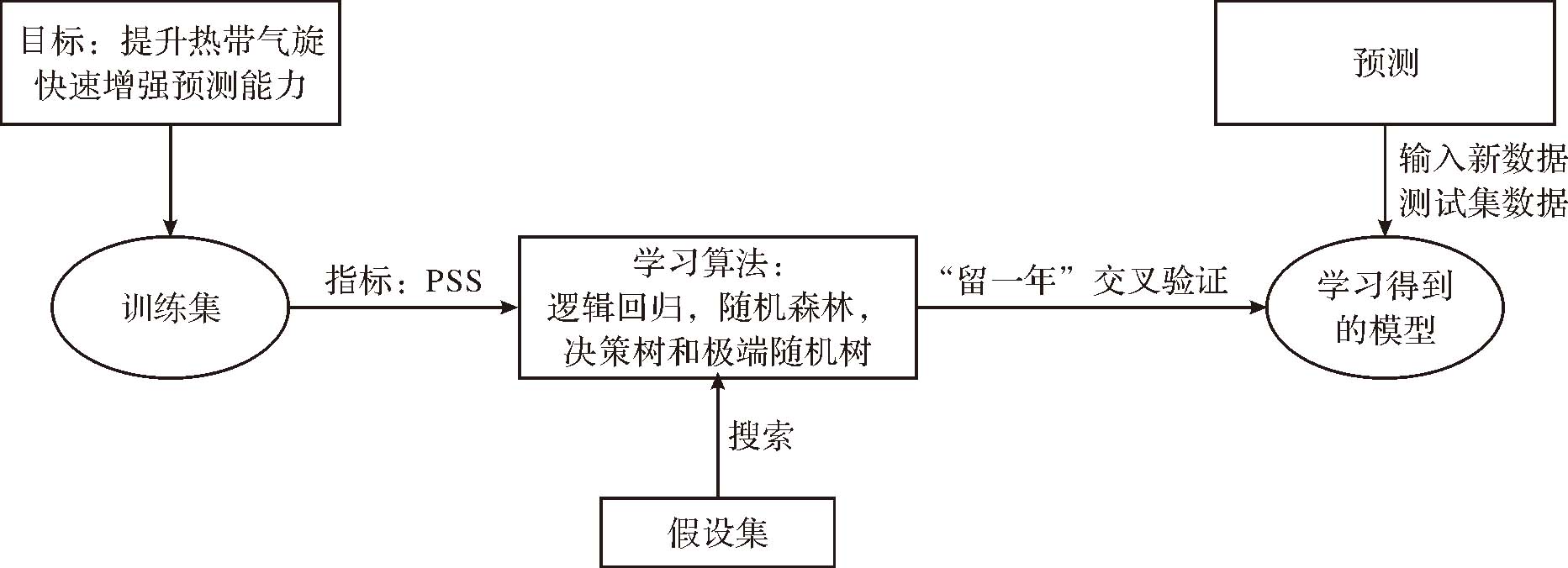
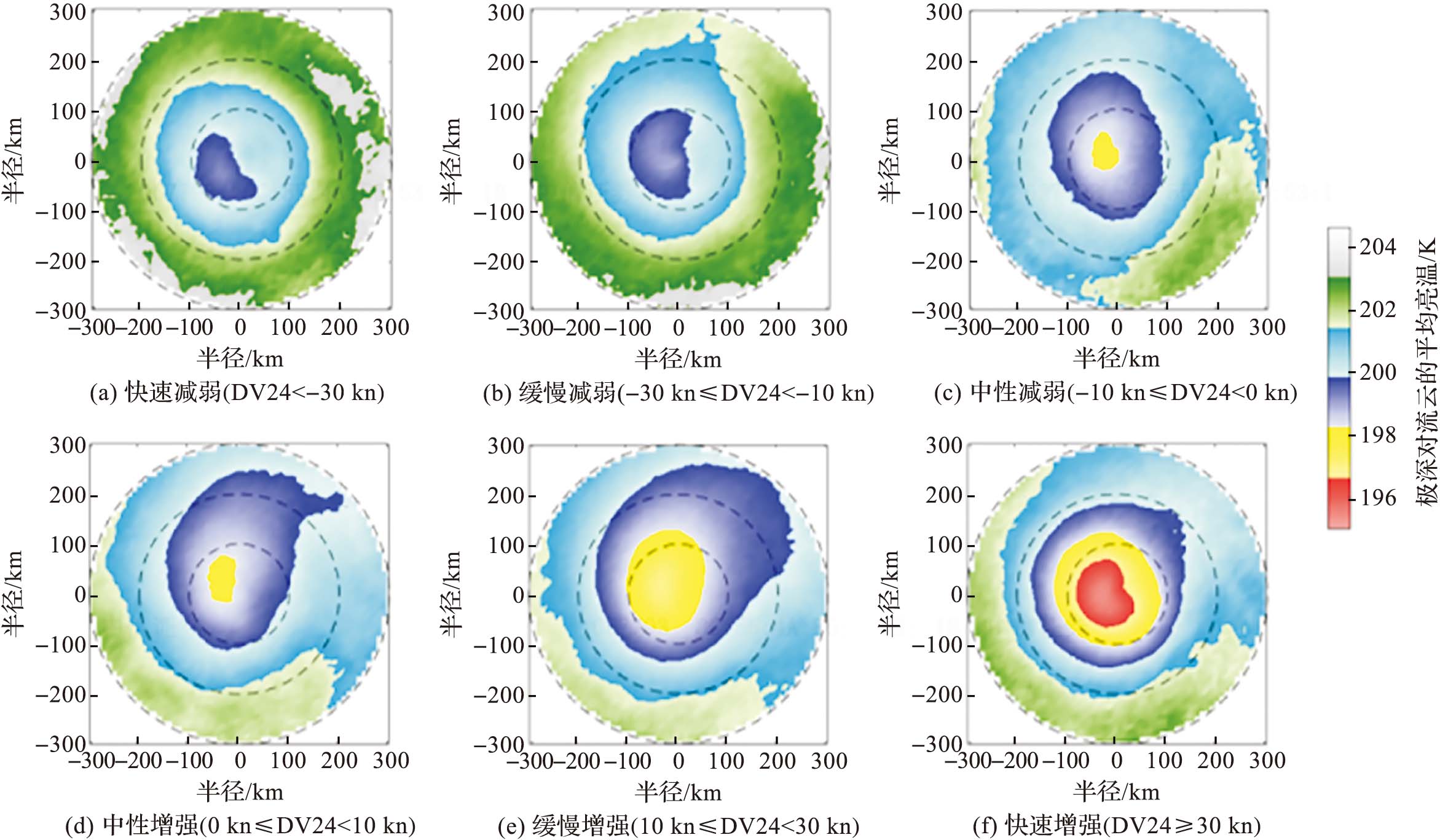
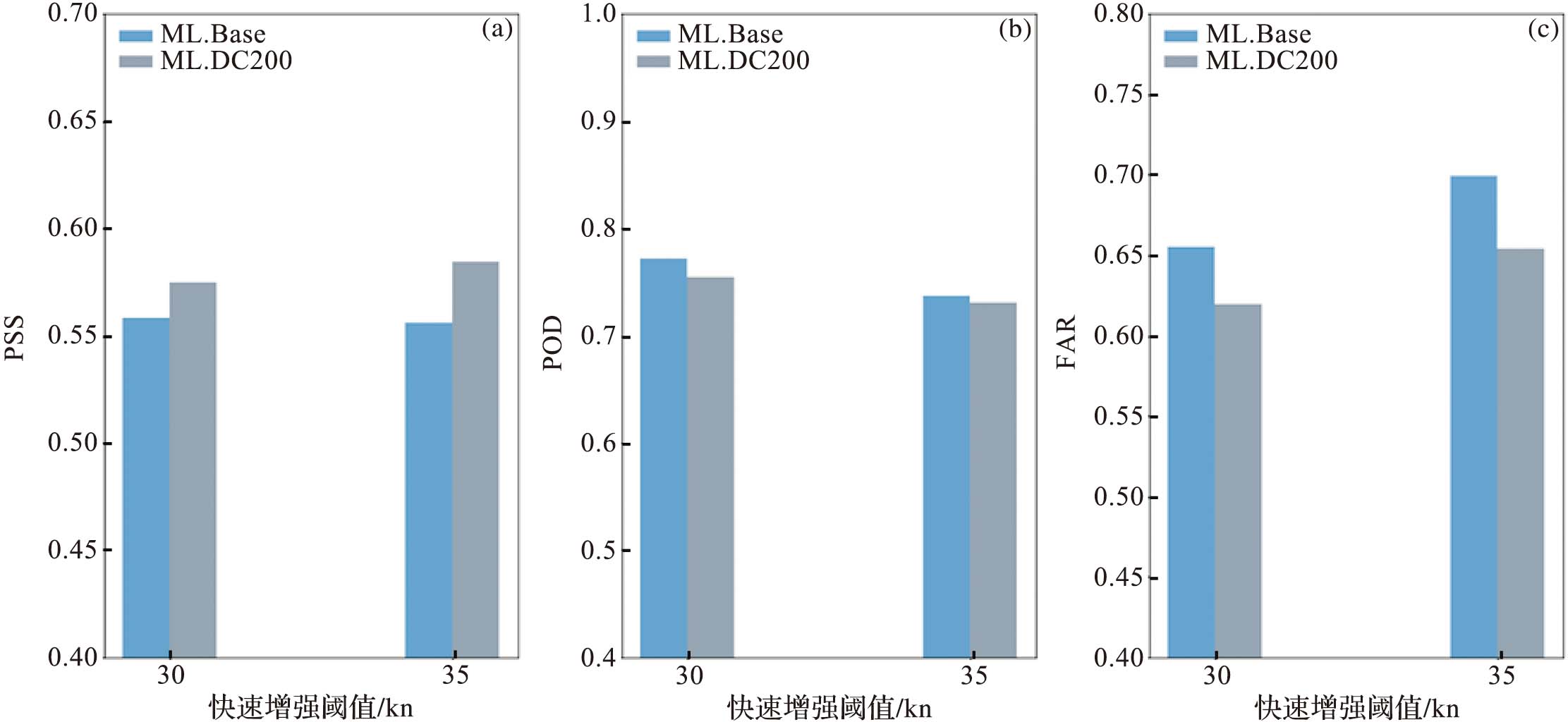
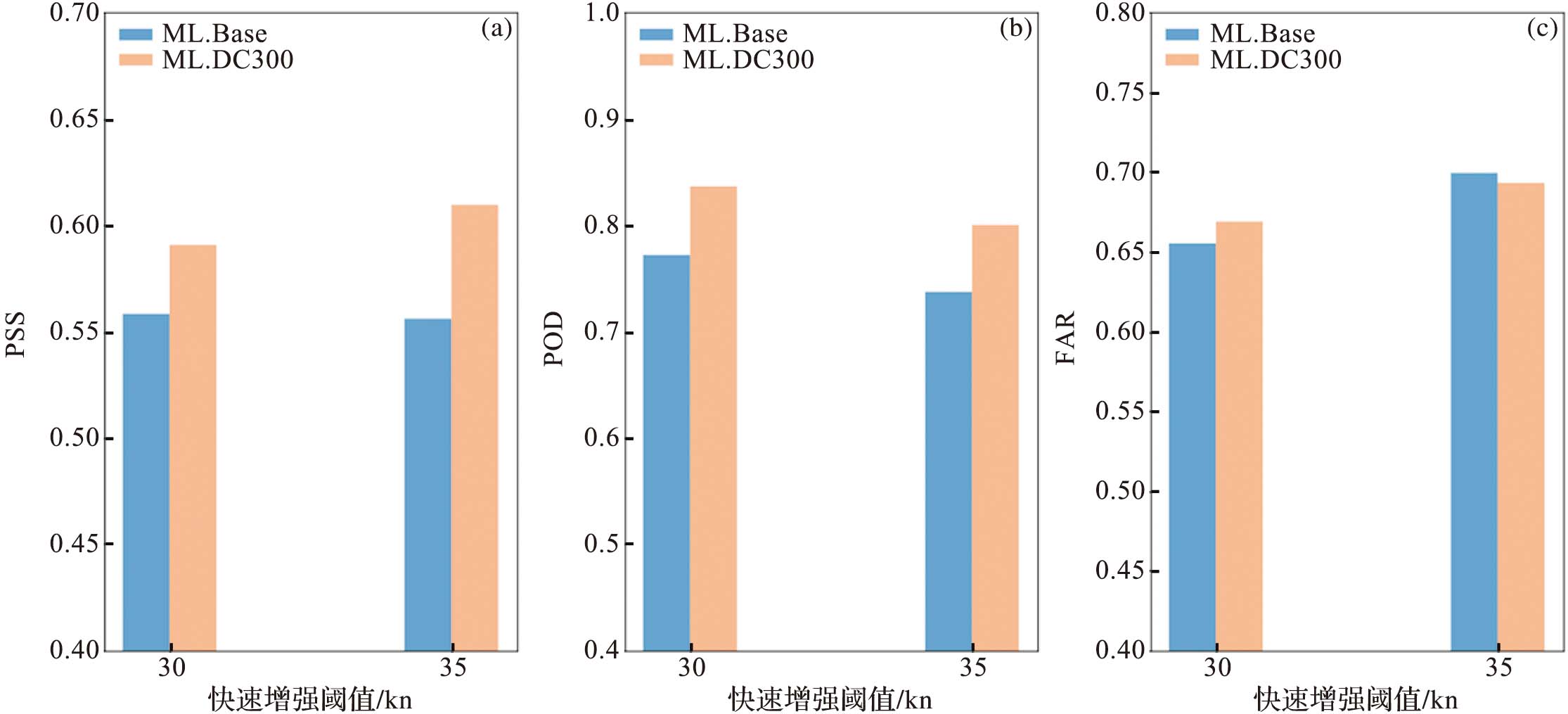
| [1] |
张娇艳, 吴立广, 张强. 全球变暖背景下我国热带气旋灾害趋势分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 2011, 27(4):442-454.
|
|
ZHANG J Y, WU L G, ZHANG Q. Tropical cyclone damages in China under the background of global warming[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 2011, 27(4): 442-454.
|
| [2] |
黄昌兴, 周国良, 郑磊, 等. 登陆我国台风的时空分布特征及其影响[J]. 水文, 2014, 34(6):81-85.
|
|
HUANG C X, ZHOU G L, ZHENG L, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of landing typhoons in China and their influence[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2014, 34(6): 81-85.
|
| [3] |
CANGIALOSI J P, BLAKE E, DEMARIA M, et al. Recent progress in tropical cyclone intensity forecasting at the national hurricane center[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2020, 35(5): 1913-1922.
|
| [4] |
TRABING B C, BELL M M. Understanding error distributions of hurricane intensity forecasts during rapid intensity changes[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2020, 35(6): 2219-2234.
|
| [5] |
KAPLAN J, DEMARIA M. Large-scale characteristics of rapidly intensifying tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic Basin[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2003, 18(6): 1093-1108.
|
| [6] |
HENDRICKS E A, PENG M S, FU B, et al. Quantifying environmental control on tropical cyclone intensity change[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2010, 138(8): 3243-3271.
|
| [7] |
CHEN H, ZHANG D L. On the rapid intensification of hurricane Wilma (2005). part II: Convective bursts and the upper-level warm core[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 70(1): 146-162.
|
| [8] |
CHEN X M, WANG Y Q, FANG J, et al. A numerical study on rapid intensification of typhoon Vicente (2012) in the South China Sea. Part II: Roles of inner-core processes[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 2018, 75(1): 235-255.
|
| [9] |
HAZELTON A T, HART R E, ROGERS R F. Analyzing simulated convective bursts in two Atlantic hurricanes. Part II: Intensity change due to bursts[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2017, 145(8): 3095-3117.
|
| [10] |
JIANG H Y. The relationship between tropical cyclone intensity change and the strength of inner-core convection[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2012, 140(4): 1164-1176.
|
| [11] |
MOLINARI J, VOLLARO D. Rapid intensification of a sheared tropical storm[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2010, 138(10): 3869-3885.
|
| [12] |
ROGERS R F, REASOR P D, ZHANG J A. Multiscale structure and evolution of hurricane Earl (2010) during rapid intensification[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2015, 143(2): 536-562.
|
| [13] |
SHI D L, CHEN G H, XIE X R. Revisiting the relationship between tropical cyclone rapid intensification and the distribution of inner-core precipitation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2023, 50(17): e2023GL104810.
|
| [14] |
GAO S, ZHANG W, LIU J, et al. Improvements in typhoon intensity change classification by incorporating an ocean coupling potential intensity index into decision trees[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2016, 31(1): 95-106.
|
| [15] |
GENG H T, SHI D W, ZHANG W, et al. A prediction scheme for the frequency of summer tropical cyclone landfalling over China based on data mining methods[J]. Meteorological Applications, 2016, 23(4): 587-593.
|
| [16] |
MERCER A, GRIMES A. Diagnosing tropical cyclone rapid intensification using Kernel methods and reanalysis datasets[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2015, 61: 422-427.
|
| [17] |
SU H, WU L T, JIANG J H, et al. Applying satellite observations of tropical cyclone internal structures to rapid intensification forecast with machine learning[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(17): e2020GL089102.
|
| [18] |
RUAN Z X, WU Q Y. Precipitation, convective clouds, and their connections with tropical cyclone intensity and intensity change[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(2): 1098-1105.
|
| [19] |
WU Q Y, HONG J C, RUAN Z X. Diurnal variations in tropical cyclone intensification[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(23): e2020GL090397.
|
| [20] |
JANOWIAK J E, JOYCE R J, YAROSH Y. A real-time global half-hourly pixel-resolution infrared dataset and its applications[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2001, 82(2): 205-217.
|
| [21] |
WU Q Y, RUAN Z X. Rapid contraction of the radius of maximum tangential wind and rapid intensification of a tropical cyclone[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2021, 126(3): e2020JD033681.
|
| [22] |
KAPLAN J, ROZOFF C M, DEMARIA M, et al. Evaluating environmental impacts on tropical cyclone rapid intensifi-cation predictability utilizing statistical models[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2015, 30(5): 1374-1396.
|
| [23] |
KAPLAN J, DEMARIA M, KNAFF J A. A revised tropical cyclone rapid intensification index for the Atlantic and eastern North Pacific basins[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 2010, 25(1): 220-241.
|
 ), HONG Jiacheng1,2,3,*(
), HONG Jiacheng1,2,3,*( )
)