Journal of Marine Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 45-60.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2023.02.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics and mechanism of ocean subsurface coherent eddies: Problems and progress
- College of Oceanography, Hohai University, Nanjing 210013, China
-
Received:2022-09-21Revised:2022-11-22Online:2023-06-15Published:2023-07-27
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GE Yuyu, LIAO Guanghong. Characteristics and mechanism of ocean subsurface coherent eddies: Problems and progress[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2023, 41(2): 45-60.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://hyxyj.sio.org.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2023.02.004

Fig.1 Subsurface coherent vortices identified by some observation methods [a: Potential temperature (θ), salinity (S), dissolved oxygen (O2), buoyancy frequency (N) and fluorescence (F1) profiles from ALOHA station (22°45'N, 158°00'W) during Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT) cruises 121 (black lines) and 122 (colored lines) [14]; b: Time-depth sections of salinity during 2007 in the upper 600 m from Argo float WMO ID 3900556, located in the eastern subtropical South Pacific Ocean[15], with the black line for salinity contours. Contours for σθ=26.0,26.2,26.5,26.7 and 27.0 kg·m-3 from top to battom are overlaid in white; c: Profile of anomalously spicy caused by California undercurrent eddy (Cuddy) observed by underwater glider from autumn 2004[4]. The figure superimposes the potential density anomaly (magenta contours), and alongshore geostrophic velocity (black contours poleward, gray contours equatorward, zero contour heavy line), The contour interval for potential density (velocity) is 0.2 kg·m-3 (0.02 m·s-1). The California undercurrent core isopycnal ofσθ=26.55 kg·m-3 is highlighted by the thick magenta line; d: Mediterranean eddy (Meddy) observed from the North Atlantic seismic reflection data[16].]
| 区域 | 温跃层内涡旋(ITEs) | 温跃层下涡旋(STEs) | 模态水涡旋 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主要结论 | 代表性文献 | 涡旋名称 | 主要结论 | 代表性文献 | 主要结论 | 代表性文献 | |||||
| 印度洋 | 表层反气旋涡与热带气旋相互作用可能产生ITEs | GORDON et al[ | 阿拉伯 涡旋 | 阿拉伯海观测到的STEs在咸水横跨阿拉伯海的运输中具有重要作用 | VIC C et al[ MAREZ et al[ | ||||||
| 在马达加斯加东南部观测到ITEs | NAUW et al[ | ||||||||||
| 大西洋 | 综合大西洋西部永久性温跃层中等温透镜体的观测结果,解释其为孤立特征,首次提出ITEs,同时在马尾藻海中观测到ITEs | DUGAN et al[ | 地中海涡旋 | 地中海涡旋将高盐的地中海水输送到亚热带大西洋,影响环流、深对流、生物化学物质等 | MCDOWELL et al[ RICHARDSON et al[ BARBOSA et al[ BOSSE et al[ | 模态水涡旋在大西洋西北部被观测到,它们通过沿密度面输送和动量搅拌热盐、化学物质等影响海洋环流从而影响生态 | MCGILLICUDDY et al[ | ||||
| 在副热带北大西洋东边界上升流潜流中观测到ITEs,其内部和周围生产力很高 | PIETRI et al[ | 北大西洋东部的海洋低氧区的形成与模态水涡旋的孤立水团输运有关 | SCHüTTE et al[ | ||||||||
| 在墨西哥湾观测到的ITEs对墨西哥湾热量、盐度再分配有影响 | MEUNIER et al[ GULA et al[ | ||||||||||
| 太平洋 | 在日本海观测到ITEs,被认为是由冬季混合层水沿副极地锋南边缘的锋面汇聚和俯冲作用形成的 | GORDON et al[ | 加利福尼亚潜流涡旋 | 加利福尼亚潜流涡旋是加利福尼亚潜流温暖、高盐水横向输送机制之一 | GARFIELD et al[ | 北太平洋次表层低位涡水团的变化和涡旋密切相关 | WEN et al[ | ||||
| 南太平洋副热带回旋的赤道13 ℃水 | 反气旋,可能来自于东边界的极向潜流 | JOHNSON et al[ | |||||||||
| 黑潮延伸体区域观测到低位涡、高溶解氧的次表层SCVs,发现它们影响中层水的俯冲 | OKA et al[ | ||||||||||
| 利用HYCOM模拟日本海的ITEs,阐述了其生成的相关机制 | HOGAN et al[ | 黑潮延伸体涡旋 | 多次观测到STEs,其内部的热盐性质表明它们可能起源于黑潮上游 | MAXIMENKO et al[ OKA et al[ ZHANG et al[ | |||||||
| ITEs不仅可以离岸运输水团,还能促进上升流区域的拓展 | HORMAZABAL et al[ | 棉兰老岛海岸涡旋 | 多次观测到STEs,它们对南北太平洋中层的混合有重要作用 | FIRING E et al[ CHIANG et al[ NAN et al[ ZHANG et al[ | |||||||
| 北冰洋 | 早期观测到次表层SCVs的地区之一,在格陵兰海、波弗特海、拉布拉多海都曾观测到,与深对流相关(D’ASARO[ | ||||||||||
Tab.1 Typical subsurface coherent vortices found in the global ocean
| 区域 | 温跃层内涡旋(ITEs) | 温跃层下涡旋(STEs) | 模态水涡旋 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 主要结论 | 代表性文献 | 涡旋名称 | 主要结论 | 代表性文献 | 主要结论 | 代表性文献 | |||||
| 印度洋 | 表层反气旋涡与热带气旋相互作用可能产生ITEs | GORDON et al[ | 阿拉伯 涡旋 | 阿拉伯海观测到的STEs在咸水横跨阿拉伯海的运输中具有重要作用 | VIC C et al[ MAREZ et al[ | ||||||
| 在马达加斯加东南部观测到ITEs | NAUW et al[ | ||||||||||
| 大西洋 | 综合大西洋西部永久性温跃层中等温透镜体的观测结果,解释其为孤立特征,首次提出ITEs,同时在马尾藻海中观测到ITEs | DUGAN et al[ | 地中海涡旋 | 地中海涡旋将高盐的地中海水输送到亚热带大西洋,影响环流、深对流、生物化学物质等 | MCDOWELL et al[ RICHARDSON et al[ BARBOSA et al[ BOSSE et al[ | 模态水涡旋在大西洋西北部被观测到,它们通过沿密度面输送和动量搅拌热盐、化学物质等影响海洋环流从而影响生态 | MCGILLICUDDY et al[ | ||||
| 在副热带北大西洋东边界上升流潜流中观测到ITEs,其内部和周围生产力很高 | PIETRI et al[ | 北大西洋东部的海洋低氧区的形成与模态水涡旋的孤立水团输运有关 | SCHüTTE et al[ | ||||||||
| 在墨西哥湾观测到的ITEs对墨西哥湾热量、盐度再分配有影响 | MEUNIER et al[ GULA et al[ | ||||||||||
| 太平洋 | 在日本海观测到ITEs,被认为是由冬季混合层水沿副极地锋南边缘的锋面汇聚和俯冲作用形成的 | GORDON et al[ | 加利福尼亚潜流涡旋 | 加利福尼亚潜流涡旋是加利福尼亚潜流温暖、高盐水横向输送机制之一 | GARFIELD et al[ | 北太平洋次表层低位涡水团的变化和涡旋密切相关 | WEN et al[ | ||||
| 南太平洋副热带回旋的赤道13 ℃水 | 反气旋,可能来自于东边界的极向潜流 | JOHNSON et al[ | |||||||||
| 黑潮延伸体区域观测到低位涡、高溶解氧的次表层SCVs,发现它们影响中层水的俯冲 | OKA et al[ | ||||||||||
| 利用HYCOM模拟日本海的ITEs,阐述了其生成的相关机制 | HOGAN et al[ | 黑潮延伸体涡旋 | 多次观测到STEs,其内部的热盐性质表明它们可能起源于黑潮上游 | MAXIMENKO et al[ OKA et al[ ZHANG et al[ | |||||||
| ITEs不仅可以离岸运输水团,还能促进上升流区域的拓展 | HORMAZABAL et al[ | 棉兰老岛海岸涡旋 | 多次观测到STEs,它们对南北太平洋中层的混合有重要作用 | FIRING E et al[ CHIANG et al[ NAN et al[ ZHANG et al[ | |||||||
| 北冰洋 | 早期观测到次表层SCVs的地区之一,在格陵兰海、波弗特海、拉布拉多海都曾观测到,与深对流相关(D’ASARO[ | ||||||||||

Fig.5 Subthermocline eddies found in Mediterranean Sea by the underwater glider[3] [a: Salinity section with density contours in white; b: Cross-section velocities (Cyclostrophic within the blue box and geostrophic outside). The large current speed contours (white contours) are overlaid, and the black contours show the smoothed density field. Blue dashed box indicates eddy interior.]

Fig.6 Schematic diagram of trapped fluid by the subsurface modal water eddy[21] (The potential vorticity distributions on isopycnals are depicted by colored and black contours. The transparent black surface, defined by the outmost closed potential vorticity contours.)
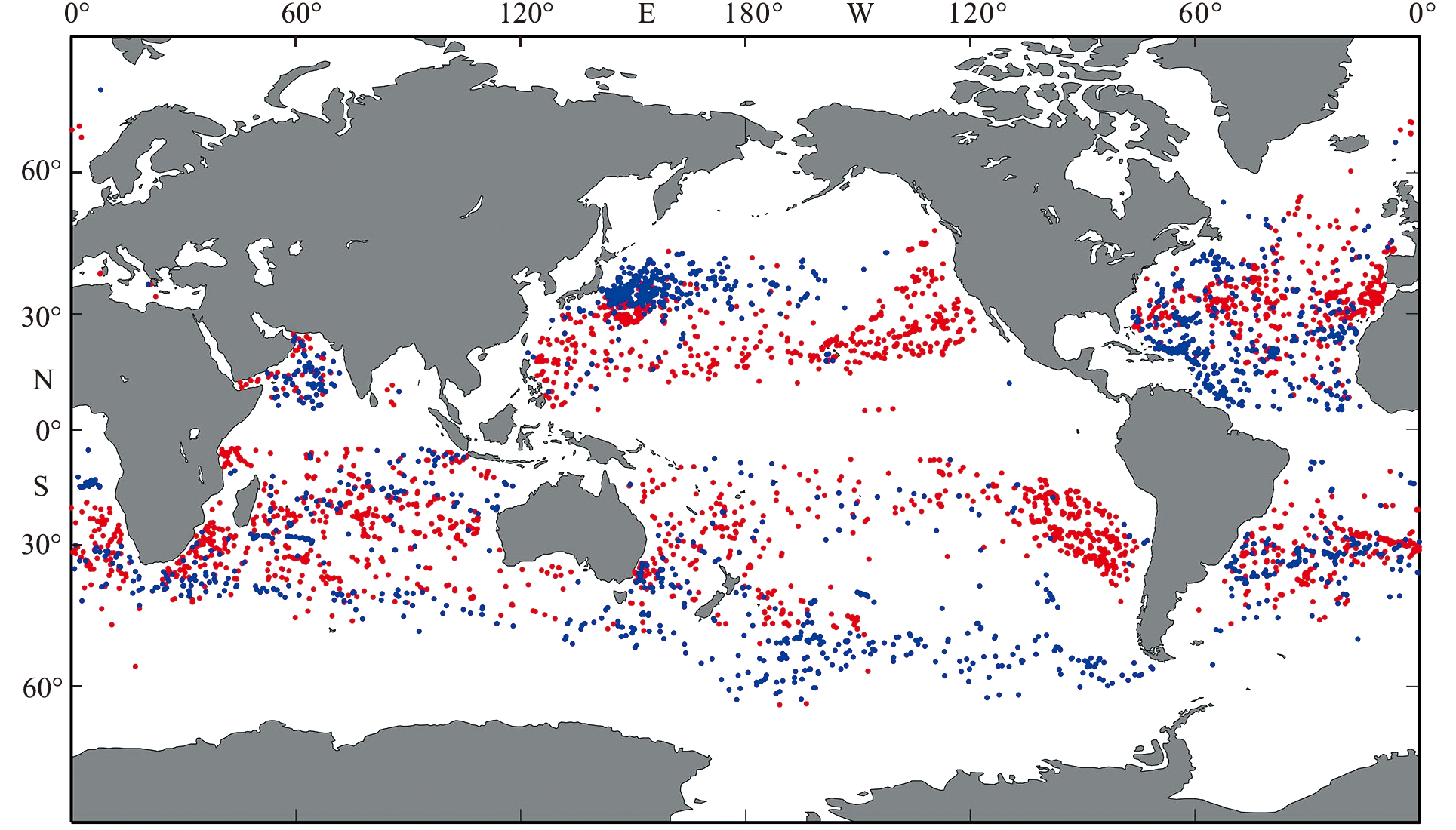
Fig.7 Distribution of all subsurface coherent vortices detected from Argo buoys during August 1997 to January 2020[19] (In the figure, red dots are the subsurfacec coherent vortexes with the high spicy center, and blue dots are the subsurface coherent vortexes with the low spicy center.)
| [1] | SWALLOW J C, WORTHINGTON L V. An observation of a deep countercurrent in the Western North Atlantic[J]. Deep Sea Research: 1953, 1961, 8(1): IN1-IN3. |
| [2] | CHELTON D B, SCHLAX M G, SAMELSON R M, et al. Global observations of large oceanic eddies[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(15): L15606. |
| [3] |
BOSSE A, TESTOR P, MORTIER L, et al. Spreading of Levantine Intermediate Waters bysubmesoscale coherent vortices in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea as observed with gliders[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(3): 1599-1622.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PELLAND N A, ERIKSEN C C, LEE C M. Subthermocline eddies over the Washington continental slope as observed by seagliders, 2003-09[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2013, 43(10): 2025-2053.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SHAPIRO G I, MESCHANOV S L. Distribution and spreading of Red Sea Water and salt lens formation in the northwest Indian Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers, 1991, 38(1): 21-34.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI C, ZHANG Z W, ZHAO W, et al. A statistical study on the subthermocline submesoscale eddies in the northwestern Pacific Ocean based on Argo data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(5): 3586-3598.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
MCWILLIAMS J C. Submesoscale, coherent vortices in the ocean[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1985, 23(2): 165-182.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
FRENGER I, BIANCHI D, STÜHRENBERG C, et al. Biogeochemical role of subsurface coherent eddies in the ocean: Tracer cannonballs, hypoxic storms, and microbial stewpots?[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2018, 32(2): 226-249.
DOI URL |
| [9] | CHAIGNEAU A, LE TEXIER M, ELDIN G, et al. Vertical structure of mesoscale eddies in the eastern South Pacific Ocean: A composite analysis from altimetry and Argo profiling floats[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2011, 116(C11): C11025. |
| [10] | FLIERL G R. Particle motions in large-amplitude wave fields[J]. Geophysical & Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics, 1981, 18(1/2): 39-74. |
| [11] | DONG C M, MCWILLIAMS J C, LIU Y, et al. Global heat and salt transports by eddy movement[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5(1): 1-6. |
| [12] |
PIETRI A, KARSTENSEN J. Dynamical characterization of a low oxygen submesoscale coherent vortex in the eastern North Atlantic Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2018, 123(3): 2049-2065.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HORMAZABAL S, COMBES V, MORALES C E, et al. Intrathermocline eddies in the coastal transition zone off central Chile (31—41°S)[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118(10): 4811-4821.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
LUKAS R, SANTIAGO-MANDUJANO F. Extreme water mass anomaly observed in the Hawaii Ocean time-series[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2001, 28(15): 2931-2934.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
JOHNSON G C, MCTAGGART K E. Equatorial Pacific 13℃ water eddies in the eastern subtropical South Pacific Ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2010, 40(1): 226-236.
DOI URL |
| [16] | MÉNESGUEN C, HUA B L, CARTON X, et al. Arms winding around a meddy seen in seismic reflection data close to the Morocco coastline[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(5): L05604. |
| [17] |
OKUBO A. Horizontal dispersion of floatable particles in the vicinity of velocity singularities such as convergences[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 1970, 17(3): 445-454.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WEISS J. The dynamics of enstrophy transfer in two-dimensional hydrodynamics[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1991, 48(2/3): 273-294.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
MCCOY D, BIANCHI D, STEWART A L. Global observa-tions of submesoscale coherent vortices in the ocean[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2020, 189: 102452.
DOI URL |
| [20] | DUGAN J P, MIED R P, MIGNEREY P C, et al. Compact,intrathermocline eddies in the Sargasso sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1982, 87(C1): 385-393. |
| [21] |
ZHANG Z G, ZHANG Y, WANG W. Three-compartment structure of subsurface-intensified mesoscale eddies in the ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(3): 1653-1664.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
THOMAS L N. Formation of intrathermocline eddies at ocean fronts by wind-driven destruction of potential vorticity[J]. Dynamics of Atmospheres and Oceans, 2008, 45(3/4): 252-273.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
GORDON A L, SHROYER E, MURTY V S N. An Intra-thermocline eddy and a tropical cyclone in the Bay of Bengal[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 1-8.
DOI |
| [24] | NAUW J J, VAN AKEN H M, LUTJEHARMS J R E, et al. Intrathermocline eddies in the Southern Indian Ocean[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2006, 111(C3): C03006. |
| [25] |
VIC C, ROULLET G, CAPET X, et al. Eddy-topography interactions and the fate of the Persian Gulf Outflow[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(10): 6700-6717.
DOI URL |
| [26] | DE MAREZ C, CARTON X, CORRÉARD S, et al. Observations of a deep submesoscale cyclonic vortex in the Arabian Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(13): e2020GL087881. |
| [27] |
MEUNIER T, TENREIRO M, PALLÀS-SANZ E, et al. Intrathermocline eddies embedded within an anticyclonic vortex ring[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(15): 7624-7633.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
GULA J, BLACIC T M, TODD R E. Submesoscale coherent vortices in the gulf stream[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2019, 46(5): 2704-2714.
DOI |
| [29] |
MCDOWELL S E, ROSSBY H T. Mediterranean water: An intense mesoscale eddy off the Bahamas[J]. Science, 1978, 202(4372): 1085-1087.
PMID |
| [30] |
RICHARDSON P L, BOWER A S, ZENK W. A census of Meddies tracked by floats[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2000, 45(2): 209-250.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
BARBOSA A A C, PELIZ Á, CARTON X. A census of Meddies in a long-term high-resolution simulation[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 2013, 116: 80-94.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
BOSSE A, TESTOR P, HOUPERT L, et al. Scales and dynamics of Submesoscale Coherent Vortices formed by deep convection in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2016, 121(10): 7716-7742.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
BOSSE A, TESTOR P, MAYOT N, et al. Asubmesoscale coherent vortex in the Ligurian Sea: From dynamical barriers to biological implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2017, 122(8): 6196-6217.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MCGILLICUDDY JR D J, ANDERSON L A, BATES N R, et al. Eddy/wind interactions stimulate extraordinary mid-ocean plankton blooms[J]. Science, 2007, 316(5827): 1021-1026.
DOI PMID |
| [35] |
SCHÜTTE F, KARSTENSEN J, KRAHMANN G, et al. Characterization of “dead-zone” eddies in the eastern tropical North Atlantic[J]. Biogeosciences, 2016, 13(20): 5865-5881.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
GORDON A L, GIULIVI C F, LEE C M, et al. Japan/East Sea intrathermocline eddies[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2002, 32(6): 1960-1974.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
GARFIELD N, COLLINS C A, PAQUETTE R G, et al. Lagrangian exploration of the California undercurrent, 1992-95[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1999, 29(4): 560-583.
DOI URL |
| [38] | WEN Z B, HU H B, SONG Z Y, et al. Different influences of mesoscale oceanic eddies on the North Pacific subsurface low potential vorticity water mass between winter and summer[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2020, 125(1): e2019JC015333. |
| [39] | HOGAN P J, HURLBURT H E. Why dointrathermocline eddies form in the Japan/East Sea? A modeling perspective[J]. Oceanography, 2006, 19(3): 134-143. |
| [40] | MAXIMENKO N, YAMAGATA T. Submesoscale anomalies in the North Pacific subarctic front[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1995, 100(C9): 18459-18469. |
| [41] | OKA E, TOYAMA K, SUGA T. Subduction of North Pacific central mode water associated with subsurface mesoscale eddy[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(8): L08607. |
| [42] |
ZHANG Z W, LI P L, XU L X, et al. Subthermocline eddies observed by rapid-sampling Argo floats in the subtropical northwestern Pacific Ocean in Spring 2014[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(15): 6438-6445.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
FIRING E, KASHINO Y, HACKER P. Energetic subther-mocline currents observed east of Mindanao[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2005, 52(3/4): 605-613.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
CHIANG T L, QU T D. Subthermocline eddies in the western equatorial Pacific as shown by an eddy-resolving OGCM[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2013, 43(7): 1241-1253.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
CHIANG T L, WU C R, QU T D, et al. Activities of 50-80 day subthermocline eddies near the Philippine coast[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2015, 120(5): 3606-3623.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
NAN F, YU F, REN Q, et al. Isopycnal mixing of interhe-mispheric intermediate waters by subthermocline eddies east of the Philippines[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 2957.
DOI |
| [47] |
ZHANG L L, HUI Y C, QU T D, et al. Seasonal variability of subthermocline eddy kinetic energy east of the Philippines[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2021, 51(3): 685-699.
DOI URL |
| [48] | D’ASARO E A. Generation of submesoscale vortices: A new mechanism[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1988, 93(C6): 6685-6693. |
| [49] |
GASCARD J C, WATSON A J, MESSIAS M J, et al. Long-lived vortices as a mode of deep ventilation in the Greenland Sea[J]. Nature, 2002, 416(6880): 525-527.
DOI |
| [50] |
LILLY J M, RHINES P B. Coherent eddies in the Labrador Sea observed from a mooring[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2002, 32(2): 585-598.
DOI URL |
| [51] | DRILLET Y, BOURDALLÉ-BADIE R, SIEFRIDT L, et al. Meddies in the Mercator North Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea eddy-resolving model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2005, 110(C3): C03016. |
| [52] |
许丽晓, 刘秦玉. 海洋涡旋在模态水形成与输运中的作用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2021, 36(9):883-898.
DOI |
|
XU L X, LIU Q Y. Mesoscale eddy effects on subduction and transport of the North Pacific subtropical mode water[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2021, 36(9): 883-898.
DOI |
|
| [53] |
ZHU R C, CHEN Z H, ZHANG Z W, et al. Subthermocline eddies in the Kuroshio extension region observed by mooring arrays[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2021, 51(2): 439-455.
DOI URL |
| [54] | KASAJIMA Y, OLSSON K A, JOHANNESSEN T, et al. A submesoscale coherent eddy in the Greenland Sea in 2003[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2006, 111(C7): C07013. |
| [55] |
PROVENZALE A. Transport by coherent barotropic vortices[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 31: 55-93.
DOI URL |
| [56] | 徐安琪. 西北太平洋次表层中尺度涡特征及其动力机制研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2021. |
| XU A Q. Research on characteristics and dynamic mechanism of subsurface eddies in the northwestern Pacific Ocean[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2021. | |
| [57] |
TESTOR P, GASCARD J C. Large-scale spreading of deep waters in the western Mediterranean Sea by submesoscale coherent eddies[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2003, 33(1): 75-87.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
TESTOR P, GASCARD J C. Post-convection spreading phase in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2006, 53(5): 869-893.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
COLLINS C A, MARGOLINA T, RAGO T A, et al. Looping RAFOS floats in the California Current system[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 2013, 85: 42-61.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
ALTABET M A, RYABENKO E, STRAMMA L, et al. An eddy-stimulated hotspot for fixed nitrogen-loss from the Peru oxygen minimum zone[J]. Biogeosciences, 2012, 9(12): 4897-4908.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
ARÉVALO-MARTÍNEZ D L, KOCK A, LÖSCHER C R, et al. Influence of mesoscale eddies on the distribution of nitrous oxide in the eastern tropical South Pacific[J]. Biogeosciences, 2016, 13(4): 1105-1118.
DOI URL |
| [62] | LEHAHN Y, D’OVIDIO F, LÉVY M, et al. Stirring of the northeast Atlantic spring bloom: A Lagrangian analysis based on multisatellite data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2007, 112(C8): C08005. |
| [63] | 张旭, 程琛, 刘艳. 西北太平洋副热带模态水形成区声传播特性分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2014, 36(9):94-102. |
| ZHANG X, CHENG C, LIU Y. Acoustic propagation effect caused by subtropical mode water of northwestern Pacific[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 36(9): 94-102. | |
| [64] | 李佳讯, 张韧, 陈奕德, 等. 海洋中尺度涡建模及其在水声传播影响研究中的应用[J]. 海洋通报, 2011, 30(1):37-46. |
| LI J X, ZHANG R, CHEN Y D, et al. Ocean mesoscale eddy modeling and its application in studying the effect on underwater acoustic propagation[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2011, 30 (1): 37-46. | |
| [65] |
JUNGCLAUS J H. A three-dimensional simulation of the formation of anticyclonic lenses (Meddies) by the instability of an intermediate depth boundary current[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1999, 29(7): 1579-1598.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
GULA J, MOLEMAKER M J, MCWILLIAMS J C. Topographic vorticity generation,submesoscale instability and vortex street formation in the Gulf Stream[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(10): 4054-4062.
DOI URL |
| [67] | SPALL M A. Frontogenesis, subduction, and cross-front exchange at upper ocean fronts[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 1995, 100(C2): 2543-2557. |
| [68] |
KRUG M, SWART S, GULA J. Submesoscale cyclones in the Agulhas current[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(1): 346-354.
DOI URL |
| [69] | GULA J, MOLEMAKER M J, MCWILLIAMS J C. Topo-graphic generation of submesoscale centrifugal instability and energy dissipation[J]. Nature Communications, 2016, 7(1): 1-7. |
| [70] | MCWILLIAMS J C. A perspective on submesoscale geophy-sical turbulence[C]//DRITSCHEL D. IUTAM symposium on turbulence in the atmosphere and oceans. Dordrecht: Springer, 2010: 131-141. |
| [1] | CUI Minghui, TU Junbiao, MENG Lingpeng, GUO Xingjie, SU Ni, FAN Daidu. Wave characteristics and their influencing factors on Nanhui tidal flats in the Changjiang Estuary [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2023, 41(2): 28-44. |
| [2] | SI Xiangcheng, CHEN Xiao, CHEN Fajin, JIN Guangzhe, SHI Ziyang, XIE Xufeng, CAI Hua. A preliminary investigation on the spatial and temporal distribution of submarine groundwater discharge in the northern Beibu Gulf as indicated by 222Rn activities [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2023, 41(2): 94-103. |
| [3] | LI Zhichao, GUO Junru, SONG Jun, BAI Zhipeng, FU Yanzhao, CAI Yu, WANG Xifeng. Distribution, movement and generation mechanism of the mesoscale eddy around the Kuroshio in the East China Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(4): 1-10. |
| [4] | SHEN Yuan, CHEN Xiangyu, ZHANG Xijiang, YE Yun, NI Yunlin. Wave diffraction from a 3D circular island [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(2): 62-68. |
| [5] | ZHANG Yipu, YU Shuo, HUANG Daji, ZHOU Zebin, . Characteristics of tide, tidal current and their effects on nutrients in Xincun Lagoon, Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(2): 69-82. |
| [6] | LIANG Haiping, LI Tuanjie, LIANG Haiyan, GAO Lu. Distributional characteristics and influencing factors of storm surge in Haikou [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(2): 83-92. |
| [7] | ZENG Dingyong, XUAN Jiliang, HUANG Daji, et al. Study on tide and tidal current near the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary based on observational data [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(1): 12-20. |
| [8] | ZHANG Shuyu, DING Tao, LIU Jinbao, et al. Dynamic analysis of tidal bore research based on bibliometric method#br# [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2022, 40(1): 89-100. |
| [9] | HE Tianqi, GUAN Weibing, CAO Zhenyi, BAO Min, LI Song, LI Yu. HighFrequency ground wave radar observation and analysis of tidal current distribution in the Niubishan Channel of Xiangshangang Bay#br# [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2021, 39(4): 109-122. |
| [10] | ZHANG Jiaying, ZHOU Feng, TIAN Di, HUANG Ting, . The characteristics and formation mechanism of the oceanic mesoscale eddy origin in northwest of Sumatra [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2021, 39(3): 1-11. |
| [11] | CUI Zijian, LIANG Chujin, LIN Feilong, JIN Weifang, DING Tao, WANG Juan. The observation and analysis of the internal solitary waves by mooring system in the Andaman Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2020, 38(4): 16-25. |
| [12] | PAN Cunhong, PAN Dongzi, ZHENG Jun, CHEN Gang. Study on influence of typhoon on tidal bore in Qiantang River [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2020, 38(4): 40-47. |
| [13] | ZHANG Jiali, ZHANG Anmin, SUN Chaohui, ZHANG Xuefeng, ZHANG Liang. The application research of Robust Vondrak filtering method in extracting internal solitary waves [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2020, 38(1): 1-8. |
| [14] | CHEN Jie, GONG Shang-peng, GUAN Zhi-xin, ZHANG Zhu, XIE zhen-dong, LEI Jia-xin, PENG Hao. Experimental investigation on irregular wave attenuation under the effects of vegetation with roots, stems and canopies [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2019, 37(4): 48-59. |
| [15] | WANG Juan, YANG Jing-song, ZHOU Li-ying, HE Shuang-yan, HE Zhi-guo, XIAO Qing-mei, LIU ANTONU K, HSU Ming-Kuang. Distribution of internal waves in the Andaman Sea and its adjacent waters based on multi-satellite remote sensing data [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2019, 37(3): 1-11. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||





