | HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. |
| [17] | WU Z, HUANG N E. Ensemble empirical mode decom-position: a noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. |
| [18] | JI F, WU Z H, HUANG J P, et al. Evolution of land surface air temperature trend[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2014, 4: 462-466. |
| [19] | 张静, 方明强. 1993—2012年中国海海平面上升趋势[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 45(1):121-126. |
| ZHANG J, FANG M Q. Sea level trends of China Seas from 1993 to 2012[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2015, 45(1): 121-126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||