海洋学研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (1): 58-68.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2024.01.006
西北太平洋中尺度涡合成结构及其对声传播的影响
- 1.南京信息工程大学 海洋科学学院,江苏 南京 210044
2.国防科技大学 气象海洋学院,江苏 南京 211102
-
收稿日期:2023-02-15修回日期:2023-04-17出版日期:2024-03-15发布日期:2024-05-11 -
通讯作者:* 丘仲锋(1979—),男,教授,主要从事海洋光学信息技术方面的研究,E-mail:zhongfeng.qiu@nuist.edu.cn。 -
作者简介:张旭东(1997—),男,浙江省舟山市人,主要从事海洋声传播方面的研究,E-mail:xudong@nuist.edu.cn。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41976165)
Composed structure of mesoscale eddy in the Northwest Pacific Ocean and its influence on acoustic propagation
ZHANG Xudong1( ), QIU Zhongfeng1,*(
), QIU Zhongfeng1,*( ), MAO Kefeng2, WANG Penghao2
), MAO Kefeng2, WANG Penghao2
- 1. School of Marine Sciences, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2. School of Meteorology and Oceanography, National University of Defense Technology, Nanjing 211102, China
-
Received:2023-02-15Revised:2023-04-17Online:2024-03-15Published:2024-05-11
摘要:
中尺度涡普遍存在于大洋中并会对声传播产生影响。利用2000—2018年AVISO卫星高度计资料和Argo浮标资料,通过涡旋合成方法构建了西北太平洋黑潮延伸体和亲潮延伸体海域中尺度涡的多年平均三维结构,对其垂直温、盐异常和声速特征进行分析,并采用Bellhop射线声学模型对中尺度涡背景下的声传播进行了模拟仿真。结果表明: 1)冷涡背景下,温度异常为负,盐度异常在上层为负,在下层为正,声速等值线抬升;暖涡背景下,温度异常为正,盐度异常在上层为正,在下层为负,声速等值线下沉。2)冷涡背景下,声传播会聚区向声源方向偏移,会聚区宽度缩小;暖涡背景下,会聚区远离声源,会聚区宽度增大。声会聚区宽度在黑潮延伸体海域较在亲潮延伸体海域更大,距离声源也更远。3)冷涡背景下,声传播的反转深度变浅,暖涡背景下,反转深度加深;在黑潮延伸体海域,反转深度总体随经度增大而变浅,在亲潮延伸体海域则相反,反转深度随经度增大而变深。
中图分类号:
引用本文
张旭东, 丘仲锋, 毛科峰, 王鹏皓. 西北太平洋中尺度涡合成结构及其对声传播的影响[J]. 海洋学研究, 2024, 42(1): 58-68.
ZHANG Xudong, QIU Zhongfeng, MAO Kefeng, WANG Penghao. Composed structure of mesoscale eddy in the Northwest Pacific Ocean and its influence on acoustic propagation[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2024, 42(1): 58-68.

图2 西北太平洋海表高度异常与涡旋的分布(2015-10-18) (图b表示Argo浮标位于涡旋外;图c表示Argo浮标位于涡旋内部;闭合曲线代表涡旋边界;红点代表涡旋中心;黑点代表Argo浮标位置;ΔxE代表Argo浮标到涡心的经向距离,ΔyE代表纬向距离。)
Fig.2 The distribution of SLA and eddy in the Northwest Pacific Ocean (2015-10-18) (Figure b shows that Argo buoy is located outside the eddy; Figure c shows that Argo buoy is located inside the eddy; the closed curve represents the eddy boundary; red dot represents the center of the eddy; the black dot represents the Argo buoy location; the ΔxE represents the meridional distance from Argo buoy to the eddy center, and the ΔyE represents the zonal distance.)
| 区域 | 子区域 | Argo剖面资料数量 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 与暖涡匹配/条 | 与冷涡匹配/条 | ||
| 区域Ⅰ 黑潮延伸体 | A | 736 | 494 |
| B | 736 | 388 | |
| C | 376 | 354 | |
| D | 309 | 229 | |
| E | 287 | 259 | |
| 区域Ⅱ 亲潮延伸体 | F | 280 | 413 |
| G | 509 | 302 | |
| H | 267 | 222 | |
| I | 147 | 105 | |
表1 西北太平洋9个子区域内符合匹配条件的Argo剖面数据
Tab.1 Number of Argo profiles conforming to the matching conditions in 9 subregions of the Northwest Pacific Ocean
| 区域 | 子区域 | Argo剖面资料数量 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 与暖涡匹配/条 | 与冷涡匹配/条 | ||
| 区域Ⅰ 黑潮延伸体 | A | 736 | 494 |
| B | 736 | 388 | |
| C | 376 | 354 | |
| D | 309 | 229 | |
| E | 287 | 259 | |
| 区域Ⅱ 亲潮延伸体 | F | 280 | 413 |
| G | 509 | 302 | |
| H | 267 | 222 | |
| I | 147 | 105 | |
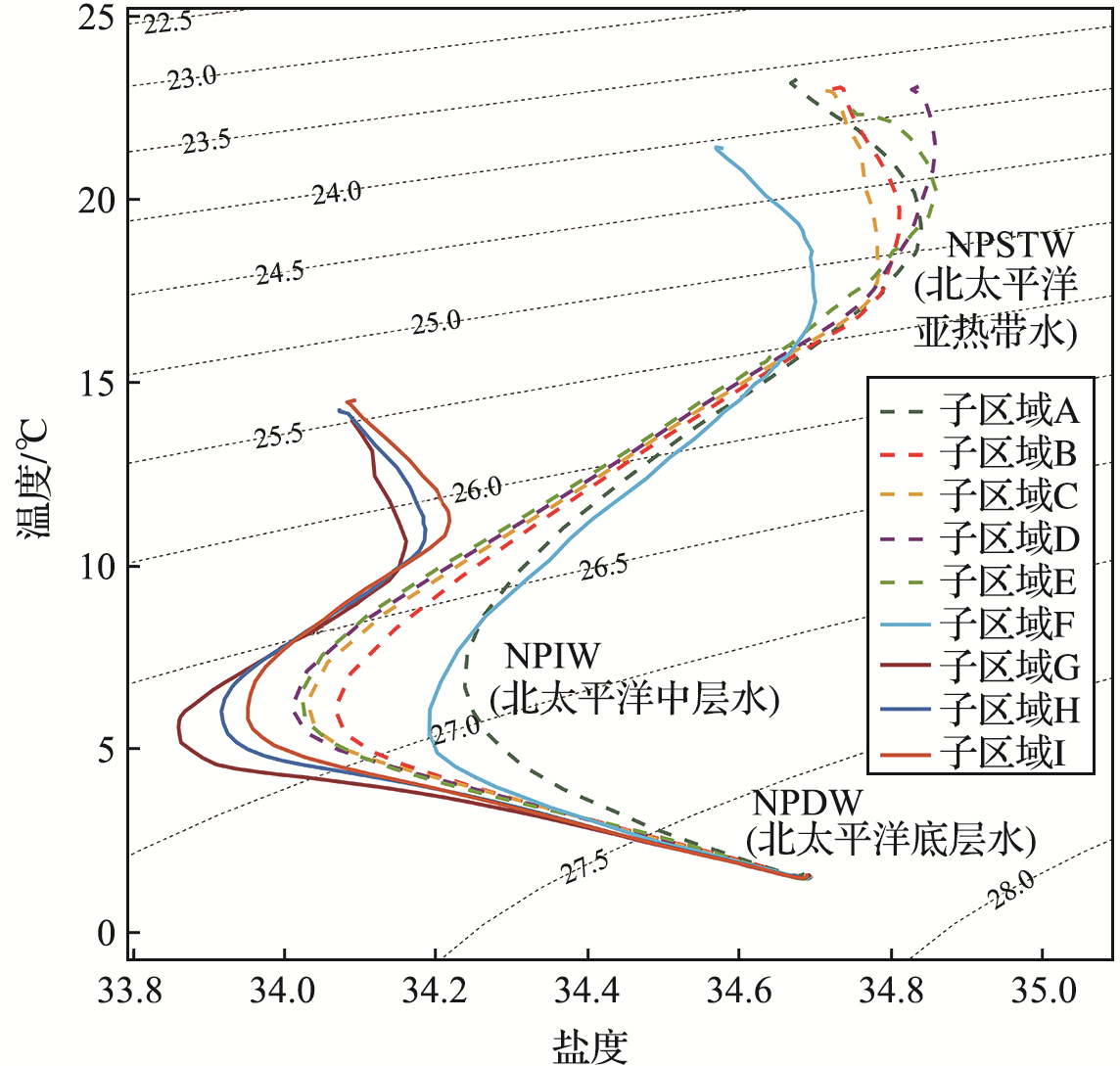
图3 西北太平洋9个子区域平均温-盐廓线 (黑色虚线为位势密度σθ。)
Fig.3 Mean temperature-salinity profile in 9 subregions of the Northwest Pacific Ocean (Black dotted lines represent the potential density σθ.)

图4 西北太平洋9个子区域合成中尺度涡在ΔY=0断面上的位温异常分布
Fig.4 Potential temperature anomaly distribution of the composed eddy in 9 subregions of the Northwest Pacific Ocean at ΔY=0 cross section

图5 西北太平洋9个子区域合成中尺度涡在ΔY=0断面上的盐度异常分布
Fig.5 Salinity anomaly distribution of the composed eddy in 9 subregions of the Northwest Pacific Ocean at ΔY=0 cross section
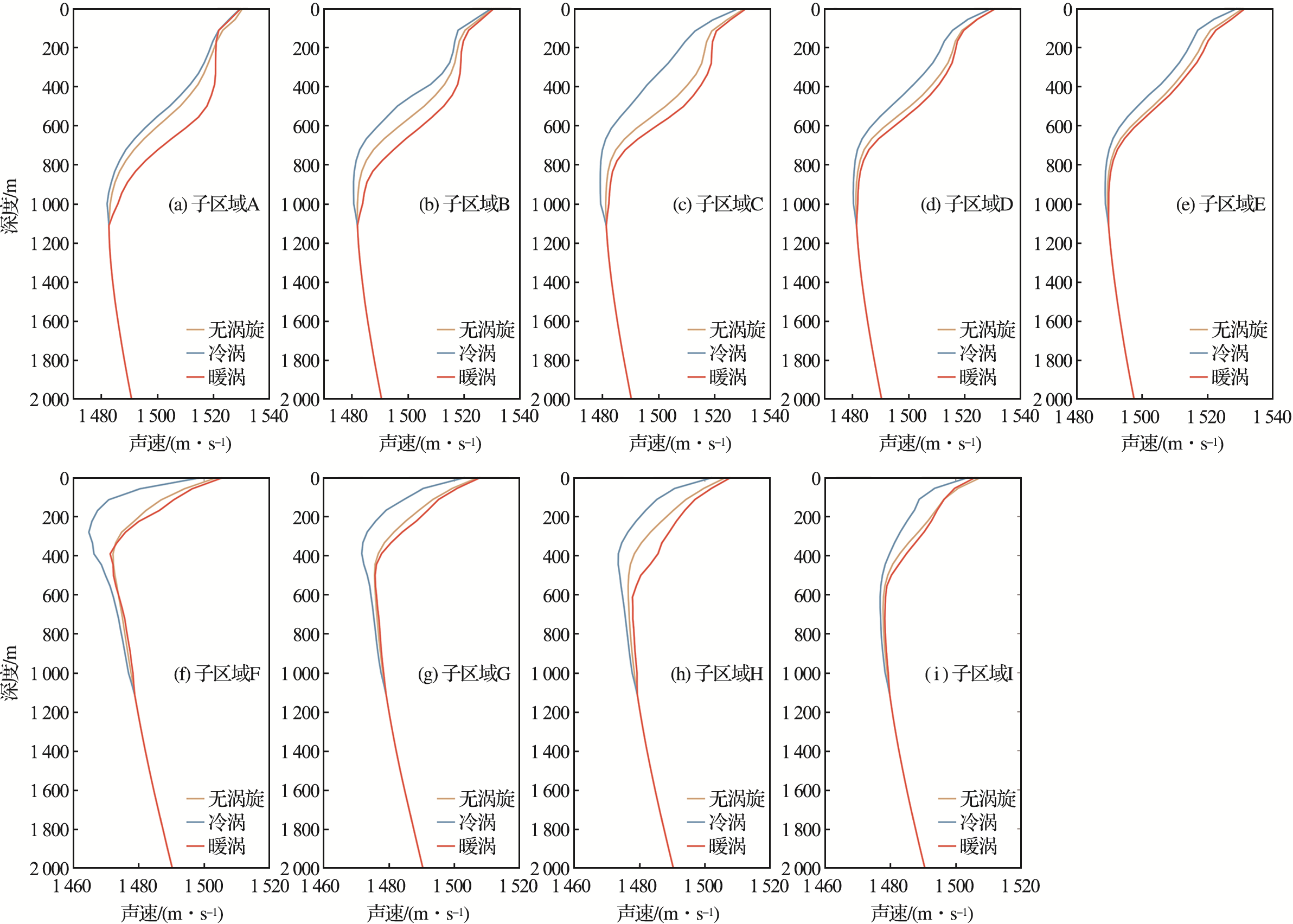
图6 西北太平洋9个子区域在无涡旋情况、冷涡和暖涡背景下涡心位置的声速剖面图
Fig.6 Sound velocity profiles at the eddy center under without eddy, cold eddy and warm eddy background in the 9 subregions of the Northwest Pacific Ocean
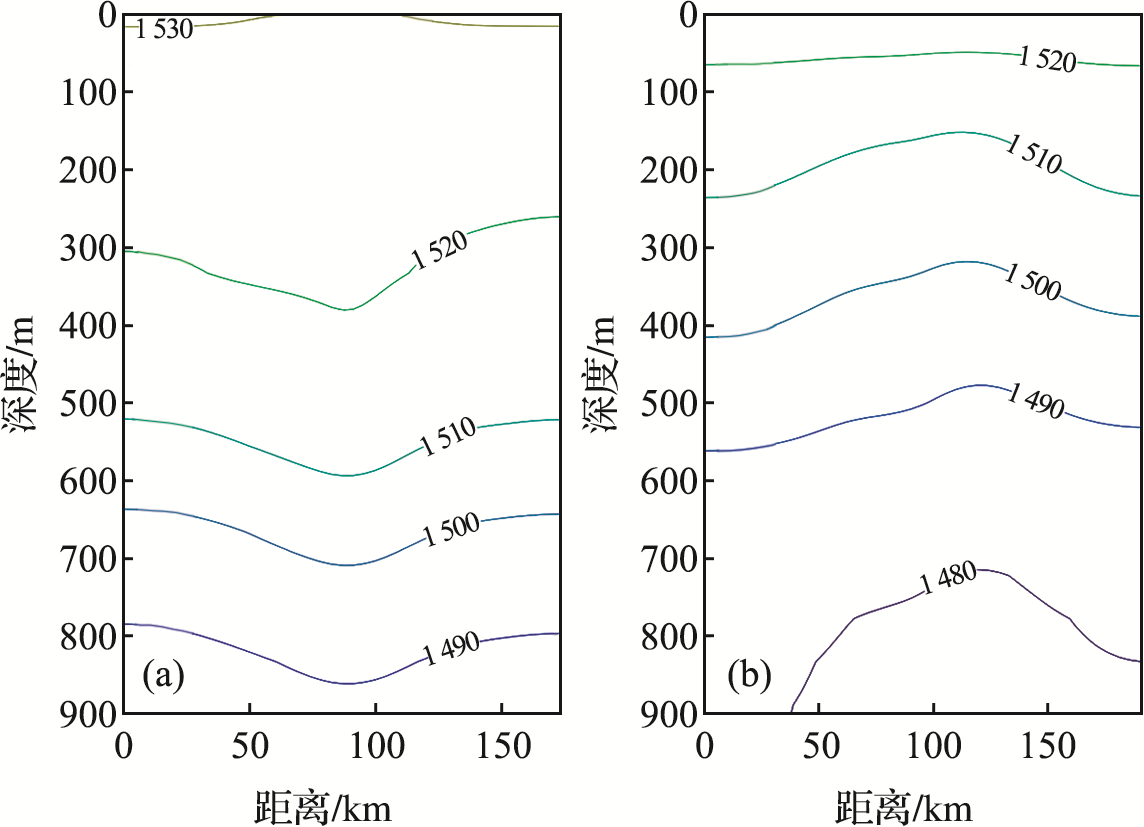
图7 西北太平洋子区域C暖涡(a)和冷涡(b)背景下涡心位置的声速等值线剖面分布图
Fig.7 Sound velocity contour of eddy center under warm eddy background (a) and cold eddy background (b) in subregion C of the Northwest Pacific Ocean

图8 西北太平洋9个子区域在暖涡、冷涡、无涡旋背景下的声传播损失
Fig.8 Acoustic propagation loss under the background of warm eddy, cold eddy and without eddy in 9 subregions of the Northwest Pacific Ocean
| 区域 | 环境背景 | 最大声速差 /dB | 会聚区与声源的距离/km | 会聚区宽度/km | 反转深度/m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d1 | d2 | W1 | W2 | ||||||
| 区域I 黑潮延伸体 | A | 无涡旋 | 62.25 | 123.24 | 8.34 | 8.82 | 4 026 | ||
| 冷涡 | 4.042 | 61.63 | 122.05 | 8.10 | 8.60 | 3 927 | |||
| 暖涡 | 10.867 | 64.07 | 127.09 | 8.68 | 9.44 | 4 058 | |||
| B | 无涡旋 | 62.05 | 122.80 | 8.12 | 8.52 | 3 885 | |||
| 冷涡 | 9.539 | 60.60 | 119.83 | 7.84 | 7.98 | 3 831 | |||
| 暖涡 | 7.958 | 63.52 | 125.78 | 8.37 | 8.98 | 3 961 | |||
| C | 无涡旋 | 61.40 | 121.76 | 8.03 | 8.26 | 3 820 | |||
| 冷涡 | 14.457 | 59.02 | 116.90 | 7.61 | 7.59 | 3 625 | |||
| 暖涡 | 6.519 | 62.64 | 124.21 | 8.22 | 8.59 | 3 847 | |||
| D | 无涡旋 | 61.05 | 121.03 | 7.55 | 8.03 | 3 809 | |||
| 冷涡 | 6.957 | 59.87 | 118.38 | 7.35 | 7.60 | 3 670 | |||
| 暖涡 | 3.254 | 61.48 | 121.95 | 7.66 | 8.45 | 3 831 | |||
| E | 无涡旋 | 59.65 | 119.00 | 7.33 | 7.9 | 3 744 | |||
| 冷涡 | 5.526 | 58.80 | 117.68 | 7.29 | 7.64 | 3 654 | |||
| 暖涡 | 1.978 | 59.83 | 119.51 | 7.44 | 8.12 | 3 821 | |||
| 区域Ⅱ 亲潮延伸体 | F | 无涡旋 | 45.12 | 85.82 | 5.72 | 8.86 | 1 742 | ||
| 冷涡 | 16.106 | ||||||||
| 暖涡 | 4.094 | 45.74 | 86.15 | 5.81 | 6.32 | 1 763 | |||
| G | 无涡旋 | 50.22 | 92.56 | 6.65 | 7.10 | 2 189 | |||
| 冷涡 | 10.023 | 42.24 | 85.54 | 5.42 | 5.62 | 1 948 | |||
| 暖涡 | 3.222 | 45.93 | 93.92 | 6.84 | 7.40 | 2 229 | |||
| H | 无涡旋 | 44.96 | 93.85 | 7.01 | 7.64 | 2 328 | |||
| 冷涡 | 8.884 | 44.02 | 91.56 | 5.80 | 6.26 | 2 119 | |||
| 暖涡 | 7.227 | 47.52 | 97.13 | 7.64 | 8.43 | 2 376 | |||
| I | 无涡旋 | 48.40 | 99.55 | 7.17 | 7.74 | 2 461 | |||
| 冷涡 | 7.563 | 45.97 | 97.16 | 6.07 | 6.31 | 2 167 | |||
| 暖涡 | 2.048 | 48.75 | 100.94 | 7.34 | 8.12 | 2 480 | |||
表2 西北太平洋9个子区域暖涡、冷涡、无涡旋背景下会聚区位置与宽度
Tab.2 Location and width of convergence zone under the background of warm eddy, cold eddy and without eddy in 9 subregions of the Northwest Pacific Ocean
| 区域 | 环境背景 | 最大声速差 /dB | 会聚区与声源的距离/km | 会聚区宽度/km | 反转深度/m | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d1 | d2 | W1 | W2 | ||||||
| 区域I 黑潮延伸体 | A | 无涡旋 | 62.25 | 123.24 | 8.34 | 8.82 | 4 026 | ||
| 冷涡 | 4.042 | 61.63 | 122.05 | 8.10 | 8.60 | 3 927 | |||
| 暖涡 | 10.867 | 64.07 | 127.09 | 8.68 | 9.44 | 4 058 | |||
| B | 无涡旋 | 62.05 | 122.80 | 8.12 | 8.52 | 3 885 | |||
| 冷涡 | 9.539 | 60.60 | 119.83 | 7.84 | 7.98 | 3 831 | |||
| 暖涡 | 7.958 | 63.52 | 125.78 | 8.37 | 8.98 | 3 961 | |||
| C | 无涡旋 | 61.40 | 121.76 | 8.03 | 8.26 | 3 820 | |||
| 冷涡 | 14.457 | 59.02 | 116.90 | 7.61 | 7.59 | 3 625 | |||
| 暖涡 | 6.519 | 62.64 | 124.21 | 8.22 | 8.59 | 3 847 | |||
| D | 无涡旋 | 61.05 | 121.03 | 7.55 | 8.03 | 3 809 | |||
| 冷涡 | 6.957 | 59.87 | 118.38 | 7.35 | 7.60 | 3 670 | |||
| 暖涡 | 3.254 | 61.48 | 121.95 | 7.66 | 8.45 | 3 831 | |||
| E | 无涡旋 | 59.65 | 119.00 | 7.33 | 7.9 | 3 744 | |||
| 冷涡 | 5.526 | 58.80 | 117.68 | 7.29 | 7.64 | 3 654 | |||
| 暖涡 | 1.978 | 59.83 | 119.51 | 7.44 | 8.12 | 3 821 | |||
| 区域Ⅱ 亲潮延伸体 | F | 无涡旋 | 45.12 | 85.82 | 5.72 | 8.86 | 1 742 | ||
| 冷涡 | 16.106 | ||||||||
| 暖涡 | 4.094 | 45.74 | 86.15 | 5.81 | 6.32 | 1 763 | |||
| G | 无涡旋 | 50.22 | 92.56 | 6.65 | 7.10 | 2 189 | |||
| 冷涡 | 10.023 | 42.24 | 85.54 | 5.42 | 5.62 | 1 948 | |||
| 暖涡 | 3.222 | 45.93 | 93.92 | 6.84 | 7.40 | 2 229 | |||
| H | 无涡旋 | 44.96 | 93.85 | 7.01 | 7.64 | 2 328 | |||
| 冷涡 | 8.884 | 44.02 | 91.56 | 5.80 | 6.26 | 2 119 | |||
| 暖涡 | 7.227 | 47.52 | 97.13 | 7.64 | 8.43 | 2 376 | |||
| I | 无涡旋 | 48.40 | 99.55 | 7.17 | 7.74 | 2 461 | |||
| 冷涡 | 7.563 | 45.97 | 97.16 | 6.07 | 6.31 | 2 167 | |||
| 暖涡 | 2.048 | 48.75 | 100.94 | 7.34 | 8.12 | 2 480 | |||
| [1] | 董昌明. 海洋涡旋探测与分析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015. |
| DONG C M. Oceanic eddy detection and analysis[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2015. | |
| [2] | LAWRENCE M W. Simple prediction of convergence zone propagation in waters around Australia[M]. Sydney: Royal Australian Navy Researche Lab Eedecliff, 1983. |
| [3] | BAER R N. Calculations of sound propagation through an eddy[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1980, 67(4): 1180-1185. |
| [4] | 刘清宇. 海洋中尺度现象下的声传播研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2006. |
| LIU Q Y. The research of wave propagation in ocean environment with mesoscale phenomena[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2006. | |
| [5] | 卢晓亭, 胡均川, 李玉阳. 海洋涡中的三维声传播分析[C]// 青年学术会议论文集, 武汉: 中国声学学会, 1999. |
| LU X T, HU J C, LI Y Y. Analysis of three-dimensional acoustic propagation in ocean vortices[C]// Youth academic Conference, Wuhan: Acoustical Society of China, 1999. | |
| [6] | 康颖. 海洋中尺度结构声传播特性分析[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2004. |
| KANG Y. Ocean mesoscale features effects on sound propa-gation[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2004. | |
| [7] | 朱凤芹, 张海刚, 屈科. 南海东北部中尺度暖涡对声传播的影响[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2021, 42(10):1496-1502. |
| ZHU F Q, ZHANG H G, QU K. Influence of mesoscale warm eddies on sound propagation in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2021, 42(10): 1496-1502. | |
| [8] | 张旭, 程琛, 邱仁贵. 一个西太平洋冷涡影响下的会聚区声传播变异特征分析[J]. 海洋通报, 2015, 34(2):130-137. |
| ZHANG X, CHENG C, QIU R G. Abnormal features of the convergence zone caused by the cold eddy in Western Pacific[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2015, 34(2): 130-137. | |
| [9] | ITOH S, YASUDA I. Water mass structure of warm and cold anticyclonic eddies in the western boundary region of the subarctic North Pacific[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2010, 40(12): 2624-2642. |
| [10] | CHEN G X, HOU Y J, CHU X Q. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: Mean properties, spatiotemporal variability, and impact on thermohaline structure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(C6): C06018. |
| [11] | CHAIGNEAU A, LE TEXIER M, ELDIN G, et al. Vertical structure of mesoscale eddies in the eastern South Pacific Ocean: A composite analysis from altimetry and Argo profiling floats[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2011, 116(C11): C11025. |
| [12] | YANG G, WANG F, LI Y L, et al. Mesoscale eddies in the northwestern subtropical Pacific Ocean: Statistical characteristics and three-dimensional structures[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(4): 1906-1925. |
| [13] | 胡冬, 陈希, 宋海波, 等. 黑潮延伸体邻近海区中尺度涡三维合成结构分析[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2021, 38(1):42-48. |
| HU D, CHEN X, SONG H B, et al. Three dimensional structures of composed mesoscale eddies near the Kuroshio extension region[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2021, 38(1): 42-48. | |
| [14] | PORTER M B, BUCKER H P. Gaussian beam tracing for computing ocean acoustic fields[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1987, 82(4): 1349-1359. |
| [15] | ZHENG Q A, TAI C K, HU J Y, et al. Satellite altimeter observations of nonlinear Rossby eddy-Kuroshio interaction at the Luzon Strait[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 2011, 67(4): 365-376. |
| [16] | LE TRAON P Y, NADAL F, DUCET N. An improved mapping method of multisatellite altimeter data[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 1998, 15(2): 522-534. |
| [17] | 童明荣, 刘增宏, 孙朝辉, 等. ARGO剖面浮标数据质量控制过程剖析[J]. 海洋技术, 2003, 22(4):79-84. |
| TONG M R, LIU Z H, SUN C H, et al. Analysis of data quality control process of the ARGO profiling buoy[J]. Ocean Technology, 2003, 22(4): 79-84. | |
| [18] | LE VU B, STEGNER A, ARSOUZE T. Angular momentum eddy detection and tracking algorithm (AMEDA) and its application to coastal eddy formation[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2018, 35(4): 739-762. |
| [19] | MKHININI N, COIMBRA A L S, STEGNER A, et al. Long-lived mesoscale eddies in the eastern Mediterranean Sea: Analysis of 20 years of AVISO geostrophic velocities[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2014, 119(12): 8603-8626. |
| [20] | PORTER M B. The Bellhop manual and user’s guide: preliminary draft[M]. California USA: Heat, Light, and Sound Research, Inc, 2011. |
| [21] | TALLEY L D. Distribution and formation of North Pacific intermediate water[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1993, 23(3): 517-537. |
| [22] | MEDWIN H. Speed of sound in water: A simple equation for realistic parameters[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1975, 58(6): 1318-1319. |
| [23] | 冯士筰, 李凤岐, 李少菁. 海洋科学导论[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1999. |
| FENG S Z, LI F Q, LI S J. Introduction to marine science[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 1999. |
| [1] | 孟宇, 陈双玲. 海水硝酸盐跃层深度计算方法研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 2023, 41(3): 1-13. |
| [2] | 李志超, 郭俊如, 宋军, 白志鹏, 富砚昭, 蔡宇, 王喜风. 东海黑潮周边中尺度涡的分布、运动规律以及生成机制[J]. 海洋学研究, 2022, 40(4): 1-10. |
| [3] | 蒋佳茗, 汪亦蕾. 热带西北太平洋0~300 m热含量的年代际变化[J]. 海洋学研究, 2022, 40(1): 1-11. |
| [4] | 张家赢, 周锋, 田娣, 黄挺, . 苏门答腊岛西北海域中尺度涡源区特征与形成机制[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(3): 1-11. |
| [5] | 许钰佳, 陈长霖, 彭旭东, 刘磊, . 西北太平洋热带气旋路径预报偏差分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2021, 39(2): 1-11. |
| [6] | 黄挺, 周锋, 田娣, 张家赢. 孟加拉湾及其毗邻海域中尺度涡旋活动的冬、夏季差异[J]. 海洋学研究, 2020, 38(3): 21-30. |
| [7] | 张桃, 李君益, 谢玲玲, 郑少军, 郑慧源. 东海陆架区中尺度涡运动路径的统计特征分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 2020, 38(1): 77-86. |
| [8] | 马志康, 付东洋, 屈科, 朱凤芹. 台风“天秤”对两种深海声道下声传播的影响[J]. 海洋学研究, 2019, 37(3): 40-48. |
| [9] | 赵文涛, 俞建成, 张艾群, 李岩. 基于卫星测高数据的海洋中尺度涡流动态特征检测[J]. 海洋学研究, 2016, 34(3): 62-68. |
| [10] | 王惠楠, 许东峰, 陈钟为, 徐鸣泉, 杨龙奇, 陈洪. 从2010年1月的1个反气旋涡探讨南海中尺度涡的输运能力[J]. 海洋学研究, 2014, 32(4): 1-10. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||

